THEdiabetes mellitus is chronic disease that every day affects more people in our country and around the world. According to the Brazilian Society of Diabetes, the disease affects about 6.9% of the Brazilian population, which corresponds to approximately 13 million of cases. And what is most frightening is that this number tends to increase.
This disease is due to insufficient production of the hormone insulin or the inability to use it. THE insulin, which is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, controls blood glucose levels, which, when there is diabetes, are elevated and cause a frame known as hyperglycemia.
→ Causes of diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is caused by problems with insulin secretion or insulin action. THE diabetes mellitustype 1 it is triggered by the destruction of the cells in the pancreas responsible for producing insulin. In this case, we notice the occurrence of an autoimmune problem, that is, the cells of the pancreas are attacked by the patient's own immune system. already in
diabetes mellitus type 2, what is verified is a problem in the secretion or action of insulin. Type 2 diabetes usually occurs in people who are overweight or obese. THEdiabetesgestational, in turn, does not have a clear cause.
Healthy eating and exercise can prevent diabetes.
It is noteworthy that there are still other specific types of diabetes, which are less common forms and triggered by genetic problems, diseases of the exocrine pancreas, problems in the endocrine system, infections, medications and other chemical agents, among others causes.
Read too:Risks of overconsumption of sugar
→ Symptoms of diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus triggers what is called hyperglycemia, which causes blood glucose levels to rise. Hyperglycemia manifests as symptoms:
Excess urine production (polyuria);
Larger urine output volume at night than during the day (nicturia);
Weight loss;
Excessive hunger (polyphagia);
Excessive thirst (polydipsia);
Dry mouth;
Weakness;
Blurred vision.
It is noteworthy that chronic hyperglycemia can trigger complications, leading to dysfunction and failure of various organs, such as eyes, kidneys, heart and nerves.
→ Classification of types of diabetes
The most common forms of diabetes are type 1 and type 2, however, other types are known. Diabetes mellitus is usually divided into four groups:
Diabetes type 1;
Type 2 diabetes;
Other specific types (they are less common forms of this disease);
Gestational diabetes.
There is also the so-called pre-diabetes, which refers to an intermediate state between diabetes mellitus and a normal patient.

Gestational diabetes mellitus is a type of diabetes that affects pregnant women.
Type 1 diabetes is one in which beta cells are destroyed, causing insulin deficiency. Due to this deficiency, the blood is left with excess glucose. Your cause may be autoimmune (when the immune system itself attacks and destroys healthy tissue) or idiopathic, that is, unknown. In the case of autoimmune diabetes, there may be associations with diseases such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Addison's disease, which are also autoimmune problems. this disease is more common in childhood or adolescence, but it can also affect adults.
Unlike type 1 diabetes, in type 2, the body is unable to use insulin properly or it is produced in small amounts. This type is the most common type of diabetes and it manifests itself more frequently in adults. It is estimated that 90% of diabetes cases are type 2 and are mainly related to the age and sedentary lifestyle. In that case, there is no destruction of the pancreas cells.
As its name implies, this type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and can directly affect the baby. The disease is related, for example, with fetal overgrowth, neonatal hypoglycemia and even the development of diseases in adulthood, such as obesity and diabetes. Gestational diabetes has some risk factors, such as: advanced age of the mother, weight gain during the pregnancy, polycystic ovaries, history of gestational diabetes in the pregnant woman's mother, hypertension and pregnancy multiple. This type of diabetes may or may not persist after giving birth.
→ prediabetes
The term pre-diabetesis used for individuals who have blood glucose levels above the recommended value. However, these levels are lower than those necessary for a case of diabetes type 2. It is estimated that half of patients at this stage will develop the problem.
→ Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus

Checking blood glucose levels is critical to diagnosing diabetes mellitus.
To correctly diagnose diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to analyze the symptoms and perform some tests to confirm the suspicions. The recommended tests are: fasting blood glucose, oral glucose tolerance test (TTG-75) and casual blood glucose. See below the criteria that should be adopted for the diagnosis of this health problem:
prediabetes |
|
Diabetes type 1 and type 2 |
|
Gestational diabetes |
|
→ Risk factors for diabetes mellitus
Some risk factors are related to the onset of diabetes mellitus. Below are the main factors for the development of type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
diabetes mellitus type 1
Family history of the disease.
diabetes mellitus type 2
Family history of the disease;
High pressure;
High cholesterol levels;
Changes in blood triglyceride level;
Overweight or obesity;
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome;
Had a baby weighing more than four kilos or had gestational diabetes;
Has a diagnosis of pre-diabetes.
gestational diabetes mellitus
Advanced maternal age;
Excessive weight gain during pregnancy;
Hypertension in pregnancy;
Overweight or obesity;
Family history;
Gestational diabetes history;
History of children born weighing more than 4 kg;
The mother of the pregnant woman had gestational diabetes.
→ Diabetes mellitus treatment
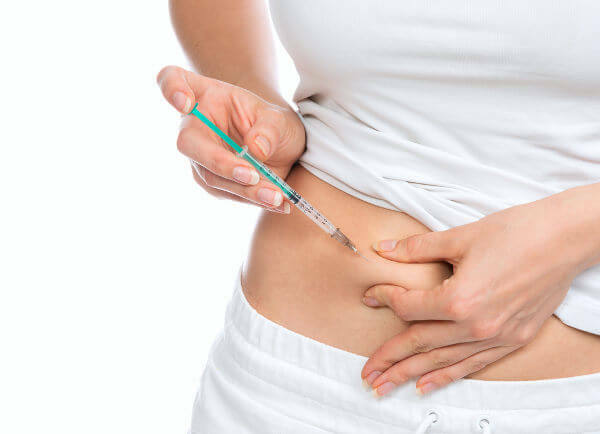
Some patients require insulin administration to treat their diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus, in its different forms, has a treatment aimed at controlling blood glucose levels and preventing complications. Among the main medical recommendations is a healthy diet with reduced amount of carbohydrates. In addition to diet, it is important to exercise. Some patients, in addition to controlling their diet, must use insulin. The frequency of hormone application varies from person to person and should be evaluated by the doctor.
Thus, we can conclude that the diabetes mellitusit can be extremely serious if not treated properly. However, a correct follow-up can prevent complications and the patient have a normal life.
Read too:Myth or Truth: Does okra help with diabetes treatment?
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/doencas/diabetes-mellitus.htm
