Given two events A and B of a sample space S, the probability of A or B occurring is given by:
P(A U B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∩ B)
Verification:
The Number of elements of A U B is equal to the sum of the number of elements of A and the number of elements of B, minus once the number of elements of A ∩ B that was counted twice (once in A and once in B). So we have:
n (AUB) = n (A) + n (B) - n (A∩B)
Dividing by n (S) [S ≠ 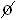 ] results
] results
P(AUB) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A∩B)
Example:
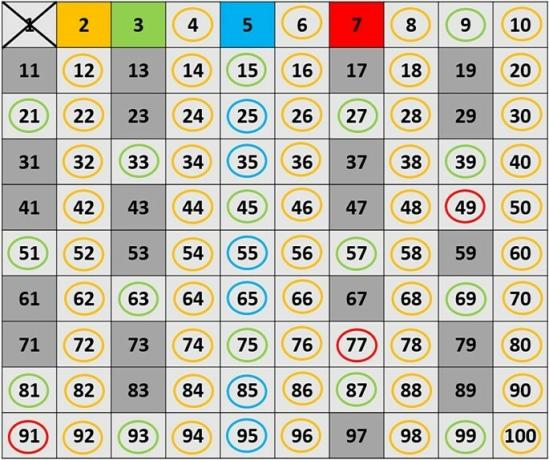
In an urn there are 10 balls numbered from 1 to 10. Taking a random ball, what is the probability of multiples of 2 or multiples of 3 occurring?
A is the “multiple of 2” event.
B is the “multiple of 3” event.
P(AUB) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A∩B) =
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
by Danielle de Miranda
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Probability - Math - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
RAMOS, Danielle de Miranda. "Union Probability of Two Events";
Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/probabilidade-uniao-dois-eventos.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.