An optical illusion or optical illusion involves images that are perceived by the visual system in a way and interpreted differently in the brain.
While the brain can process some of the attributes of the image or object, there are aspects that are misleading and therefore lead to errors in the perceptual process.
Types of Optical Illusion
There are three generally recognized types of optical illusions. These are the literal illusions, cognitive illusions and physiological illusions.
literal optical illusion
When the mind receives visual information, it fills in details or gaps that don't really exist. The eye and brain will choose and focus on specific objects that make part of the image appear one way or another.
Depending on what the brain chooses to focus on, it can perceive two different images in one, this type of optical illusion is the literal illusion.
The image below is a standard example of a literal optical illusion. The artist drew only a young woman, in profile.
However, as our minds use borders to identify objects and people, we see not only the young woman drawn, but features of an old woman, in the same image.
 Example of literal optical illusion.
Example of literal optical illusion.
cognitive optical illusion
A cognitive illusion refers to the type of illusion that distorts the experiencer's knowledge and assumptions about a physical element or object and its environment.
Dr. Herman Helmholtz, a German physician, suggested that a cognitive illusion arises when there is an interaction with the world's beliefs and assumptions, resulting in unconscious inferences.
Most psychologists agree with the four types of cognitive illusions, namely:
- geometric-optics: geometric optical illusions are those that have distortions in length, shape, size, curvature and/or position;
- ambiguous: ambiguous illusions are images of objects that trigger an exchange between possible alternatives at the perceptual level. These illusions include so-called "impossible objects";
- fictional: fictional illusions are illusions that provoke the perception of a figure who is not actually present in the stimulus;
- paradoxes: the illusions of paradox are those that are made by paradoxical or improbable objects.
Physiological Optical Illusion
Physiological illusions are the effects on the eyes or brain of excessive stimulation of a specific type—brightness, tilt, color, movement, and so on.
The theory is that this repetitive stimulation of just a few channels tricks the visual system.
 Example of physiological illusion.
Example of physiological illusion.
Images and examples of optical illusion
As we saw above, there are numerous types of optical illusions. Some are widely used and disseminated on the internet.
Listed below are some of the most popular images:
The Lilac Hunter Illusion

In the purple hunter illusion, it is possible to observe several different visual effects over a period of about thirty seconds.
Follow the pink dot movement for a few full rotations and then look at the black cross in the middle. You will notice a green dot that will erase any pink dots from the image.
First described in 2005, the illusion is caused by several different factors, including negative afterimages and what is known as Troxler fading.
Hermman Grid

At the Hermann Grid Illusion, the white dots in the center of each square appear to change from white to gray.
The effect seen in this image is one of many optical illusions that take advantage of the way our visual system processes contrast information.
A neural explanation of illusion points in terms of receptive fields: Some retinal ganglion cells gather information about many photoreceptors.
the optics of art

Optical art images appear to be moving, even if they are not animated. Most theories about the illusion of motion in optical art have to do with the brain's inability to process different colors and shapes simultaneously.
In short, there is so much going on in these images that movement is perceived where there really is none.
These images are most often associated with psychedelic art, but other schools also use art techniques. Optical art, which has its roots in Impressionism, Dada, Cubism and other more art forms. classics.
Many artists see this style as a way to challenge viewers' perceptions or get them to interact with the work, rather than simply viewing it.
See also the meaning of Dadaism and cubism.
Rabbit-Duck Head Illusion
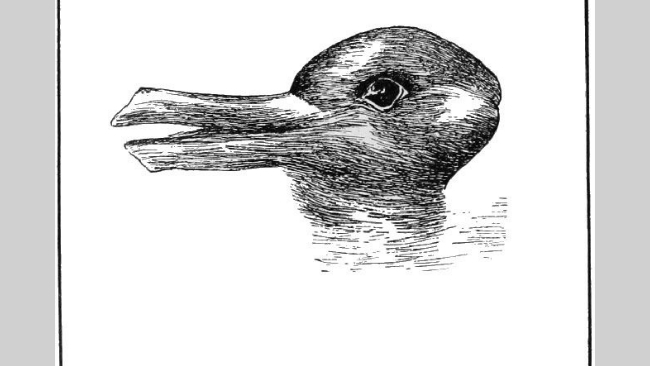
One of the first examples of an ambiguous illustration, the Rabbit-Duck Head illusion was first published in Germany in the late 19th century.
These hidden images were quite popular at the time. In this particular example, the duck's beak becomes the rabbit's ear and the eye is designed in such a way that it fits both the right and left side animals.
illusion of ponzo
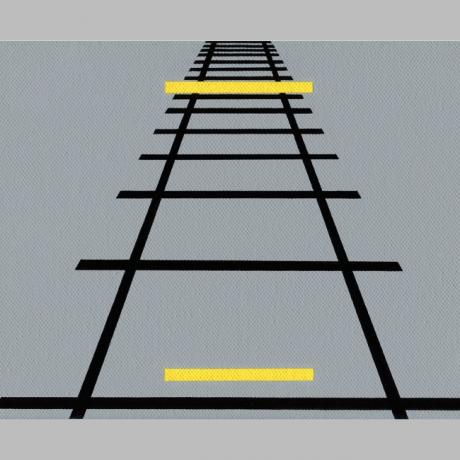
In the Ponzo illusion, two identically sized lines appear to be different sizes when placed on parallel lines that appear to converge as they recede into the distance.
The reason the top horizontal line looks longer is because we interpret the scene using a linear perspective.
As the vertical parallel lines appear to come closer together across the image, we interpret the upper yellow line as larger than the lower one.
3D Optical Illusion
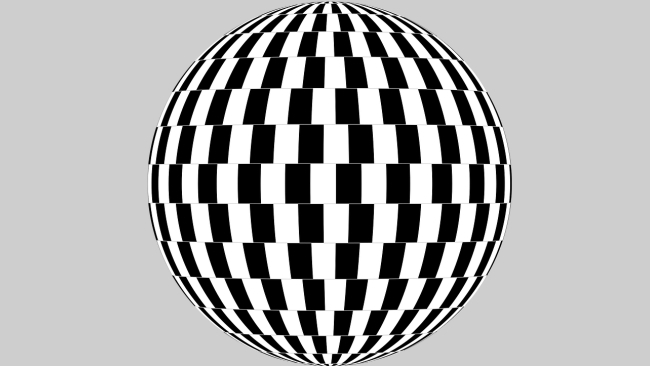
The image above is a kind of 3D illusion. By focusing your eye from a distance, you can see that the image appears to have different dimensions.
See also the meaning of perspective, impressionism and Op Art.
