The types of energy are the different ways in which energy manifests. Energy is the capacity of a body to produce work, that is, to promote action or movement.
Electricity
Electric energy is one of the most used types of energy in the world, it is easily transported by cables and can be produced from various energy sources, such as water, wind, the sun and burning substances fuels.
Electrical energy or electricity is the result of moving small particles called electrons, which are carried by wires.
All electronic devices and lights that we turn on in our homes are powered by electricity. Electricity is produced in power plants and reaches our homes via electrical cables.
 Electric cables distribute the energy produced in the plants.
Electric cables distribute the energy produced in the plants.
What are the sources of electrical energy?
At the plants, electrical energy is produced by generators, which are activated from the movement of the turbines. The movement of turbines can basically happen in two ways:
- mechanical energy: when turbines are moved by the force of water and wind, as in hydroelectric and wind power plants.
- chemical energy: when the turbines are moved by steam from burning fuels, as is the case with thermoelectric and nuclear power plants.
Some examples of fuels used in thermoelectric power plants are: coal, oil, natural gas and biomass. Nuclear power plants use radioactive elements such as uranium and plutonium.
Mechanical Energy
Mechanical energy refers to the ability of a body to move into motion. Mechanical energy is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy.
- Kinetic energy: it is the energy related to the movement of the body, it exists whenever it acquires speed;
- Potential energy: is the energy of a body that is in a position but can move. It's an energy that can turn into kinetics.
An example of potential energy is a metal ball attached to a pendulum. When we lift the ball with our hand, it acquires potential energy, as it will go into motion when we release it.
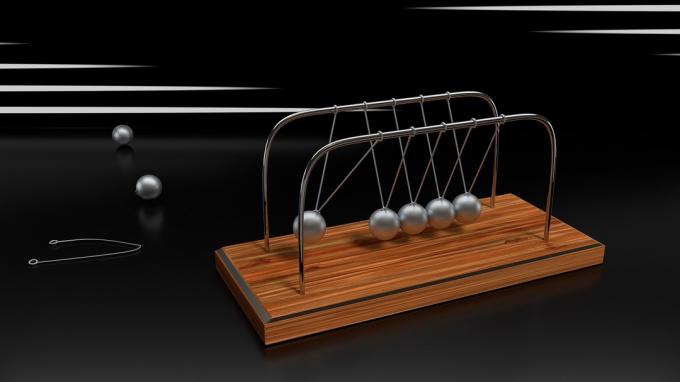 A ball suspended from a pendulum has potential energy when it is stationary and kinetic energy when it is in motion.
A ball suspended from a pendulum has potential energy when it is stationary and kinetic energy when it is in motion.
What are mechanical energy sources?
Mechanical energy exists in any moving body or in a position from which it can generate movement, that is, do work.
We can find examples of mechanical energy in our daily lives, such as the wind, a ball thrown into the air, a person running or a car in motion.
The power of water is one of the most used mechanical energy sources for the production of other types of energy, such as electricity.
In a hydroelectric plant, the force of a large waterfall is used to move the turbines, which drive the generators and transform mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Learn more about mechanical energy.
Thermal energy
Thermal energy is the internal energy of a body or substance and is the result of the vibration of its atoms and molecules.
Thermal energy is obtained from heat: the hotter a substance is, the faster the particles will move and the higher the thermal energy.
We can think of several examples of thermal energy in our daily lives, such as the heaters we use in the cold, the oven where we bake a cake and a cup of hot chocolate.
To make hot chocolate, for example, we put cold milk in a milk jug and turn on the stove. The flame heats the milk and stirs its molecules, resulting in an increase in thermal energy.
