THE photosynthesis transforms solar energy into chemical energy, using the latter to carry out the synthesis of organic compounds, such as sugars, from carbon dioxide and water.
→ How does photosynthesis take place?
THE photosynthesis it is a process carried out by organisms autotrophic photosynthesizers, like plants,seaweedand some prokaryotes. They capture sunlight, transform it into chemical energy and produce organic compounds (carbohydrates or sugars) from water and carbon dioxide. At the end of the process, oxygen is released into the environment.
Read too: autotrophic and heterotrophic beings
→ Chloroplasts and photosynthetic pigments
photosynthesis occurs US chloroplasts, which are organelles present in the cells of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. these organelles we store photosynthetic pigments, which are responsible for absorbing light. There are several types of photosynthetic pigments, such as chlorophylls and carotenoids. The main one is chlorophyll-The.
You chloroplasts are made up of double membrane eDNA itself. present a internal space called stroma, where enzymes are present that are used in the carbon fixation phase of photosynthesis. In chloroplasts, flat vesicles, between membranes called lamellae, are also found. thylakoids. These are stacked forming structures called money, where do we find the pigments.
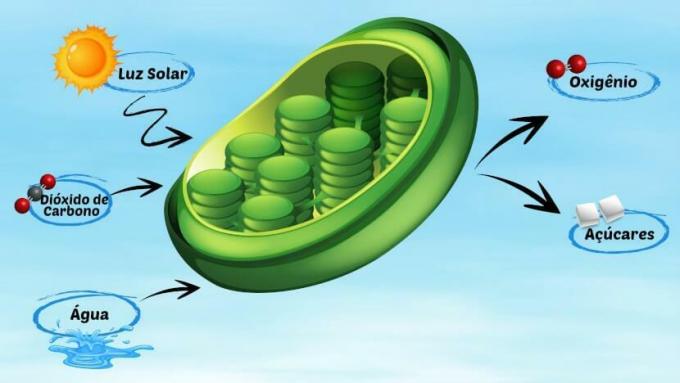
Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts and produces sugars and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water.
→ Photosynthesis steps
THE photosynthesis can be divided into two steps or phases, the luminous and the one of carbon fixation:
→ Light or photochemical phase
In this step, which occurs USthylakoids of chloroplasts, occur to captureinenergyluminous and the transformation in energychemistry. In this process, the pigment molecules pass to a excited state, andemitting part of the absorbed energy. These pigments are organized into two photosystems, which can be defined as light-gathering units present in thylakoids. At the photosystem I, pigments absorb wavelengths of 700 nm or longer; already in the photosystem II, wavelengths 680 nm or less are absorbed. Generally, the two photosystems work together.
At this stage, the energyluminous é absorbed by pigments in photosystem II and transferred for moleculesinchlorophyll of the reaction center. You electrons energized are transferred for one receiver of electrons. According to the transfer of these electrons, they are replaced by others from the photolysis of water. Here, oxygen is also produced.
Some pairs of electrons pass into photosystem I, stimulating ATP synthesis. THE absorbed energy at this moment it stimulates the moleculesinchlorophyll of the reaction center of this photosystem, and the electronsenergized they are accepted for one NADP+ molecule. The electrons removed from chlorophyll are replaced by others from photosystem II.
→ carbon fixation phase
This phase occurs at thestroma of the chloroplast and starts with the processinfixationofcarbon in an organic compound. at this stage NADPH and ATP molecules are used produced in the light phase for the production of sugars from the reduction of fixed carbon. The reactions that occur here are called Calvin cycle and, in this process, the biggerpartofcarbon fixed is convertedinsucroseorstarch.
readalso:Is it dangerous to sleep with plants in the bedroom?
→ photosynthesis equation
The photosynthesis process can be summarized in the following equation:
6 CO2 + 12 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O |
Although this equation is widely used to describe the photosynthesis process, in reality, atfirstmolecules to be formed no they are of glucose (C6H12O6), but sugarsmoresimple with just three carbon atoms.
→ Importance of Photosynthesis
THE photosynthesis is essential for life to exist on Earth in the way we find it today, because through photosynthesis, oxygen existing on the planet is produced. In addition, photosynthesis is also responsible for the production of energy for practically all beingsalive. Thus, photosynthetic organisms are the basis of food chains both terrestrial and aquatic.
readalso:How does the plant's body transport substances?
You organismsphotosynthesizers (autotrophic) capture sunlight, transforminenergychemistry, they produce organic compounds from water and carbon dioxide and release oxygen into the environment. already the organismsheterotrophicconsume Those compoundsorganic to get the energy needed for your metabolism. In this process of obtaining energy, they oxidize these organic compounds with oxygen released into the environment by photosynthetic organisms and release carbon dioxide, thus maintaining the balance.
Take the opportunity to check out our video lesson on the subject:



