The fertility rate is a demographic indicator which represents an estimate of how many children a woman has in her lifetime. It expresses the conditions of reproduction in a certain place.
With this indicator, it is possible to analyze the demographic dynamics. That is, predictions about the size of the population in the future - whether there will be an increase, a decrease or even a stagnation of population.
This information is extremely important for planning public policies in the areas of health, education, security, social security and urbanization, for example.
Although the fertility rate is different between regions of the world, there is a tendency for this index to decrease. In the 60s, women had an average of 4.92 children, today this number is 2.45.
How is the fertility rate calculated?
There are two types of fertility rate: a total fertility rate (TFT) and the specific fertility rates (FET).
The specific fertility rates are rates corresponding to the different age groups within the childbearing age - from 15 to 49 years.
The ranges are: 15-19, 20-24, 25-29, 30-34, 35-39, 40-44, 45-49. To calculate this rate, simply divide the number of births in an age group by the number of women in that age group.
The total fertility rate would be an average of all specific fertility rates, that is, an average of the number of children a woman has at the end of her reproductive period.
Why is the fertility rate decreasing?
The fertility rate in the world suffered a reduction from about 5 to 2.5 between the years 1960 and 2010. This means that the number of births has halved in about 50 years.
This reduction is the result of cultural, economic and political changes related to women. Some of the factors that stand out are:
- Increased education for women.
- Greater participation of women in the labor market.
- Sex education and family planning policies.
- Greater access to contraceptive methods.
In recent decades, women stopped occupying domestic spaces and started to insert themselves more and more in the labor market and to invest in their education.
Today, it is common for women to finish their studies and reach certain levels in their professional careers first, before planning to have children.
Many couples also choose not to have children, a decision that is often related to the high costs of parenting.
As the opportunities for study, work and access to information are related to higher income, it is natural that fertility rates are lower in more developed countries or in more developed regions of a parents.
However, even in underdeveloped countries, there is a reduction in the number of children per woman.
See also the meaning of demographic density and vegetative growth.
population replacement rate
The population replacement rate is the fertility rate needed to balance the number of inhabitants in the world.
This rate is 2,1, which would be two children to replace the parents and the fraction 0.1 to compensate for the number of people who die before reaching reproductive age.
This means that if, for a long period of time, a country has a fertility rate equal to 2.1, it will not have population growth. On the other hand, a country that has a fertility rate below 2.1, in the long run, will have its population reduced.
understand what it is population and absolute population.
Fertility rate in Brazil
Brazil is a country where the fertility rate is below population replacement rate. The average number of children a woman has throughout her fertile life is 1,7 - index similar to that of developed countries.
And this index continues to decrease. According to IBGE, in 2000 the total fertility rate was 2.39 and in 2015 it dropped to 1.69. See below the chart for this period:
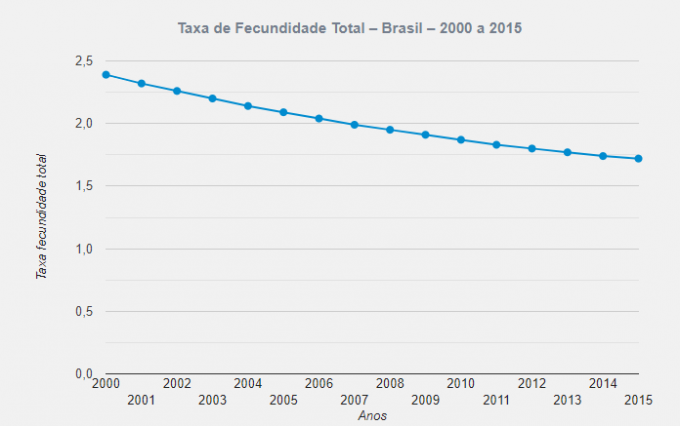
Source: IBGE.
According to data from the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), this reduction was observed in all regions of the country and was more significant in the poorest and least educated social strata.
In the extract of women who have between zero and four years of schooling, the index dropped from 3.45 to 2.9, a reduction significant if compared to women who have more than 12 years of schooling, an extract in which there was a reduction of 1.56 to 1.18.
This reduction is the result of more access to information it's from social programs awareness and family planning.
Despite the fertility rate showing a convergence trend throughout Brazil, there are still regional differences: at one extreme we have the southern region with 1.57 children per woman and 2.06 in the north.
See the variation in the fertility rate between 2000 and 2016 in the five regions of Brazil in the graph below.
| Year | 2000 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 2,39 | 1,69 |
| North | 3,18 | 2,06 |
| North East | 2,72 | 1,93 |
| Southeast | 2,11 | 1,58 |
| South | 2,17 | 1,57 |
| Midwest | 2,25 | 1,67 |
Source: IBGE data.
fertility rate in the world
The fertility rate in the world is falling. In the last 50 years, this number has halved if we consider the world average.
Some countries even register rates close to 1 child per woman, as is the case of the Cyprus and Taiwan. In the long run, this rate represents the shrinking and aging population of these countries.
Low fertility rate is a more common phenomenon in developed countries, where women have more opportunities to study and work and more access to information.
However, there are still countries where the fertility rate is high, such as the Niger, where the average number of children per woman is 7,6. This happens in underdeveloped countries and, in particular, in Africa.
See the chart below for the conditions of reproduction in different regions of the world. The lightest regions are the countries where the fertility rate is lower and the countries in dark red represent the highest numbers of children per woman.

Source: Our World in Data.
Both the insufficiency of births in developed countries and the population growth resulting from high rates of fertility in poor countries represent challenges for States and require public policies to balance rates demographics.
Difference between fertility rate and fertility rate
The fertility rate is related to physiological capacity of having children, that is, the reproductive potential of women. The fertility rate, on the other hand, is the concrete result of the average number of children that women have in a given location.
In general, the fertility rate will always be less than the fertility rate, as many women who can have children will not have them. This may be due to women's preferences for not having children or even due to birth control policies.
Also know the birth rate and the mortality rate.