the pampa is a biome which is located in the state of Rio Grande do Sul (in Brazil), in Uruguay and in some provinces of Argentina (such as Buenos Aires, Santa Fé, etc.)
Along with the Amazon, the cerrado, the caatinga, the Atlantic forest and the wetland, the pampa is part of the set of six terrestrial biomes existing in Brazil.
Biomes are the set of animals and plants that determine and define the landscape of a region. The pampa biome is characterized by vast fauna and undergrowth and shrubby vegetation.
The word pampa is a term of indigenous origin (from the Quechua peoples) that means "flat region". This name was given due to its extensive plains that configure the predominant landscape in the region.

Pampa characteristics
The pampa is a typical South American plain, whose main characteristic is its mostly undergrowth. The word "pampa" is a term of indigenous origin that means "flat region".
pampa climate
The climate of the pampa is seasoned, tending to be subtropical in the north and semiarid in the west.
Temperatures recorded throughout the summer do not usually vary as much as those recorded in winter. On average, they are between 28°C and 33°C.
Winter has very different temperature averages. Thermometers typically register between 12 °C and 19 °C during the day and between 1 °C and 6 °C at night. In the southern and western part of the pampas, the temperature can reach -10 °C.
Spring and autumn are usually milder. However, as it happens during winter, in spring the temperature tends to be quite variable, but with an intense rainy season.
Despite occurring throughout the region, frost happens more regularly in the southwestern part.
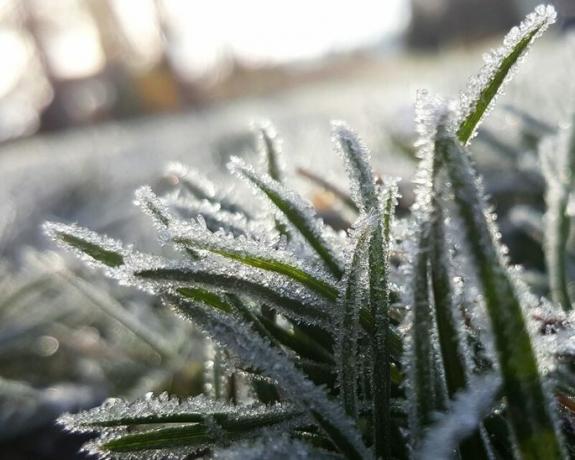

The rainfall index varies between 600 and 1,200 mm, which are usually distributed throughout the year and, therefore, the soil remains always fertile for agriculture.
pampa vegetation
The vegetation of the pampa is mostly composed of grasses and low-lying plants.
Trees and small shrubs can also be found in the region, but in a minority and sparsely.

It is estimated that the flora of the pampas encompasses about 3,000 species of plants, including native fields, forests and rocky outcrops.
Some examples of plants that are part of the pampas are: nhandavaí, parrot, pau-de-leite, cedar, canjerana, guajuvira, aloe vera, guatambu, grapia, dwarf palm, fork grass, carpet grass, pig's hair, arrows, wild goats, Cat's claw, bracatinga, cabreúva, red angico, caroba, native peanut, native clover, cacti, timbaúva, araucarias, canafístula, algarrobo, etc.
pampa animals
The pampa fauna has a very rich biodiversity, with an abundance of species (among them birds, mammals, arthropods, reptiles and amphibians).
Small animals and insects such as the wood wasp and the apple worm can also be found in the region.

