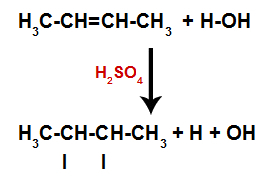
Ethylene is an organic compound responsible for fruit ripening. Also known as ethylene, this compound works as a hormone and is present in the entire structure of the fruit, from the skin to its interior, it is produced from the cells.
The reaction that produces ethylene is the oxidation of lipids, when it is carried out, it causes a break in the fruit's fibers, making it soft. The sweetness of ripe fruits is explained by the breaking of the starch bonds present in its composition. Ethylene is also responsible for breaking down the chlorophyll molecules present in the fruit's peel, which gives it a green color and that after maturation acquires a reddish or yellowish color (according to the fruit).
Now a secret to speeding up the ripening process of fruits like tomatoes and bananas: put them together in a closed container. It is known that bananas, like tomatoes, give off ethylene when they are ripe, by placing them covered you prevent the ethylene - which is a gas - escapes, it is retained in the container and accelerates the ripening process of unripe fruits.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUZA, Líria Alves de. "Ethylene and ripe fruits: what is the relationship?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/etileno-frutas-maduras-qual-relacao.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.