As explained in the text “Catalysis and Catalyst”, catalysts are chemical species that accelerate the speed of reactions. Its use is very useful in chemical industries, where it is sought to save as much time as possible in production.
However, in certain situations it is more interesting that the reaction proceeds more slowly; as, for example, when you want to determine the speed of very fast reactions. To achieve this feat, controlling and studying these reactions, it is customary to add a substance that slows down the reactions, which are called inhibitors, poisons or anticatalysts.
These chemical species combine with the catalyst, nullifying or decreasing its action. This is possible because the catalyst's mechanism of action is to decrease the activation energy, facilitating the reaction process and increasing its speed; already inhibitors act inversely, meaning they increase the activation energy needed for reactants to reach the activated complex.
An example that can be mentioned is arsenic (As), which has this function in the Haber-Bosch reaction, a reaction widely used in industry for the production of ammonia, using iron (Fe
(s)) as its catalyst. Thus, the efficiency of iron becomes very small in the presence of arsenic, which inhibits it, that is, it is the catalyst poison of this reaction, which is shown below: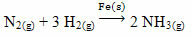
Arsenic can also exert an anti-catalytic action when using metallic platinum (Pt(s)) as a catalyst for the SO combustion reaction2(g), for the production of sulfur trioxide (SO3(g)). The presence of arsenic, even in small amounts, cancels out the catalytic action of platinum, which can paralyze part of the production. That is why, normally, in industries that deal with this production, divanadium pentoxide is used (V2O5(s)) as a catalyst in place of platinum.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Another example occurs in the following hydrogen peroxide decomposition reaction:
2 hours2O2(aq) → 2 H2O(1) + 1 O2(g)
In this case, an inhibitor that can be used is some acid, because when the medium is acidic, the reaction proceeds more slowly.
But the inhibitor is also widely used by the industry, mainly to act as a reaction retarder of the natural degradation of foods, beverages, cosmetics and medicines.
Cosmetics, for example, can take a long time to reach the consumer; thus, various preservatives are used in them, such as propylparaben, which is used in the oil phase and acts as an antifungal, and methylparaben, which is used in the aqueous phase and which has an antiseptic effect. Their respective structures are shown below:
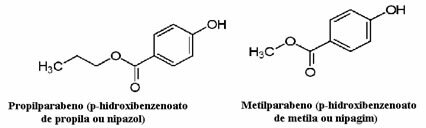
It is interesting that on many cosmetic labels there is the following phrase: “It does not contain parabens”. This means that this cosmetic does not have these preservatives that we mentioned and that, normally, they have not been tested on animals.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Catalyst Inhibitors"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/inibidores-catalisador.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.