THE plane geometry is the field of mathematics that studies the geometric shapes of up to two dimensions, that is, those that can have width and length, but have no depth.
In honor of a great mathematician named Euclid of Alexandria, considered the “father of geometry”, plane geometry is also known as Euclidean geometry.
The development of plane geometry, both in terms of concepts and properties, as its name suggests, is done from a structure called flat.
What is the plan?
The plane is a two-dimensional region, with width and length, which allows the study of flat geometric figures.
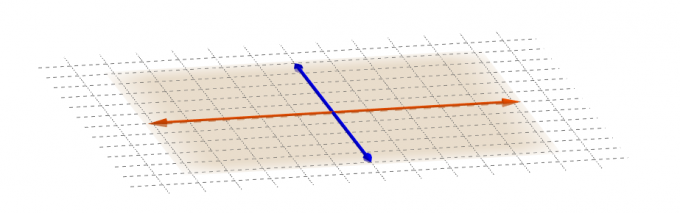
A plane can be determined by three non-aligned points, a line and a point outside it, or two intersecting lines, as shown in the figure below.
flat geometric figures
Plane geometric figures are objects of study of plane geometry. Among them, the circles, squares, rectangles and triangles.

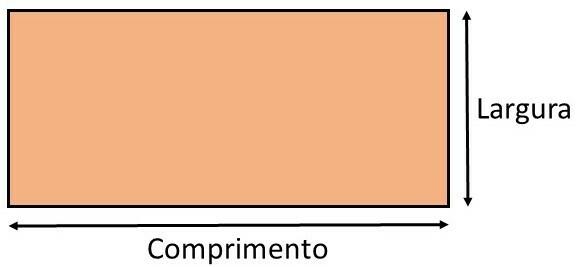
All flat figures have two dimensions: width and length. See the example in the rectangle:
- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Math Games Course in Early Childhood Education
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course
Flat figures can be classified into two main groups: polygons and non-polygons.
Polygons
You polygons are the flat figures formed by a closed line, which does not cross and whose sides are only straight segments.
In other words, polygons do not have curvature, they are those geometric figures that we draw only with the ruler, since line segments are small parts of a line.

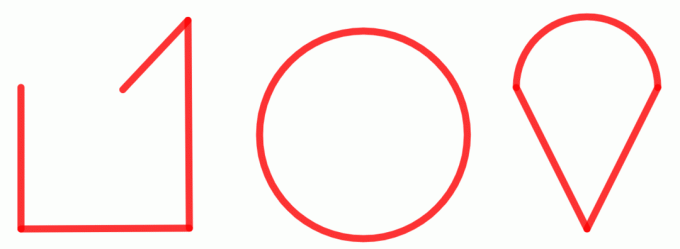
not polygons
Flat figures that do not qualify as polygons are called non-polygons. They are figures whose line is open, have some crossing point or some type of curvature.
You may also be interested:
- Spatial Geometry
- analytic geometry
- fractal geometry
- Flat Figure Areas
- Perimeter of flat figures
The password has been sent to your email.

