O Amazon biome is a set of biological units characterized by climatic aspects, soil type, vegetation, hydrography, among others. This biome constitutes the largest river basin in the world, as well as biggest rainforest on the planet, being considered the region with the greatest biodiversity on Earth.
This biome is the biggest in Brazil, Yet is not unique to the country, it can be found in Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, French Guiana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela. It covers, in Brazil, according to the IBGE, an area of approximately 4,196,943 million km2 , about 40% of the national territory.
The federative units comprised by this biome are: Acre, Amapá, Amazonas, Pará, Roraima, Rondônia, Mato Grosso, Maranhão and Tocantins, which are distributed by regions North, Northeast and Midwest from the country.
Read too: Brazilian Biomes
In the area occupied by the biome, there are approximately 33 million inhabitants, including around 1.6 million indigenous people. According to the Ministry of Environment, the region encompassed by this biome is considered the largest reserve of tropical wood in the world and has large reserves of rubber, nuts and minerals.
Amazon Map
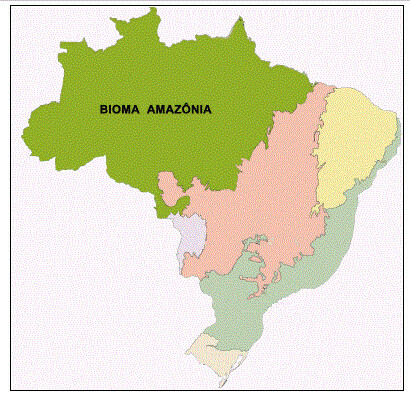
Location of the Amazon biome, according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE).
Vegetation and flora
THE vegetation of the Amazon biome is characterized especially by the presence of the largest tropical forest in the world, the Amazon rainforest. This forest covers an area that exceeds 5 million km2. The forest houses about 2,500 species of trees it's from 30,000 species of plants of a total of approximately 100,000 species in Latin America, according to the World Fund for Nature (WWF Brazil).
The main characteristic of the vegetation in this biome is the presence of a dense forest with large trees classified into three categories:
dry land forest |
This type of vegetation can be found in high altitude regions. Therefore, they do not flood, remaining dry throughout the year. Characterized by the presence of large trees. |
igapó forest |
This type of vegetation can be found in low altitude regions. Therefore, it is flooded almost all the time. Characterized by the presence of shrubs and mosses, as well as water lilies. |
floodplain forest |
This type of vegetation can be found in regions of intermediate altitudes. Therefore, it is flooded during a period of the year. Characterized by the presence of tree species up to 40 meters high. |
THE flora from the Amazon has high medicinal power and economic potential. The Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (Embrapa) released a survey of the main Brazilian medicinal plants, including those from the Amazon. Species such as jaborandi (Pilocarpus microphyllus) contain pilocarpine in its leaves, being used for the treatment of primary glaucomas, and crajirú (Arrabidaea chica) a climbing plant whose leaves are used as an anti-inflammatory.
readmore:What is fauna and flora?
Fauna

The jaguar is one of the symbols of the fauna of the Amazon biome.
The Amazon biome has a fauna extremely diverse and rich. According to Embrapa, there are about 30 million species of animals, however not all have been found, studied and cataloged by scholars.
Animals like monkeys stand out, Jaguar, anteaters, manatees, alligators, snakes, frogs, several species of fish, among others. There are also more than a thousand species of birds in the region, such as toucans and macaws.
Climate
The Amazon biome region is characterized by high air humidity, which can reach 80%, due to long periods of rain, whose rainfall varies between 1,500 mm to 3,600 mm per year. O climate predominant is the wet equatorial, with temperatures ranging between 22ºC and 28ºC.
Read more:Why does it rain a lot in the Amazon?
Hydrography

The Amazon is a region rich in natural resources, such as water. It comprises the area of the largest hydrographic basin in the world, the Amazon River Basin, which, according to the Ministry of the Environment, has about 6 million km2 and more than 1,100 tributaries. The main river in this basin is the Amazon river, which releases approximately 175 million liters of water per second into the sea.
Other important rivers in this biome are: the Rio Negro, considered the largest tributary on the left bank of the Amazon River; Tapajós River, which flows into the right bank of the Amazon River; Madeira River, which rises in the Andes Mountains in Bolivia.
Rivers have different characteristics in relation to the color of the water. There are, in this region, more turbid and muddy rivers, due to the high concentration of nutrients, such as the Amazon River; rivers with clear water due to lack of nutrients, such as the Xingu River; and black water rivers with a high concentration of humus, such as the Rio Negro.
Ground
Oground characteristic of the Amazon biome is generally sandy. Due to the presence of dense vegetation, a thin layer of nutrients from the decomposition of leaves and animals.
However, not all the soil in the region is considered fertile, since in regions without vegetation cover, the surface runoff of water ends up "washing" the soil and removing its nutrients (a process known as leaching). What allows the existence of this dense forest and vegetation rich in species is, therefore, the existence of this layer of organic matter that accumulates in the soil.
Devastation of the Amazon Biome
Despite being considered one of the most preserved biomes in the country, the Amazon has been suffering from devastation. Questions like the logging, fires, illegal mining and farming have caused several environmental problems.
About 17% of the biome has been devastated in the last 50 years, according to a survey conducted by American researcher Thomas Lovejoy (professor at George Mason University) and the Brazilian Carlos Nobre (coordinator of National Institute of Science and Technology for Climate Change).
According to the researchers, the maximum limit for devastation would be 20%. This means that exceeding this limit, the consequences would be irreversible to the biome, putting biodiversity at risk, altering the climate and the hydrological cycle.
Curiosities
The largest freshwater fish in the world can be found in the biome: the pirarucu.
The water lily is one of the symbols of the Amazon, measuring up to 2 meters in diameter.
The anaconda, a species of snake from the Amazon, can reach up to 10 meters in length.
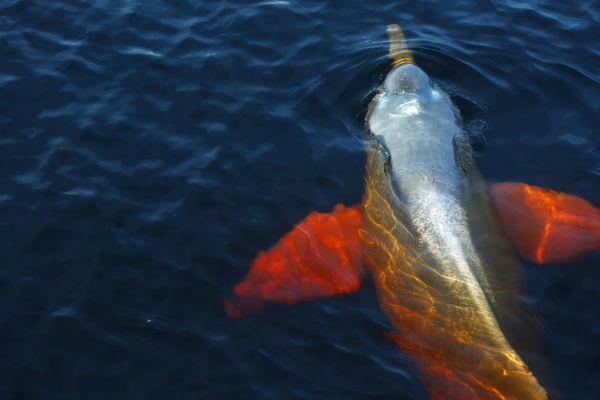
The boto can be found on Amazon. It is known as a freshwater dolphin.
About 85% of fish in all of South America are found in the rivers of the Amazon biome.
Also know:Amazonian manatee


