THE Belarus, also known as Belarus, is a country located in the east of the European continent and which has the city of Minsk as its capital. It extends over 207,000 km² and borders Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia and Ukraine. In the latter country, in 1986, the Chernobyl disaster took place, which severely affected Belarus, as 70% of the radiation traveled to that country.
Belarusian territory integrated the USSR until its dissolution, guaranteeing its independence in 1991. Even today, it has an economy centered on the State, with primary production and the transformation industry as its flagship.
Read too: What are the countries in Europe?
Belarus general data
Nameofficial: Republic of Belarus or Republic of Belarus
Gentile: Belarusian
Extensionterritorial: 207,600 km²
Location: eastern europe
capital: Minsk
Climate: continental seasoned
Government: presidential republic
Divisionadministrative: six provinces and one municipality (Minsk)
Language: Russian and Belarusian
-
religions:
christianity: Orthodox (48.3%) and Catholic (7.1%)
no religion and atheists: 41,1%
others: 3,5%
Population: 9,449,000 inhabitants (UN, 2020)
Demographic density: 46.6 inhab./km² (UN, 2020)
Human Development Index (HDI): 0,823
Coin: Belarusian ruble (BYR)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): US$ 60.2 billion (IMF, 2021)
GDP per capita: US$ 6400 (IMF, 2021)
Gini: 0.253 (World Bank, 2019)
Timezone: GMT +3 hours
-
foreign relations:
world Bank
Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS)
IMF
UN
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Etymology
Since 1991, when the country declared its independence, Belarus has adopted the name Belarus. Bel is a word from Belarusian and means "white", while rus is derived from Old Slavic and designates the Slavic population that lived in Eastern Europe, in the area where Belarus, Ukraine and part of Russia are now located. Belarus therefore means “White Rus”. The name Belarus has the same meaning and originated at the time of the Russian Empire (1721-1917).
Belarus History
The occupation of the area where Belarus is now located is very old., dating back millennia before the present era. Over time, several peoples settled in that region, among which we can quote the slavs, who arrived there between the 6th and 8th centuries. With the end of control of rus, Belarus was under the rule of other populations, which today are part of its neighboring nations. Russian rule, which began in the period of imperial Russia, was the main one and the one that maintained ties with that country, in several of its sociocultural aspects.
Occupied by Germany in the context of First World War, Belarus announced its independence as a democratic republic in 1918. The following year, however, after a few years of Russian revolution, Bolsheviks Announce Creation of Belarus Socialist Soviet Republic. In the year 1922, it became one of the main republics of the USSR. Shortly thereafter, the country was the scene of devastating battles of the Second World War.
The 1980s marked a sad chapter in the history of Belarus and Eastern Europe in general. In 1986, in Pripyat, Ukraine, the Chernobyl power plant nuclear accident. The winds carried almost 70% of all radioactive dust into Belarusian territory, resulting in the contamination and death of people and the environment in the short and medium term.
THE fall of the berlin wall, in 1989, and the end of the USSR, later, marked the independence of Belarus, declared in 1990 and effective in 1991.
Read too: How was the end of the Soviet Union?
Belarus Map
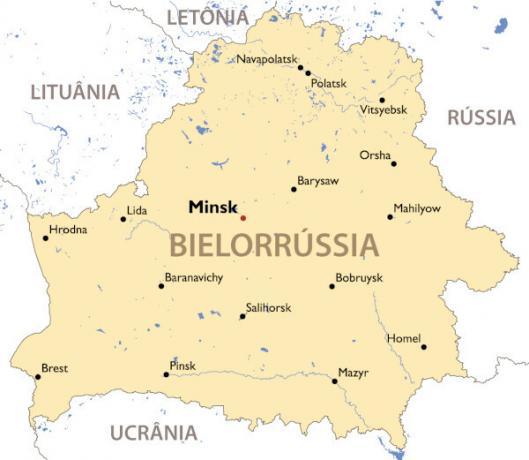
Belarus geography
Belarus is a European country located in the eastern region of the continent. Does chevron:
to the east and north, with the Russia
to the south, with the Ukraine
to the west with Poland
to the northwest, with the Lithuania and also with the Latvia
Thus, Belarusian territory has no maritime borders. Its extension is 207,600 km², making it the 86th country in the world in area.
Belarus climate
Located in the Northern Hemisphere, in one of the temperate zones of the planet, and under a low influence of maritime life, the predominant climate in Belarus is the Tcontinental hardwood. Temperatures are low throughout the year, including in the summer, when the thermometers show, on average, 18 ºC. The rainy season in the country extends from April to October. The annual average, however, is relatively low and varies between 600 mm and 700 mm annually.
Belarus relief
The Belarusian landscape is formed predominantly by plains, being characterized by little rugged terrain and modest altitudes that are around 160 meters. The country's highest point is on Mount Dzyarzhynskaya, just 346 meters above sea level.
Belarus Vegetation
Belarusian vegetation cover is composed of deciduous and coniferous forests, which are more common, respectively, in the southern and northern lands of the territory. On the Polish border is located the Belovezhskaya Forest, one of Europe's largest and main pristine forest conservation areas.
Historical records indicate the existence of the Parch Nstock of Belovezhskaya since at least the year 983. There you can find oaks over 500 years old, pine, silver fir and rare species of grass. In addition, its fauna includes the largest bison population on the European continent. As it is a site of historical importance and a great shelter biodiversity, the Belarusian portion of the forest was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1992.