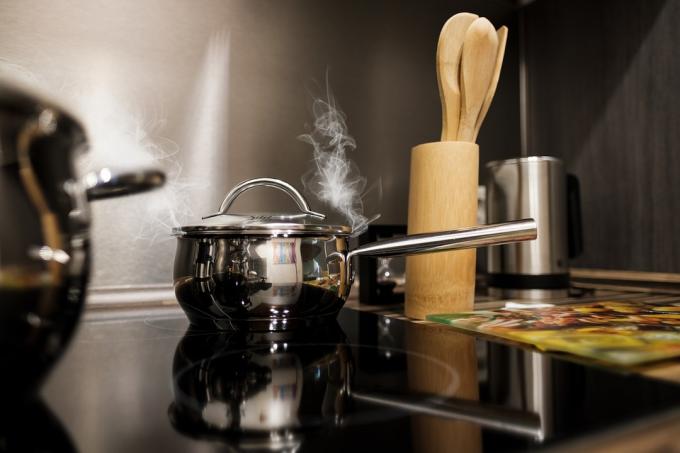 Food heated on a stove acquires thermal energy.
Food heated on a stove acquires thermal energy.
What are the thermal energy sources?
Thermal energy can be obtained from burning some fuel such as gas, oil or wood and can also be obtained from the sun's rays and the heat produced inside the Earth.
Thermal energy is used in some plants to produce other types of energy, such as electrical and mechanical energy, or it can be used directly as thermal energy in heating systems.
Learn more about Thermal energy.
Nuclear energy
Nuclear energy is the energy existing in the nucleus of an atom and which is released when the nucleus is fissioned or broken.
Atoms are particles that form all objects existing in nature (including our bodies). They are made up of protons, electrons and neutrons and a nucleus, where the energy comes from.
Nuclear energy is used for the production of electrical energy in several countries around the world, but it has also been used for military purposes in the production of atomic bombs.
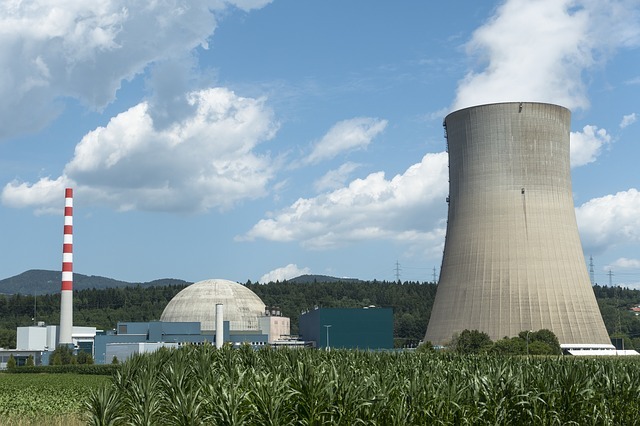 Nuclear power production plant.
Nuclear power production plant.
What are the sources of nuclear energy?
The main source of nuclear energy is uranium, a radioactive element found in rocks. This element is obtained from nature and transformed into pellets that will be used in nuclear reactors.
The energy production process takes place as follows:
- The uranium nucleus is broken by neutrons that are hurled towards it;
- With the disruption of the nucleus, two uranium atoms are formed;
- When the nucleus is broken, energy and new neutrons are released;
- These neutrons head towards other uranium nuclei, causing them to break, starting a chain reaction.
Learn more about nuclear energy.
Chemical Energy
Chemical energy is potential energy and is stored in the bonds of chemical elements. When a chemical reaction takes place, this energy is released.
The chemical reaction usually produces heat and when it does, the parent substance is transformed into a completely new substance. One of the main examples of chemical energy reaction is combustion.
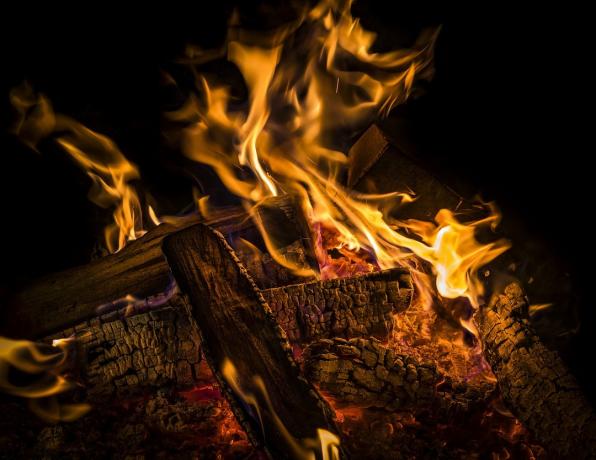 Wood has chemical energy, which is released with combustion.
Wood has chemical energy, which is released with combustion.
What are the sources of chemical energy?
Chemical energy is present in elements that when burned produce energy, such as coal, biomass, wood and oil.
These elements are formed by chemical bonds and when they combust they release energy and their atoms reorganize, forming a new chemical substance.
Let's look at the hydrogen combustion reaction (H2), which happens with half an oxygen molecule (½ O2):
H2 + ½ the2 → H2O
When a hydrogen molecule reacts with half an oxygen molecule, a reaction occurs in which energy is released and whose product is a water molecule.
Another example would be the combustion of coal (C) which reacts in contact with oxygen (O2):
C + O2 → CO2
The carbon molecule reacted with the oxygen molecule, changing the chemical bonds and forming a carbon dioxide (CO) molecule.2). In this process there is also the release of energy.
Learn more about chemical energy.
Energy sources: what are renewable and non-renewable energy?
Energy sources are the raw materials used to produce energy. Energy is used for the operation of machines, means of transport and electronic devices.
Energy production can have major impacts on the planet's natural resources and sustainability. In this regard, energy sources can be classified as renewable and non-renewable.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energies are energy sources that are not depleted with use, such as wind or solar energy. Regardless of how much these resources are used for energy production, their availability in nature has not diminished.
The main sources of renewable energy are:
- water: the force of water movement turns the turbines and activates the generators that produce energy;
- wind: the force of the winds turns the windmills or pinwheels and activates the wind turbines that produce energy;
- Geothermal: Steam and hot water from the heat inside the Earth are used to turn turbines and produce energy. This energy source is obtained from the drilling of deep reservoirs;
- Solar: solar panels capture energy from heat and sunlight, which passes through an inverter and is transformed into electrical energy;
- biomass: is the energy obtained from burning organic matter of animal or vegetable origin. Biomass can be obtained from the decomposition of food and plant waste, animal manure and garbage;
- oceans: is the energy obtained from the movement of the tides (tidal motion) or sea waves (ondomotive). The movement of water drives electrical generators that are semi-submerged in the sea and store energy.
Learn more about renewable energy.
Non-renewable energy sources
Non-renewable energy sources are those that can be depleted with use, as nature is not capable of renewing them at the same speed as they are used.
These sources are of organic origin, both plant and animal, and are formed by nature in slow processes that can last up to millions of years.
The main non-renewable energy sources are:
- Mineral coal: coal is a fossil fuel obtained by mining and is used to produce electricity in thermoelectric plants. It is also used as thermal energy for industrial processes;
- Petroleum: Oil is a fossil fuel obtained from drilling in the ocean floor. It is used for the production of electric energy and also in motor vehicle fuels;
- Natural gas: Natural gas is also a fossil fuel and is generally found close to oil. Natural gas is also used as fuel and for generating electricity;
- nuclear fuels: Nuclear energy is obtained mainly from uranium, a material available in limited quantities in nature. In addition to not being renewable, nuclear fuels are dangerous due to their radioactivity.
Learn more about non-renewable energies.
What are the main energy sources in Brazil?
According to 2016 data from the Ministry of Mines and Energy, Brazil is one of the countries that most uses energy from renewable sources, they represent 42.9% of its energy matrix.
Considering the whole world, the percentage of renewable energy is only 13.7%, which represents an advantage in terms of sustainability for the country. In addition, there is a diversification in energy sources, check it out.
