The type of vegetation in a given region will primarily depend on its type of climate. However, this rule applies only to natural or native vegetation, as plant formation is the first element of the landscape that man modifies and, therefore, is in constant transformation.
Brazil, due to its continental territorial dimensions, is home to eight main types of natural vegetation. Are they:
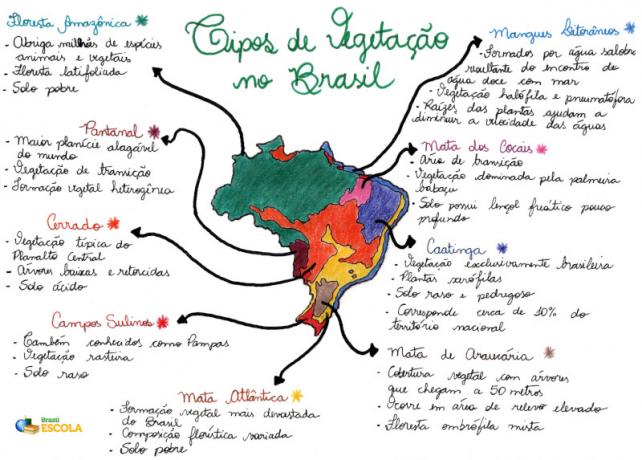
Amazon rainforest: with an equatorial climate and known as the Legal Amazon, it is home to millions of animal and plant species, and is of vital importance to the planet's environmental balance. It is classified as a forest formation Latifoliate, for its leaves are broad and densely bunched, usually reaching great heights.
Atlantic forest: characterized as a broadleaved tropical forest with a humid tropical climate, it was the vegetation that suffered the most devastation in Brazil, with only 7% of its original cover remaining. It was a vegetation that extended from Rio Grande do Norte to Rio Grande do Sul, but which was intensely degraded by the Portuguese for the extraction of wood and planting of sugar cane.
Mind Map: Types of Vegetation in Brazil

* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
Caatinga: is a typical vegetation of semiarid climate, located in northeastern Brazil. It has thorny and nutrient-poor plants. In recent years, it has been suffering several environmental aggressions that cause impoverishment of the soil, making the development of this region even more difficult.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Thick: typical of the Brazilian Central Plateau and with a semi-humid tropical climate, it is the second largest plant formation in Brazil. Despite its landscape being composed of low, gnarled trees, it is the most biodiverse vegetation on the planet. It is only in recent years that environmentalists have been concerned about this ecosystem, which suffers from various environmental damages caused by the planting of soy and sugarcane and by cattle raising.
Wetland: located in Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, it is considered a transitional vegetation, that is, a heterogeneous plant formation composed of different ecosystems. At certain times of the year, some portions of the area are flooded by the floods of rivers and it is only during droughts that vegetation develops.
Southern fields: also known as “pampas” and characteristic of a subtropical climate, they present low vegetation with a predominance of grasses and grasses.
Araucaria Forest: with the predominance of pine trees and located in the state of Paraná, it is a typical vegetation of a subtropical climate. Its original coverage is almost non-existent due to the intense exploitation of wood for the manufacture of furniture.
Mangroves: is a type of vegetation with coastal formation, mainly characterized by encompassing different vegetation, occurring in low areas and, therefore, subject to tidal action.
By Regis Rodrigues
Graduated in Geography
*Mental Map by Rafaela Sousa
Graduated in Geography
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
ALMEIDA, Regis Rodrigues de. "Types of Vegetation"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/brasil/os-tipos-vegetacao.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.