Belarus hydrography
Most of Belarus is located in the Dnieper river basin, which crosses the eastern portion of the country, from north to south, towards Ukraine. In the south, in the west-east direction, one of its tributaries flows, which is the Pripyat river. Other important water courses are the Berezina and the Neman.
The flat relief also provides the formation of swamps and great lakes. Among these stands out the Braslaw complex, in the northwest of the country, where the Drivyaty and Snudy lakes are located, as well as the Naroch lake.
Belarus Flag

Belarus Demographics
The latest UN data indicate that Belarus has almost 9.5 million inhabitants, the seventh country in population in Eastern Europe. THE demographic density is 46.6 inhab./km², a distribution that is homogeneous throughout the territory. As in most nations, however, large urban centers are areas that end up concentrating a larger population.
The current country's urbanization rate é of 79.9%, and the capital, Minsk, which is located in the north-central region, is home to a total of 2,016,700 inhabitants. This figure is equivalent to 21.3% of all Belarusians. Other important cities are Gomel (or Homiel) in the southeast and Mahilyow in the east, respectively, the second and third most populous.
Following the trend that has taken hold in other European countries, Belarus is going through a process of population-ageing and deceleration of growth rates, registering, more recently, a decrease in the population. The median age of the country's inhabitants is 40.9 years, while birth rates are among the lowest in the world, and those of death, among the highest.
The population gain that was observed in the early 2000s was due to migrations originating mainly from Russia and other neighboring nations. Thus, the population of Belarus is made up of Russians, Poles and Ukrainians, in addition to those born in the country itself. Russian and Belarusian are its two official languages, the former being the most widely spoken.
See too: What are the most populous countries in the world?
![Minsk Gate in the Belarusian capital.[1]](/f/dd90dbff556afe099db0cadaada3f2b7.jpg)
Belarus Economy
Until the early 1990s, Belarus was part of the USSR, thus following its model economic, which had the State as the center of action and decision-making, that is, it was an economy planned. With the end of the Soviet regime and the independence of the country, there was an attempt to promote its economic opening through the flexibilization of the socialist system, heading towards the so-called market socialism.
A small portion of industries and agricultural production went through the privatization process, although these sectors remain essentially state-owned. After a long period of instability, the Belarusian economy grew from the 2000s onwards, later affected by the 2008 economic crisis. Belarus's GDP is currently US$ 60.73 billion, thus representing the 78th economy in the world, according to the IMF.
THE agriculture remains one of the main economic activities in the country., being responsible for the production of wheat, corn, potatoes, sugar beet, barley and rye. Livestock stands out for swine and poultry farming, as well as for milk production.
The industry is led by Potassium extraction and the production of derivatives as fertilizers. Belarus's mineral reserves are among the largest in the world. Other branches that make up the country's industry are the production of machinery and appliances, motorcycles and textiles. Also noteworthy are the advances in the technological sector in the development of software and games.
Belarus Culture
With few remnants of its original peoples, the Belarusian cultural matrix is formed by traditions and customs incorporated by foreign populations who exercised dominance over that region at some point, as well as migrants.
The country has a long tradition in theater and performing arts in general, which is reflected in its landscape and in the large buildings dedicated to the reproduction of this art. One of them is the Theater of Opera and Ballet, which is located in the capital, Minsk. Countless theater festivals are held annually across the country, as well as film and music festivals. The innovative building of the National Library of Belarus celebrates that country's literary originality and has also become an important symbol of its architecture.
![National Library of Belarus in Minsk.[2]](/f/1bf4157e16e268908961a01ff976e10e.jpg)
Some of the most traditional holidays in Belarus are Constitution Day (03/15), Victory Day (05/09) and Independence Day (07/03).
In gastronomy, the potato is the main protagonist of the preparations, of which the draniki, which is a thin dough made only with potatoes and fries. The beet soup, the machanka made from pork, and cream with flour and cream are other typical Belarusian dishes.
Belarus Infrastructure
As we have seen, Belarus is essentially an urban country and, as such, has a wide infrastructure network to serve its population. Data for the year 2020 showed that almost 82% of Belarusians living in cities had access to the treated water network, while, in the rural population, this reach was 76.4%. Sanitation facilities, in turn, covered almost all inhabitants urban areas and 94% of them in rural areas.
Electrification reaches most of the population. It is noteworthy that Belarus is the 32nd country in the world in terms of electricity imports. The production that takes place within the country's borders comes mainly from fossil fuels, other renewable and hydroelectric sources. The first nuclear reactor became part of the Belarusian energy matrix at the end of 2020.
Belarus government
Since the year 1994, when its first Constitution as an independent country was promulgated, the form of government in Belarus has been the democracy representative. In theory, the country's president is chosen through popular elections, being the head of state. The head of government, in turn, is the prime minister appointed by the president.
A change in the constitutional text meant that the first president remained in power since his election in the 1990s to the present day, a situation that causes a series of protests for the parents.
Curiosities about Belarus
With a flat relief, the only mountains observed in the Belarusian landscape are those produced with salt by mining activities. These shapes are generally convex and light in color, drawing attention to the landscape.
Author Svetlana Alexievich was the first Belarusian woman to win a Nobel Prize, what happened in 2015. she wrote the book Chernobyl Voices, in which it brings reports from those who lived up close to the consequences of the tragedy, including the author herself. Four other Belarusians had won the same award in their respective areas.
Four sites in the country are listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The main sport in the country is ice hockey.
Image credits:
[1] Grisha Bruev / Shutterstock
[2] BAHDANOVICH ALENA / Shutterstock
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher


