O cartilage tissue it is one of several types of connective tissue found in our bodies, but it is not just humans who have this type of tissue. Some fish, called cartilaginous fish, such as streak it's the shark, have no bones and their skeleton is formed only by cartilage.

Sharks are examples of animals that have cartilaginous skeleton
Vertebrate animals, including humans, when they are in the embryonic stage, that is, when they are still forming inside the mother's belly, present cartilaginous skeleton. At this stage, this skeleton formed by cartilage presents the chondroblasts, cells that produce a substance that gives it a cartilaginous consistency. When this embryo matures, cartilages give way to bones and the chondroblasts get older, being called chondrocytes.
In our body, it is possible to find cartilage in our nose, ears, trachea, bronchi and also in the bone tipss that communicate with others, preventing friction between them and, consequently, wear and tear.
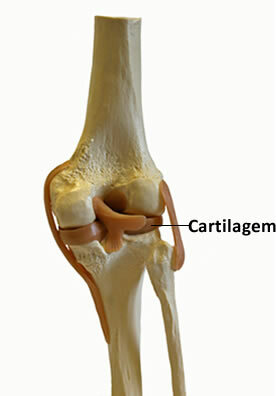
Cartilage between bones prevents friction and wear between them.
They exist three types of cartilage, they are: the hyaline cartilage, a elastic cartilage and the fibrous cartilage.
THE hyaline cartilage is found in our trachea, bronchi, tips of our bones. It is this type of cartilage that forms vertebrate embryos, as we saw in the second paragraph.

Our trachea and our bronchi are made up of hyaline cartilage
THE elastic cartilage looks a lot like hyaline cartilage, but it's tougher. It can be found forming our nose and ours ears.

Our ears are made of elastic cartilage
THE fibrous cartilage it is extremely tough and is found forming the rings that exist between our vertebrae, as shown in the figure below.

The cartilage between the vertebrae prevents them from maintaining contact



