Organochlorine compounds are part of the organic function of organic halides. Halides are formed by replacing one or more hydrogens bonded to carbon with the same amount of halogens (elements in the 17th family of the periodic table). When halogen is chlorine, we have an organochlorine compound.
The nomenclature of organochlorines follows the following rule:
Amount of Cl (mono*, di, tri etc.) + chlorine + hydrocarbon name
*The mono prefix is optional (usually it is not placed).
Examples:
H3C ─ Cl: Chloromethane
H3C CH2 ─ Cl: Chloroethane
Cl─CH2 ─ Cl: Dichloromethane
Cl ─ CH ─ Cl: Trichloromethane
│
Cl
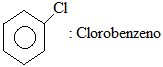
Chlorobenzene formula
In most cases, it is necessary to indicate the location of the chlorine, which in this case is not considered as the functional group, but rather as a substituent. This means that by numbering the main chain, we don't necessarily start closest to chlorine, but start closest to unsaturation. If there is no unsaturation, but ramifications, we adopt the rule of smallest possible numbers. See the examples below:
Cl
│
H3C CH2 CH2 ─ CH ─ CH3: 2-chloropentane
Cl
│
H2C ═ CH ─ CH2 ─ CH ─ CH3: 4-chloropent-1-ene (note that it is not 2-chloropent-4-ene, as it starts to number the chain closest to the unsaturation);
CH3
│
H3C ─ CH ─ CH2 ─ Cl: 1-chloro-2-methylpropane (note that it is not 3-chloro-2-methylpropane because of the smallest possible number rule);
CH3 Cl
│ │
H3C ─ CH ─ CH2 ─ CH ─ CH2 CH3: 4-chloro-2-methyl-hexane (see that it is not 3-chloro-5-methyl-hexane).
Today, there are around eleven thousand industrially produced organochlorines, which are used in various areas, such as in the production of plastics and pesticides, mainly, and in toothpaste and hygiene solutions oral.
Among the main organochlorine compounds, we can highlight:
*Chloroform: is trichloromethane (CHCl3) shown below. In the past, it was used as an inhalation anesthetic in surgeries, but this use stopped being applied when it was discovered that it was toxic and could lead to death, as has already happened. More details about this aspect can be seen in the text Composition and Applications of Chloroform.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
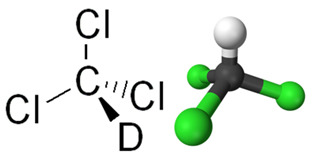
Structural formula of chloroform
*Insecticides: Two examples of organochlorine insecticides are BHC (hexachlorobenzene) and DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane), whose official nomenclature is 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-di(p-chlorophenyl)ethane.
the DDT was first used in 1942, during World War II, to combat the mosquito transmitting malaria and other diseases, such as yellow fever, as well as preventing head lice. transmit typhus. DDT was very effective in this regard, however, it has been banned in many countries. In countries where it is still allowed, its use is controlled.
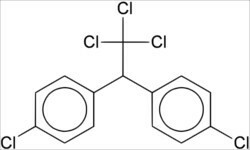
DDT structural formula
Organochlorine pesticides are very much in evidence mainly because of environmental problems that they cause, thus configuring itself as a very complex issue and that generates divergences of opinions.
Those who are against their use point to the fact that they are compounds that have high persistence in the environment (high resistance to chemical degradation and biological) and high lipid solubility, that is, they accumulate in fatty tissues of the human and animal organism, causing serious problems, especially to the liver.
DDT is also "accused" of decimating entire populations of birds, seals, among other animals, of attacking bird eggshells, of causing cancer in humans and altering hormone levels, causing feminization in males, birth defects, infertility, immune system depression, and impaired mental functions.
* Dioxins: Group of bioaccumulative and toxic organochlorine compounds. The most dangerous is 2,3,7,8-TCDD (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin).
This substance is mainly released in the burning of chlorinated compounds, such as in the incineration of PVC. It is also released in the production of PVC, in the use of chlorine as a bleach in the paper industry, during the production of herbicides selective and may appear in some foods of animal origin (such as eggs), as dioxin accumulates along the food chain.
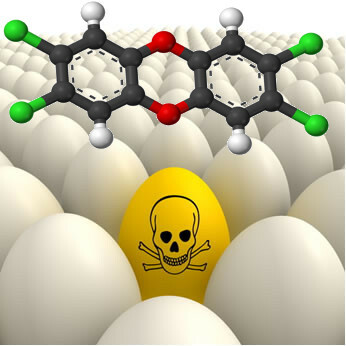
Dioxin can appear in eggs because of its cumulative effect.
* Plastic PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): is a polymer formed by the successive addition of several vinyl chloride molecules:
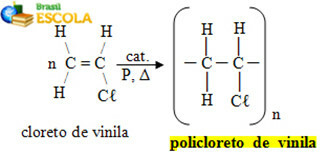
Polyvinyl chloride formation reaction
This plastic is used as a substitute for leather, in the manufacture of shoes, bags and clothing; in the upholstery of furniture and in the upholstery of automobiles. It is also used in food wrapping films and in diapers, tablecloths, bathroom curtains, wire coating and electrical cables. It is noteworthy that the main application of rigid PVC is in pipes for plumbing.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry



