It is a treatment that consists of providing extra oxygen to improve the quality of life and treat people who have respiratory disorders and therefore cannot get oxygen naturally.
Oxygen is a gas that the human body needs to function. Normally, the air we breathe is obtained naturally, however, certain breathing disorders can prevent this from occurring.
During treatment, oxygen is artificially sent to the lungs through nasal appliances, masks or breathing tubes.
Who is oxygen therapy intended for?
As stated earlier, oxygen therapy is prescribed for people who cannot get enough oxygen on their own.
This is usually due to lung conditions that prevent the lungs from absorbing oxygen, including:
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- pneumonia;
- asthma;
- bronchopulmonary dysplasia;
- underdeveloped lungs in newborns;
- cardiac insufficiency;
- cystic fibrosis;
- sleep apnea;
- lung disease;
- trauma to the respiratory system.
To determine whether a person will benefit from oxygen therapy, doctors test the amount of oxygen in the arterial blood.
Another way to check is by using a pulse oximeter that indirectly measures oxygen levels without requiring a blood sample. Low levels mean that a person may be a good candidate for supplemental oxygen use.
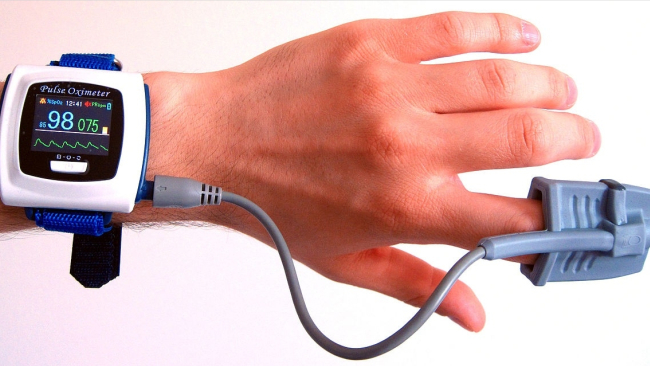 Oximeter device.
Oximeter device.
Normal arterial blood oxygen levels are between 75 and 100 mmHg (millimeters of mercury). An oxygen level of 60 mmHg or less may indicate the need for supplemental oxygen.
Some people need oxygen therapy all the time, while others need it only occasionally or in certain situations.
Different types of oxygen therapy
nasal cannula
A nasal cannula, also known as nasal catheter, is a double-ended tube device connected to an oxygen source. The "teeth" sit at the entrance to the nostrils with the tube anchored over the ears to hold it in place.
Nasal cannulas provide a low flow rate of oxygen mixed with ambient air and are suitable for those with minimal breathing difficulties or those who require prolonged use of oxygen.
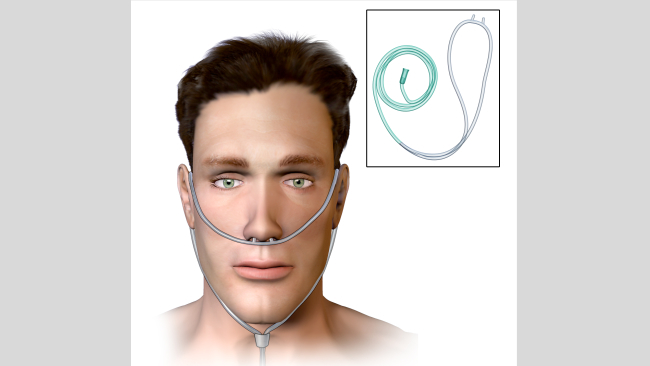 Nasal cannula.
Nasal cannula.
simple face mask
For an oxygen concentration delivery greater than 40% to 60%, a plain face mask, also known as a Hudson Mask, is the most recommended form of oxygen therapy.
The mask fits over the nose and mouth with a metal piece that conforms to the shape of the nose on top and an elastic strap around the head to hold the mask in place.
The oxygen source connects to the mask and exhalation ports, allowing carbon dioxide to escape, as well as mixing supplied oxygen with ambient air.
The two best known types of simple face mask are: Hudson mask and Venturi mask.
 Simple face mask.
Simple face mask.
tracheostomy masks
Partial breathing and no breathing masks are considered reservoir masks.
These masks provide higher concentrations of oxygen for people with severe respiratory illnesses: 70 to 90% of a partial respiratory mask.
Both types of masks resemble a simple face mask, except that they have a reservoir bag attached. Reservoir masks have one-way valves to keep out outside air.
 Tracheostomy mask.
Tracheostomy mask.
See also the meaning of oxygen.
