O bone tissue is a kind of connective tissue. It is the tissue that forms the bones of all vertebrate animals, with the exception of cartilaginous fish, as we saw in the article “Characteristics of cartilaginous tissue".
We know that the skeleton, which is formed by the bones, has important functions in our body, such as protect internal organs (brain, lungs and heart), support the body, assist in the movements, serve as calcium reservoir. That's why bones are very hard, because if they were formed by cartilage, they would bend easily and we would not be able to stand upright.
Our bones are made up of two parts, the organic part and the inorganic part.
THE organic part it stays inside the bones. In it we find collagen fibers, The red bone marrow, responsible for the production of blood cells and the yellow bone marrow, known by many people as marrow. already the inorganic part is found coating the organic part. It is formed by minerals such as Calcium phosphate, which gives the rigidity to bones.
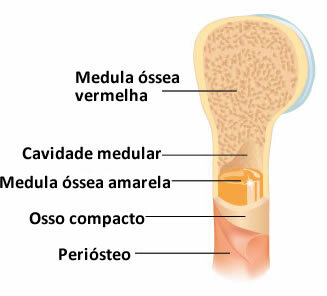
Image illustrating the organic and inorganic part of a bone
The cells responsible for the production of bone tissue are called osteoblasts and, in addition to these cells, this tissue has other cells that are called osteoclasts. You osteoclasts are very important for bones, as they work by destroying areas of bone that are aged or damaged, so that the bones then osteoblasts can recompose them.
THE osteoporosis, a disease that affects the bones, making them more fragile, can be caused by the action of osteoclasts that, stimulated by a hormone produced by the parathyroid glands, increase their quantity and begin to damage the bones, making them thinner and, consequently, more fragile. It is important to remember that this disease can also be caused by a lack of some vitamins that help bone formation.