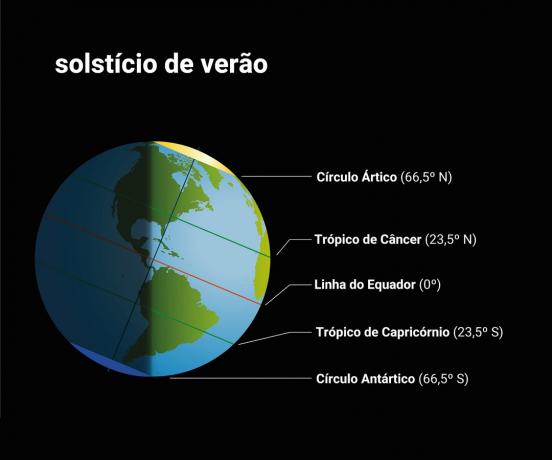
Winter Solstice is an astronomy phenomenon that marks the early winter. With reference to the Southern Hemisphere, the winter solstice is the time when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted about 23.5° towards the Sun.
The term solstice has its origin in Latin solstitius which means "point where the sun's trajectory does not appear to move". Consists of sun + sister which means "stopped".
The winter solstice is the shortest day of the year and consequently the longest night of the year, in terms of illumination by the Sun.
The solstice happens thanks to the phenomena of rotation and translation of planet Earth, because thanks to these events sunlight is unevenly distributed between the two hemispheres of the planet Earth.
Winter Solstice in the Southern Hemisphere
When the countries of the Southern Hemisphere, such as Brazil, are going through the Winter Solstice, the countries of the Northern Hemisphere are going through the opposite phenomenon: the Summer Solstice.
Thus, they are phenomena that happen at opposite times, depending on the hemisphere in which a particular country is located. For this reason, when it is winter in Brazil (Southern Hemisphere), it is Summer in Portugal (Northern Hemisphere) and vice versa.
Winter Solstice in 2021
In the Southern Hemisphere the 2021 Winter Solstice will take place on June 21, 2021 at 00:32.
See also the meanings of Solstice and Summer Solstice.
Equinox
The equinox is also an astronomical phenomenon that marks the beginning of two seasons of the year, in this case the beginning of autumn and spring. As with the Solstices, the equinoxes happen at opposite times in the Southern Hemisphere and the Northern Hemisphere.
In the Southern Hemisphere, the Autumn Equinox usually occurs between the 20th and 21st of March and the Spring Equinox takes place on the 22nd or 23rd of September.
See more about the meaning of Equinox, Autumn Equinox and Spring Equinox.