Renewable energies represent 42.9% of the Brazilian energy matrix
- Sugarcane biomass: 17%
- Hydraulics: 12%
- Firewood and charcoal: 8%
- Bleach and other renewables: 5.9%
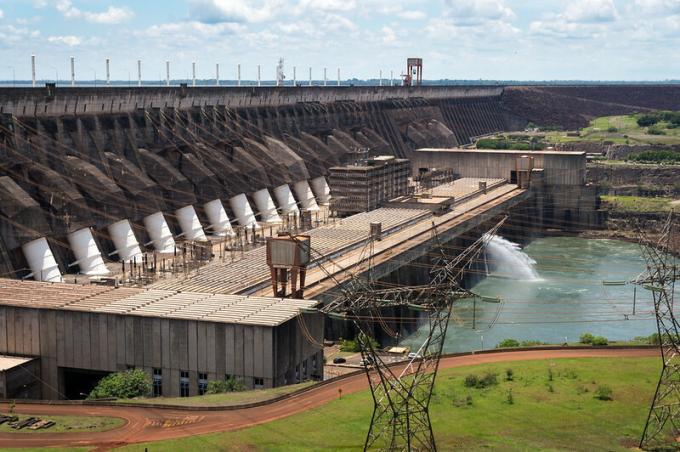 Itaipu is the largest hydroelectric plant in Brazil and the second largest in the world.
Itaipu is the largest hydroelectric plant in Brazil and the second largest in the world.
Non-renewable energies represent 57.1% of the Brazilian energy matrix
- Oil and derivatives: 36.4%
- Natural gas: 13%
- Coal: 5.7%
- Uranium: 1.4%
- Other non-renewables: 0.6%
 Oil extraction platform in Angra dos Reis, Rio de Janeiro.
Oil extraction platform in Angra dos Reis, Rio de Janeiro.
Primary energy sources are transformed into secondary energy
The primary energy sources are those that come directly from nature and are transformed into secondary energies to be used by man. Some primary energy sources are: water, sun, wind, fossil fuels, sugarcane and uranium.
These energies are captured in transformation centers, such as power plants and refineries, and are transformed into secondary energies. Some examples of secondary energy are: electricity, biogas, petroleum products, ethanol, gasoline and charcoal.
3 examples of environmental impacts caused by energy production
Since the Industrial Revolution, the demand for energy has grown at very high rates. Energy is needed for the operation of industries, transport, generation of electricity in homes, for agriculture, etc.
This high need for energy production causes major environmental impacts, such as air and ocean pollution and ecosystem imbalance. See some of the main environmental impacts of energy production:
1. Fossil fuels are most responsible for global warming
Currently, the most used energy sources in the world are fossil fuels. Together, oil, natural gas and coal represent 81% of all energy production and consumption in the world.
Fossil fuels are made up of all living matter (plants and animals) that have been decomposing over millions of years. This means that your production happens very slowly.
These fuels have a large amount of carbon in their composition and the chemical reaction that takes place during their combustion releases energy and gases such as carbon dioxide.
What is the relationship of fossil fuels with global warming?
Burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O).
These gases build up in the atmosphere and prevent the sun's rays from being reflected back into the atmosphere. Some of the heat that should be reflected is trapped on the Earth's surface, raising its temperature.
Global warming results in the melting of the polar ice caps and rising sea levels, the extinction of species and the imbalance of ecosystems.
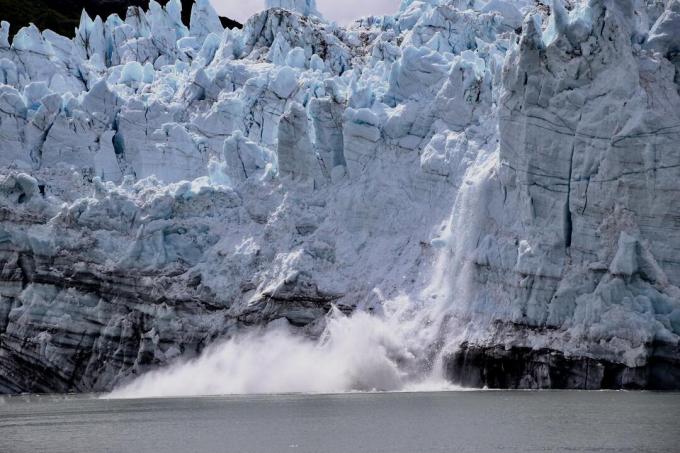 Global warming causes glaciers to melt.
Global warming causes glaciers to melt.
2. Nuclear fuels are radioactive and life-threatening
The production of nuclear energy is the target of much criticism due to the risks involved with the use of radioactive materials. The biggest impacts of this type of energy are:
Risk of contamination by tailings
The elements used in the production of nuclear energy, such as uranium and plutonium, present a great risk to life, as they are highly radioactive.
For the production of nuclear energy, uranium dioxide pellets are used, which remain toxic for thousands of years and must be stored in lead reservoirs.
If these residues are not stored correctly, they can contaminate soils and waters, causing imbalances in ecosystems and posing risks to all forms of life.
Risk of contamination in accidents
Nuclear power plants follow strict safety protocols, but pose risks of leakage and accidents, such as those that happened in Chernobyl (1986) and Fukushima (2011).
The radiation emitted in these accidents can cause deaths, diseases such as cancer, malformation of fetuses, genetic mutations in insects, plants and animals and burns.
Sea water heating
Nuclear energy production plants use seawater to cool the reactors, which move the turbines and reach very high temperatures.
In this process, the sea water used for cooling is heated and returned to the sea 60° C warmer than ambient temperature, which can impact the marine ecosystem.
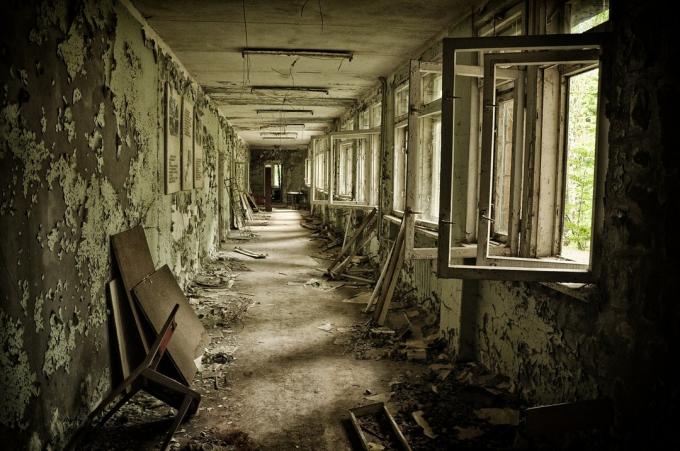 Construction destroyed after the accident in Chernobyl, Ukraine.
Construction destroyed after the accident in Chernobyl, Ukraine.
3. Hydroelectric energy is renewable, but it causes environmental impacts
Hydroelectric power plants use the mechanical energy of the power of water to move the turbines, but in order for the water to reach the necessary strength, dams are built that dam the water.
When the dam fills, the dams are opened and the water comes down with great pressure, moving the turbines to generate electricity.
Despite being renewable, to build a dam it is necessary to flood a very large area, causing major environmental impacts, such as the extinction of species and alteration of ecosystems.
In addition, because they use very large areas, the construction of hydroelectric plants usually remove riverine communities, who are forced to leave their homes and start over in others locations.
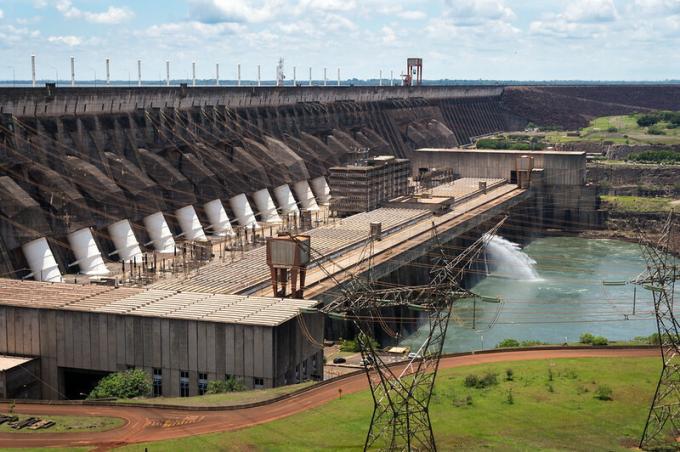 Itaipu power plant dam.
Itaipu power plant dam.
Know more about: fossil fuels and global warming and greenhouse effect.

