Supply and demand are economic concepts used to explain how markets work. These are fundamentals of microeconomics, which explain how the price formation based on the interaction between consumers and companies.
THE offer it refers to the amount of goods and services that companies are willing to offer. THE demand (or demand) is the quantity of those goods and services that consumers are interested in purchasing.
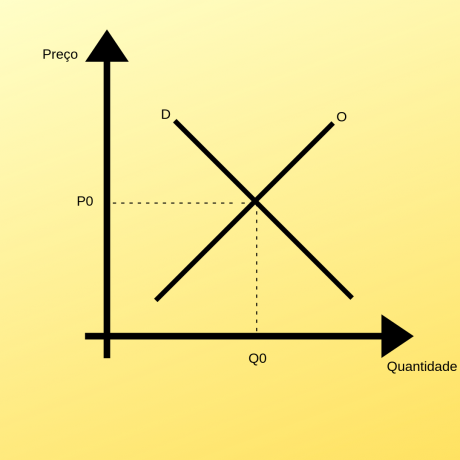
According to the law of supply and demand, the interaction between the two tends to a balance point. At the break-even point, price and quantity meet the desires of consumers and producers at the same time.
What is demand?
Demand is the amount of a good or service that consumers are interested in purchasing in a given period of time. This amount, in addition to other factors, will depend on the price of this good.
According to the law of demand, consumers will be willing to consume greater quantities of a product, the lower its price. This means that there is a inverse relationship between price and quantity.
In other words, the more expensive a product, the fewer units the consumer will be willing to buy, and vice versa. See this relationship in the chart of demand curve:
 Demand curve.
Demand curve.
Other factors that influence demand:
In addition to the price of the product in question, demand will vary according to other factors, such as:
Price of other goods
The price of other products can also influence the quantity demanded of a specific product. This can happen when there is a relationship of replacement or of complementarity between two products.
Example 1: a reduction in the price of prime beef can reduce demand for premium beef. Now, if better quality meat is at a lower price, more people will prefer to buy it instead of buying inferior meat.
In this case, that's because the second-rate meat is a substitute good of first-rate meat.
Example 2: a reduction in car prices will increase demand for gasoline. This is because the reduction in car prices leads to an increase in the demand for vehicles and, as a consequence, an increase in the demand for gasoline.
In this case, car and gasoline are complementary goods, because the consumption of one leads to the consumption of the other.
| Substitute goods | When the price of one product drops, it reduces demand for another product. |
|---|---|
| Complementary goods | When the price of one product drops, the demand for another product increases. |
consumer income
Consumer income also influences demand. This is because, if your income increases, the quantity of products demanded will also increase. But notice that this happens with normal products - products that we consume more when we have an increase in income.
There are also the inferior goods, which have their demand reduced when there is an increase in income. An example of an inferior good is second-rate meat. In this case, if the consumer's income increases, he will start buying better quality meat.
know more about demand and microeconomics.
What is an offer?
Supply is the amount of goods and services that companies are willing to sell in a given period of time. This quantity, among other factors, depends on the price of these goods and services.
According to the law of supply, companies will be willing to sell larger quantities of the product on the market, the higher its price. This means that the relationship between price and quantity supplied is positive.
In other words, the more expensive a product, the more units the company is willing to sell, and vice versa. See the relationship in the chart of supply curve:
 Offer curve.
Offer curve.
Other Factors Influencing Supply
In addition to the price of the product in question, the offer will vary according to other factors, such as:
Cost of production factors
Factors of production are all the costs that companies have to produce a given good, such as raw materials, wages and rents. If any of these factors have a high cost, the producer will be willing to offer a smaller quantity of the product in the market.
Technological changes
Technological advances can reduce costs and increase companies' productivity. When this happens, companies will be willing to offer a greater amount of products on the market.
know more about offer and economy.
law of supply and demand
According to the law of supply and demand, when there is the intersection of both curves, we can find the balance point of a good or service on the market.
At the break-even point, buyers are willing to buy all the products that companies want to sell at a certain price. That is, at the equilibrium price, the quantity that sellers and consumers are willing to transact is the same.
Learn more about law of supply and demand and concept of invisible hand by Adam Smith.


