The equatorial climate occurs in places close to the equator and is due to the more direct incidence of the sun. Is characterized by high temperatures and high moisture content.
In Brazil, the states that have an equatorial climate are located mainly in the northern region of the country: Amapá, Amazonas, Rondônia, Roraima and Tocantins. It also occurs in Maranhão (northeast region) and Mato Grosso (central-west region).
Where is the equatorial climate in the world?
The equatorial climate exists in places close to the equator, which is why it is called equatorial. In these regions there is low latitude, which is the measure of the distance of a point from the equator. The closer to the line, the lower the latitude.
In addition to Brazil, some countries located in South and Central America, such as Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Jamaica, Peru and Venezuela are examples of places with typical climate equatorial.
The central region of Africa (such as Nigeria, Cameroon and Congo) and the Southeast region of the Asian continent (such as Thailand, India and Malaysia) also have an equatorial climate.
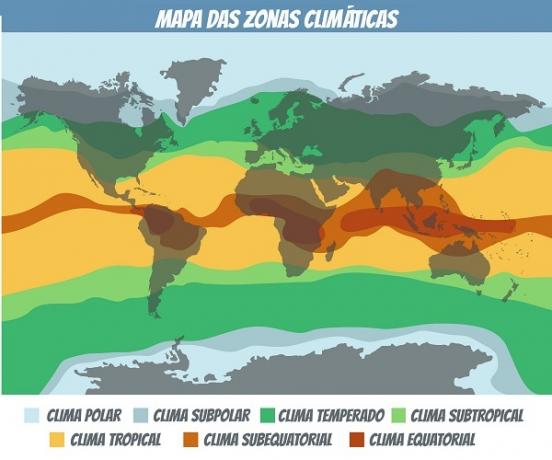 Distribution of climatic zones in the world.
Distribution of climatic zones in the world.
Equatorial climate characteristics
In addition to being hot and humid, the equatorial climate is also characterized by the high air humidity, high rainfall and presence of hot air masses.
Rains tend to be frequent during practically the whole year, which can cause regions to have higher humidity levels compared to others. The annual average is approximately 2000 millimeters of rain.
The temperature does not vary much during the year, with annual averages around 26 degrees. The same happens with the variation of temperatures between day and night. This phenomenon is called low thermal amplitude, that is, the temperature variation is small.
As a result of these characteristics, in regions with an equatorial climate, the seasons of the year are not well defined, as there are no great thermal variations.s
Vegetation
The vegetation is called equatorial forest. It is mainly formed by dense forests typical of regions with high humidity.
The vegetation is quite varied, formed by lots of green and leafy and abundant species, well adapted to high temperatures and high humidity.
The soil, which is considered poor in nutrients, is not suitable for the cultivation of other species that do not adapt to humidity.
The Amazon forest, which extends over the territories of several countries (such as Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Venezuela), is an example of an equatorial forest.
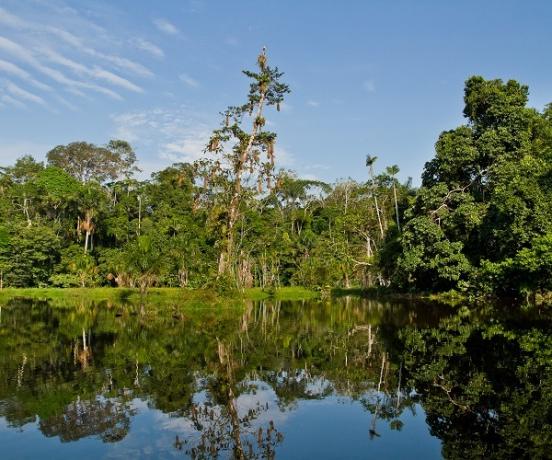 Amazon rainforest in the Yasuní National Park (Ecuador).
Amazon rainforest in the Yasuní National Park (Ecuador).
animal species
The fauna of the equatorial climate is quite diverse, consisting of animals adapted to life in humid and hot climates. Some examples are: parrots, toucans, monkeys, capybaras, jaguars and macaws.
Several species of insects and amphibians are also found in the fauna of the equatorial climate.
Wet and semi-humid equatorial climate
The equatorial climate, according to very specific characteristics, can be divided into two types: humid and semi-humid.
At the wet weather rain is constant throughout the year and occurs in large amounts, which increases humidity levels. Also, temperatures are high during all seasons.
At the semi-humid climate, temperatures are also high. The difference in relation to the humid climate is the amount of rain, which is scarcer at any given time of the year. Thus, in the semi-humid climate there is a rainier season and a drier season.
See also the meanings of Climate, Tropical weather, polar climate and types of weather.