Solar radiation is the energy emitted by the sun in the form of radiation - electromagnetic waves. It is emitted by the photosphere, the outermost layer of the sun, which is approximately 300 km long.
It is a source of energy for the planet, in addition to being responsible for its heating. It is also critical for determining the Earth's climate.
The amount of radiation varies depending on the region of the globe: the areas that receive it most are those close to the Equator. The lowest incidence of radiation occurs in extreme areas.
How does solar radiation reach Earth?
Solar radiation travels through the atmosphere and reaches the earth's surface, heating it. Much of the radiation received is absorbed, and this part is responsible for the planet's warming. Another fraction - infrared - is reflected and does not reach Earth.
The control of radiation reaching the surface is due to the atmosphere, which filters it in different ways, depending on the wavelength.
A part of the solar radiation that reaches the Earth (ultraviolet) is absorbed by the
ozone layer, a layer formed by ozone gas (O3) which is around the Earth. It's what prevents high levels of radiation from reaching the planet.Read more about the importance of ozone layer.
Types of solar radiation
Solar radiation is divided into three types, which are classified according to wavelength and intensity: visible, ultraviolet and infrared.
visible radiation
Radiation gets its name because it is visible to humans. It is the simplest form of electromagnetic radiation and concentrates much of the energy that comes from the sun.
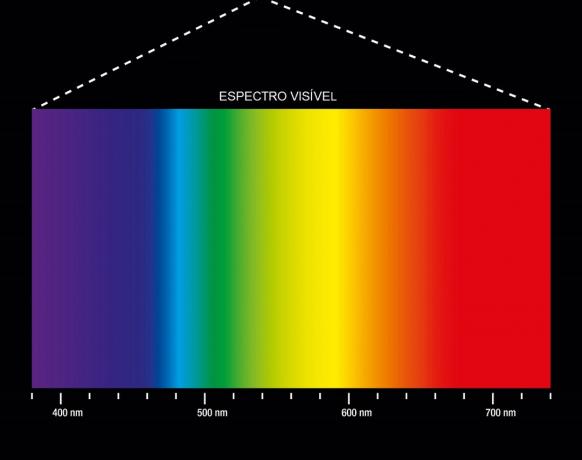 Color spectrum of visible radiation.
Color spectrum of visible radiation.
As we see in the image, it is composed of a spectrum of the following colors: red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue and violet. Color wavelengths vary between 380 nm (violet) and 740 nm (red).
ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation contains the least part of solar energy. Its wavelength is shorter and for this reason it is not visible.
It has three classifications, according to the wavelength: UVA (between 400 nm and 315 nm), UVB (between 315 nm and 280 nm) and UVC (between 280 nm and 100 nm).
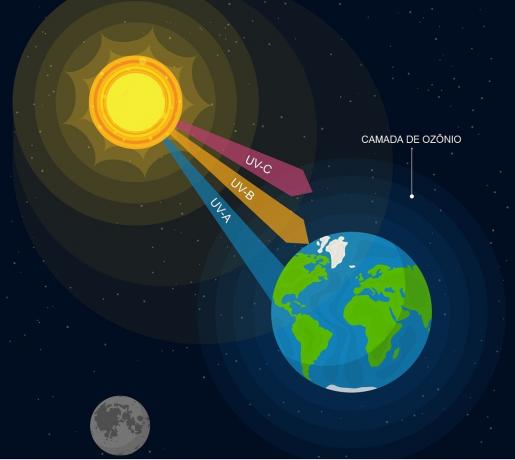 UVA, UVB and UVC waves have different wavelengths.
UVA, UVB and UVC waves have different wavelengths.
UVA radiation corresponds to almost all the ultraviolet radiation that reaches the Earth. On a smaller scale, UVB radiation also reaches the surface. These two can cause sunburn.
UVC radiation, on the other hand, because it has the shortest waves, does not reach the earth's surface, being completely absorbed by the atmosphere.
See more about UVA and UVB.
infrared radiation
Infrared radiation contains most of the solar energy, reaching almost 50%, and is also not visible to humans. Its length varies between 780 nm and 1 mm, which means that it is longer than light.
It has the characteristic of producing great thermal agitation. Therefore, this radiation can damage human tissues that are formed by many water molecules, such as the eyes.
Read more about greenhouse effect and global warming.
Solar radiation as an energy source
Solar radiation reaching Earth can be used to produce energy. The result of this process is called photovoltaic energy. The generation takes place through solar panels, formed by small silicon structures (voltaic cells).
The panels are installed in areas with high incidence of sunlight, and the energy is generated from a reaction between photons present in the radiation and cells composed of silicon.
 Photovoltaic energy production system in operation.
Photovoltaic energy production system in operation.
The system has many advantages: it is non-polluting, does not require much maintenance and has a high durability.
Disadvantages include the high price of installing the panels and the instability of energy production, which varies according to local climatic conditions.
Also learn about other types of radiation.