Down syndrome it is a chromosomal alteration numerical in which the individual has a chromosome 21 more. This syndrome, which occurs in both women and men, was first described in 1866 by the English physician John Langdon Down.
The physician's work described patients with a phenotype (observable characteristics of the organism that result from the genetic composition and environmental factors) classic: short stature, oblique palpebral fissure, flat nose and deficit intellectual.
Read too: aneuploidy
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
→ Characteristics of a person with Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a chromosomal alteration characterized by trisomy 21. This trisomy leads to the development of certain featuresphysicalstriking, such as:
- Short;
- slanted eyes;
- Almond eyes;
- Brows together;
- Flat face;
- Small ears and low set;
- Excess skin on the neck;
- Wide and thick neck;
- Fat little hands;
- Short fingers;
- Single pleat on palm of hands;
- Fine and straight hair;
- Small mouth;
- More curved roof of the mouth;
- Tongue sticking out of mouth.
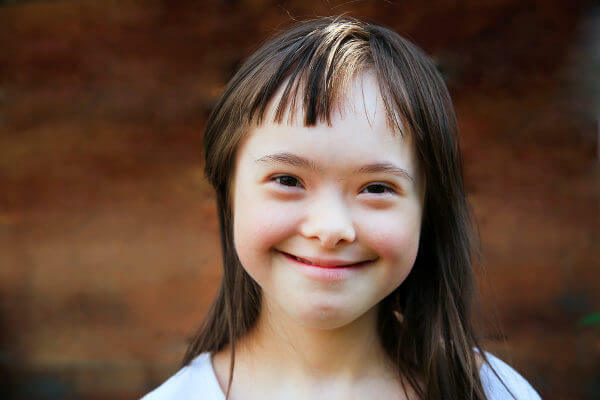

A person with Down syndrome has some observable features, such as an almond-shaped eye.
In addition to physical characteristics, people with Down syndrome are more likely to develop some health problems. Look the main problems that can happen in people with this chromosomal alteration:
- Child development delay;
- congenital heart disease (abnormality that occurs in the structure or function of the heart);
- Hypotonia (decreased muscle tone);
- Hearing problems;
- Vision problems;
- Back problems;
- Thyroid gland disorders;
- Neurological problems;
- Obesity;
- Premature aging;
- Increased risk of developing leukemia.
→ Is Down Syndrome curable?
Down syndrome is a chromosomal alteration that cannot be modified. It is noteworthy that Down syndrome it's not a disease, but a syndrome, that is, a set of signs and symptoms. Since Down syndrome is not a disease, we cannot talk about a cure or even a treatment.
Read too: Difference between diseases, syndromes and disorders
→ Diagnosis of Down syndrome in pregnancy
It is possible to diagnose Down syndrome during pregnancy through exams performed during prenatal care. Ultrasounds, for example, are a way of looking at the characteristics of the fetus and can provide information that indicates the syndrome.
However, confirmation of the Down syndrome diagnosis can only be made after examinations such as amniocentesis, which analyzes amniotic fluid, and chorionic villus biopsy, which looks at a sample of the placenta.
→ Development of a person with Down syndrome
People with Down syndrome have some limitations. Thus, It is essential that these individuals are stimulated in childhood. in order to overcome these limitations and so that it is possible to discover their potential.
It is noteworthy that people with Down syndrome, if well stimulated, can lead a relatively normal life. An important point is that these people they can attend a regular school, play sports and work like any other.
The development of individuals with Down syndrome can be even greater if some professionals are monitored. Among the professionals who can help in this process, the physiotherapists, which can help motor development; speech therapists, that can help in articulating sounds and strengthening the muscles of the face and mouth; and occupational therapists, that can act in the stimulation of fine motor and intellectual skills.
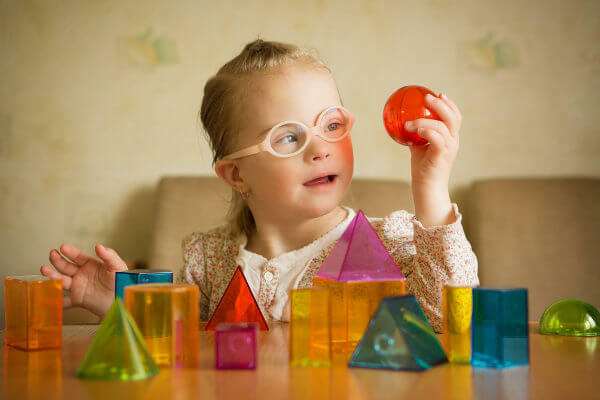

The performance of therapies can be essential for the development of a person with Down syndrome.
→ Cause of Down syndrome
Down syndrome is also known as trisomy 21 because a person has three 21 chromosomes instead of two. Look below for the Down syndrome karyotype and see the change in the number of chromosomes 21:

There are three different types of trisomy 21: free trisomy 21, trisomy 21 in translocation and trisomy 21 in mosaicism. See below a little more about them:
- Free Trisomy 21: there is a no disjunction during the process of cell division (meiosis) that gave rise to gametes. In this case, one of the gametes has an extra 21st chromosome and, after fertilization, generates a zygote with trisomy. This type is the moreordinary of trisomy 21 and, generally, it is a consequence in the errorgivesformationofgametematernal. In this situation, the karyotype is written as follows: 47, XX + 21 (female) or 47 XY + 21 (male).
- Trisomy 21 in translocation: é littleordinary, occurring in 3% to 4% of cases. In this case, one does not observe a freest chromosome 21, but a part of a 21 chromosome linked to another chromosome. There is therefore twochromosomes of the complete pair 21 and moreachunk from a third chromosome 21 glued to another chromosome from another pair.
- Trisomy 21 in mosaicism: it's the any lessordinary. There is the formation of first cell with the normal number of chromosomes (46), however, occurserrorin thedivisionscell phones that occur in the sequence. So we have individuals with normal cells and with trisomal cells.
The syndrome occurs more often in children of women over 35 years of age. It is estimated that the chance of a child being born with Down syndrome as the daughter of a 20-year-old woman is 0.07%. A 40-year-old woman already has a 1% chance of having a child with this genetic abnormality. This happens because women at birth already have their oocytes in the ovary and, during development, these mature and also age. With age, the greater the chances of chromosomal non-disjunction occurring.
Read too:Turner Syndrome
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Down's syndrome"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/doencas/sindrome-de-down.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.