THE hemoglobin is a protein found in the blood of vertebrates, more precisely inside the cells of the blood called red blood cells. This protein is a proteinglobular which presents a quaternary structure, being formed by four subunits. It is the respiratory pigment of almost all vertebrates and is responsible for typical red color of blood.
Read too:Red Cells
→ Hemoglobin structure
Hemoglobin is a protein with a quaternary structure formed by four subunits. Each subunit is formed by a portionprotein (globin) and a groupprosthetic (heme). There are different types of globins, hemoglobin being formed by two alpha globins and two non-alpha globins. The heme group, in turn, has an iron atom, which is usually in the ferrous form.
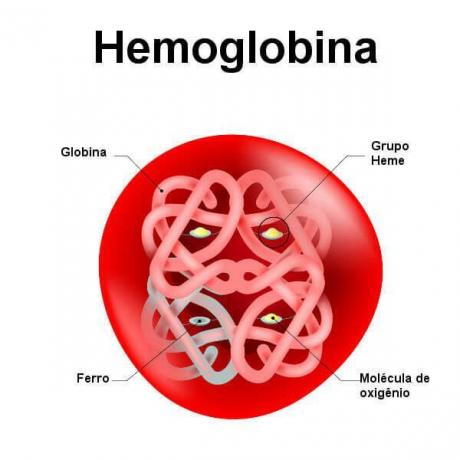
Look at the schematic illustrating the structure of hemoglobin.
→ Types of Hemoglobin
Variations in polypeptide chains cause different types of hemoglobin to be observed. The hemoglobins: A1, A2 and F are considered normal.
Hemoglobin A1- In the normal adult, this hemoglobin represents about 97% of the hemoglobin found.
Hemoglobin A2- This hemoglobin represents 2% of the hemoglobin found in adults.
Hemoglobin F- This hemoglobin is found in the fetus and is called fetal hemoglobin. In the fetus, we only find this type of hemoglobin, which decays after birth. By the time a person reaches the eighth month, he or she has only 1% of this hemoglobin.
Read too: Blood donation
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
→ Hemoglobin function
Hemoglobin is a protein mainly related to the transportinoxygen by our body. In hemoglobin, we have four subunits, each with the oxygen binding site. As these sites are filled more, the oxygen affinity increases.
This happens because when a subunit captures oxygen, it causes a change in the hemoglobin molecule that favors the uptake of other oxygen molecules. Thus, when the hemoglobin-rich red cell is in places with a high concentration of oxygen, such as our lungs, for example, its affinity for it will be greater.
It is noteworthy that in tissues it is observed that the pressure of O2 it is low and the oxygen present in the red blood cells is released to the tissues. Red blood cells also combine with CO2, but most of the CO2 is transported dissolved in the plasma.
When hemoglobin binds to oxygen it is called oxy-hemoglobin. When it is not linked to oxygen it is called deoxy-hemoglobin. It is still called carbamino-hemoglobin when combined with carbon dioxide.
→ Carbon monoxide and hemoglobin
Hemoglobin has the main function of transporting oxygen throughout the body, however, it can also combine with other substances, such ascarbon monoxide. When this combination occurs we call the hemoglobin of carboxyhemoglobin.
Hemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon monoxide than for oxygen, with an estimated 200-fold affinity for carbon monoxide. When this combination occurs, oxygen cannot be transported by hemoglobin, thereby causing a deficiency in oxygenation of the body's tissues. This problem is serious and can cause respiratory discomfort, headache, visual changes, tachycardia, syncope and even death.
→ Low blood hemoglobin concentration
The low concentration of hemoglobin in the blood characterizes the anemia. In some cases, anemia arises from a low amount of erythrocytes, at other times, however, the erythrocytes have little hemoglobin. This health problem can occur due to bleeding and dietary deficiencies, for example. Anemia triggers a range of unpleasant symptoms, such as tiredness, weakness, pallor, and loss or loss of physical strength.
Read too: Recommendations for healthy eating
→ sickle cell anemia
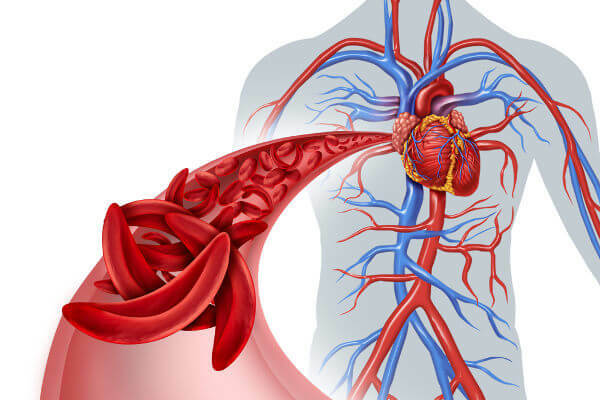
In sickle cell anemia, red blood cells have a sickle shape.
THE sickle cell anemia it is a health problem triggered by a change in hemoglobin. What is observed in these cases is that an amino acid in hemoglobin is replaced, forming an abnormal hemoglobin (Hb S). This hemoglobin triggers the formation of a red cell with different shape, which resembles a sickle. This red blood cell is more fragile than normal, it does not have flexibility and its life is short.
A person with sickle cell anemia may experience different signs and symptoms, such as fatigue,pallor, ache, due to obstruction of blood vessels, increased cases of infection and leg wounds. Treatment depends on each case and involves, in some patients, blood transfusion.
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Hemoglobin"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/hemoglobina.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.