This type of animal serves as food for the birds, and with that, the pampa is one of the places on the planet where the population of birds is more preserved.
Some examples of animal life in the pampas:
- blood tie,
- capybara,
- burrowing owl,
- pampas deer,
- Jaguar,
- raccoon,
- Guara wolf,
- guan,
- perdigão,
- will come out,
- Leashed sloth.
Other common animals of the flora of the pampas: macuco, black anum, field otter, field flycatcher, marsh-jararaca, green-bellied caboclinho, lapwing, joão-de-barro, sabiá-do-campo, jacutinga, field woodpecker, blue-bearded hummingbird, vine snake, partridge, chimango hawk, weeping woodpecker, white-tailed woodpecker spur, ferret, otter, veritable gaturamo, tuco tuco, araponga, tanager, rhea, heron, teal, armadillo, graxaim, marsh ray, zorrilho, cavy, Red-bellied frog, etc.
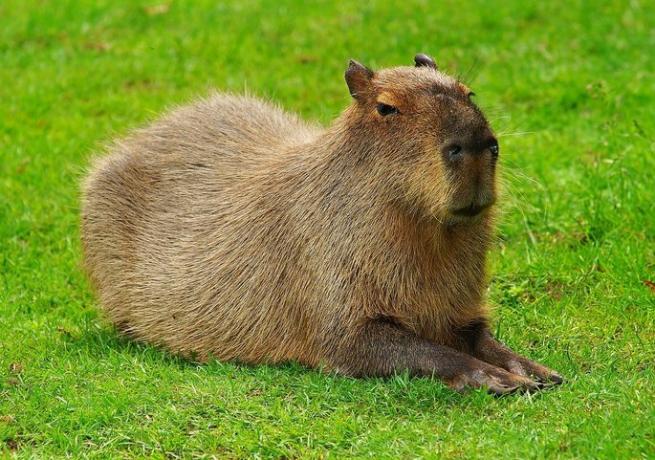

About 40% of animals in the pampas are endemic, that is, they are of species that are not found anywhere else in the world.
The extinction of animals in the pampas
Some species of animals in the pampa are at risk of extinction. One of the main reasons is the logging, which makes the animals have to migrate to another location and often this change of habitat makes it difficult for them to find food and even to reproduce.
Another reason that contributes to the risk of disappearance of certain species is the illegal wildlife trafficking, which mainly focuses on rare animals.
Some of the animals that may cease to exist over the years are:
- Jaguar

- Man-tailed Sauim
- Golden Lion tamarin
- pampas cat
- Anteater

- capuchin monkey
- jacutinga
- Ocelot
- red-bellied frog
The pampa in Brazil
In Brazilian territory, the pampa is also called Pampas, Campanha Gaúcha, Campos Sulinos or Campos do South and is fully concentrated in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, occupying an area of 176,496 km² (IBGE, 2004).
This area represents 63% of the state's territory and 2.07% of the Brazilian territory.
According to estimates by IBAMA (Brazilian Institute for the Environment and Renewable Natural Resources), in 2002 only 41.32% of the native vegetation of the pampas still existed.
In 2008, this percentage dropped to 36.03%.
It is estimated that the growing habit of monoculture and grazing has contributed to the degradation of the pampa's natural landscape.
Curiosity about the Brazilian pampa
Considered a cultural, genetic and natural heritage, the Gaucho pampa concentrates much of the Guarani Aquifer, the second largest aquifer in the world.
This aquifer has enough water to supply the Brazilian population for around 2,500 years.
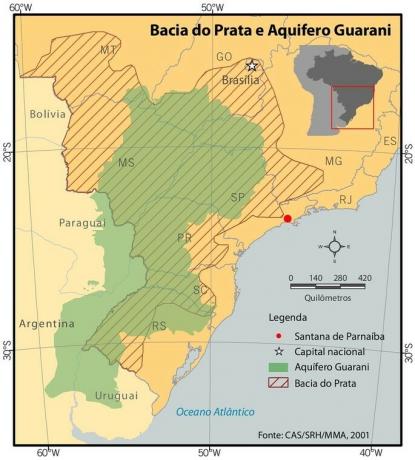
Territory occupied by the Guarani Aquifer: Uruguay (58,500 km²), Argentina (255 thousand km²), Paraguay (58,500 km²) and Brazil (1,200,000 km²)
See the meaning of biome, learn more about the Brazilian biomes it's the thick.
