Rain is a type of precipitation that occurs in liquid form and at temperatures above 0ºC. Rainfall can be characterized based on criteria such as intensity, acidity or origin (this is the most common form of classification). According to the origin, the rains can be orographic, frontal and convective.
types of rain
1. Front rain
Front showers occur when a mass of warm, moist air meets a mass of cool, dry air. THE air mass cold, as it is denser, elevates the hot air mass to higher points in the atmosphere, so the process occurs of condensation (goes from the gaseous state to the liquid state), which results in precipitation in liquid form (rain). This type of rain is characterized by being continuous and having low intensity.

The frontal rain is characterized by the meeting of two air masses.
2. Orographic rain or relief rain
Also known as relief rain, happens when clouds encounter obstacles such as mountain ranges and mountains. A mass of moist air from the ocean, upon encountering a land elevation, is forced to ascend to great heights. As it rises, the cloud cools down and there is a process of condensation followed by precipitation. Orographic rains generally have longer duration and low intensity.
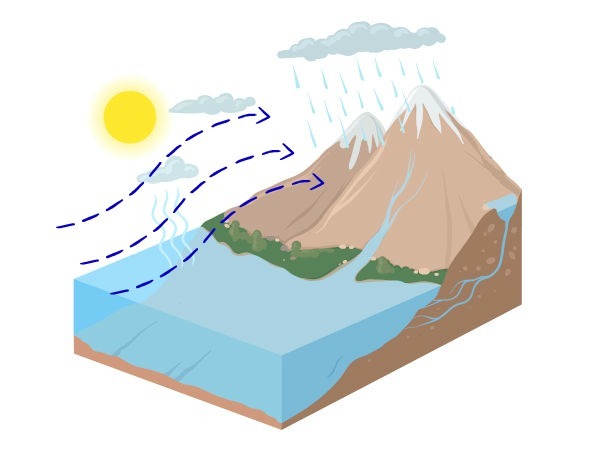
Orographic rain occurs when a cloud encounters an obstacle, such as mountains.
3. Convective rains or summer rains
Convective rains are frequent in regions with a tropical climate, that is, they are typical of regions with high temperatures. Also known as summer rains, they occur due to the difference in temperature in the layers close to the Earth's atmosphere. It is a rain of local coverage (small areas) and occurs when there is air movement, that is, cold air descends, because it is denser, and hot air rises, because it is lighter. When rising, the hot air carries all the moisture, the process of condensation starts and then precipitation occurs. They are generally rains of short duration, however they have high intensity.

Convective rains are also known as summer rains.
Read too:Tropical climate characteristics
Acid rain
Every rain has a certain degree of acidity. The normal pH of rain (pH is a scale that indicates the acidity or basicity of a solution) is usually around 5.6. When it is below 4.5, there is an abnormal acidity, setting up acid rain. In this type of rain, you can find sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
THE acid rain it is considered an atmospheric problem and occurs because of human actions. Burning fossil fuels, for example, releases sulfur and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, which end up reacting with water vapor and causing this problem.
At main consequences of acid rain they are damage to crops, contamination of water tables and threats to the health of living beings, triggering respiratory problems. The term acid rain became known through the chemist and climatologist Robert Angus Smith, who described an acid rain that hit the city of Manchester, England.
Summary
Rains, which represent a type of precipitation in liquid form, are classified based on some criteria, the most common of which is its origin. According to the origin, the rains can be frontal (occur when a mass of hot and humid air meets a mass of cold and dry air), orographic or from relief (occur when a cloud encounters a natural obstacle, such as mountains) and convective (occurs due to the temperature difference in the layers closest to the surface). There is also acid rain, a phenomenon caused by human actions, which alters the pH of the water, causing this environmental problem.
How does precipitation occur?
In order for there to be rain, it is necessary for the water to condense, that is, to pass from a gaseous state to a liquid state. Clouds are made up of water vapor or ice crystals. When a cloud consisting of water vapor comes into contact with low temperatures (but above 0°C), there is an increase in the condensation (water returns to its liquid state), which causes the precipitation of clouds in liquid form towards the surface.
Take the opportunity to check out our video lesson on the subject:



