THE chainelectric it's the movement of electrical charges, like electrons, which happens inside different materials, due to the application of an electrical potential difference. The electric current is the greatnessphysics that allows us to know what is the the amountincharge that crosses the cross section of a conductor every second. According to the international system of units, the electric charge is measured in A.s (amperes times seconds), this unit, in turn, is called the coulomb (C).
Lookalso: All about Electrostatics
Types of electrical current
There are two types of electrical current: continuous electric current and alternating electric current. Although both are dealing with a movement of electrical charges, they are fundamentally different.
continuous electric current
THE continuous electric current is the one in which electrons are forced to move in one way. This does not mean, however, that all electrons are moving in an orderly fashion, as in reality the movement of electrical charges is quite chaotic and slow. This is the result of several collisions suffered by the electrons with the crystalline network of the conductors while being dragged by the action of a
electric field external.Lookalso:Electric circuits - what are they, elements, types
alternating electric current
At chainelectricalternating, the sense of movement of the electrons is periodicallyinverted due to a reversal in the polarity of the potential that is applied to the conductor. In this type of electric current, the electrons remain oscillating around the same position, this causes that there is less energy loss due to the Joule effect, transformation of electrical energy into energy thermal. In Brazil, the oscillation frequency of alternating electric current is 60 Hz, that is, the electrons inside the wires move back and forth about 60 times per second.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
electric current formula
Electric current can be calculated as the ratio of the magnitude of the electrical charge that passes through a conductor over the time interval. The simplest formula that is used to calculate the electrical current is shown below, check it out:
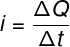
i – electric current (A)
ΔQ – electric charge (C)
t – time interval(s)
In the case of metalsconductors, in which conduction is carried out by the movement of electrons, we can calculate the electric current as a function of the number of electrons that pass through us each second. For this, it is necessary to remember the quantization of electrical charge, this property of matter tells us that the amount of total charge stored in a body is given by an integer multiple of the fundamental charge (e = 1.6.10-19 C) present in protons and electrons.
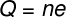
no – number of electrons
and – fundamental electric charge
If we combine the two equations shown, we can write the following formula for the electric current:

The formulas shown are useful for solving most exercises involving electric current, however they are not useful for cases where the electric current is variable. In such cases, it is common for a graph such as the one shown below to be provided, note:
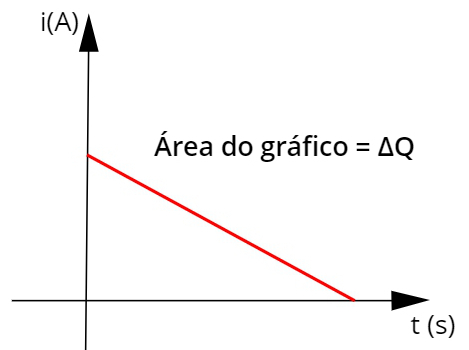
The graphic shown above shows the module of a variable electrical current as a function of time. Note that the magnitude of this electrical current is decreasing. In these cases, it is very useful to calculate the graph area, which corresponds to amount of cargo conducted during that time interval.
Lookalso:What is an electric field?
Mind Map: Electric Current

*To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
Conventional sense and real sense of electric current
O real sense of the electric current is the one in which the electrons travel in towards thehigher electrical potential (positive), since its electrical charge is negative. However, for purely arbitrary reasons, it is possible to assume that electrons have positive charges and that they move towards the lowest electrical potential, in order to facilitate the understanding and calculations related to the current electric.
Check out a table that summarizes the concepts of real sense and conventional sense:
real sense |
Electrons with a negative charge move towards the positive potential |
conventional sense |
Positively charged electrons move towards the negative potential |
electric current and power
When electric current passes through materials that present electrical resistance, a phenomenon called joule effecttransforms part of the stored energy in the cargo carriers in heat.
Through the electric current module, it is possible to calculate what is the dissipated power, that is, the amount of heat that is generated each second, due to the passage of an electric current. Check below the main formulas used to calculate the dissipated electrical power:
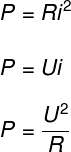
P – Power (W)
R – Electrical resistance (Ω)
i – electric current (A)
U – electrical voltage or electrical potential (V)
Above, we have three possible ways to calculate electrical power. We call U the drop in potential or voltage, established between the conductor terminals, the electrical resistance, R, measures the opposition offered by some means to the passage of current electric.
Effects of electric current

Electric current is capable of producing different effects when conducted through bodies. Among them, we can highlight:
Thermal effects: when electrical current passes through some medium that has electrical resistance, collisions between the electrons and the atoms in the conductor cause a great deal of heating to occur.
Chemical Effects: Some chemical reactions can be induced or even catalyzed when they occur in the presence of electrical currents.
Magnetic Effects: The passage of electrical current in conductors causes a magnetic field to appear around them.
Physiological effects: When electrical current passes through living things, their muscles can contract strongly. Some electrical current values are potentially fatal.
Light Effects: Electric current can generate light by passing through certain types of ionized gases, such as those used in fluorescent lamps or mercury lamps.
Among the effects mentioned above, one of them is of great importance for our safety, since the physiological effects of electrical current can be quite severe in humans.
Check out a table that lists the intensity of the electric current with the possible consequences of its passage through the human body:
Electric current intensity (A) |
Most common physiological effect |
0.001 to 0.01 |
Small tingles; |
0.01 to 0.1 |
Muscle contractions, pain, difficulty breathing, cardiac arrest; |
0.1 to 0.2 |
Ventricular fibrillation; |
0.2 to 1.0 |
Cardiac arrest and cardiorespiratory arrest; |
1.0 to 10.0 |
Severe burns, cardiac arrest and possibly death |
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock


