THE microbiology is the branch of biology that studies microorganisms.
Microorganisms are small living beings, whose dimensions do not allow them to be observed with the naked eye by man. Thus, they can only be viewed under a microscope.
The word microbiology is derived from the combination of the Greek words micros, "little", BIOS and logos "study of life". Thus, the study of microbiology encompasses the identification, form, way of life, physiology and metabolism of microorganisms, in addition to their relationships with the environment and other species.
In general, microorganisms contribute to soil fertilization, substance recycling and participate in biogeochemical cycles. They can also be used in the manufacture of products such as yogurt, wines, cheeses, vinegars and breads.
There are also pathogenic microorganisms that cause diseases in humans, animals and plants.
Microorganism groups
The main groups of microorganisms are: viruses, bacteria, protozoa, algae and fungi.
Virus

You virus are microscopic organisms that have no cells. Therefore, they are considered intracellular parasites.
Viruses can only carry out their vital activities inside another living cell.
Some viruses are pathogenic and cause human disease. Some examples are: flu, measles, yellow fever, meningitis, mumps, hepatitis, AIDS and smallpox.
Bacteria

At bacteria they are unicellular and prokaryotic beings. They are part of the Kingdom Monera.
Bacteria can be found in different environments and are capable of withstanding environmental conditions inhospitable to most living beings.
Even though it is imperceptible, bacteria perform important functions in the environment. They act in biogeochemical cycles and in the production of food and medicine.
Some bacteria can be pathogenic and cause diseases such as cholera, diphtheria, typhoid, leprosy, meningitis, tuberculosis.
Learn more about:
- prokaryotic cells
- Diseases caused by bacteria
- Bacteria exercises
Protozoa
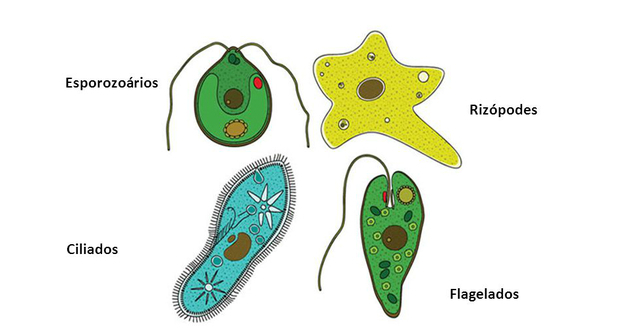
You protozoa are eukaryotic beings, unicellular and heterotrophs. belong to Protist Kingdom, along with algae, which are aquatic organisms that have the ability to carry out photosynthesis. They can be micro or macroscopic, eukaryotes or prokaryotes.
Protozoa have various body shapes and occupy moist environments or the interior of other organisms.
Some are parasites, causing disease. Among the diseases caused by protozoa are: amoebiasis, giardiasis, malaria and chagas disease.
Also read about:
- Algae
- eukaryotic cells
- Diseases caused by Protozoa
Fungi

You fungi are beings macroscopic or microscopic, unicellular or multicellular, eukaryotes and heterotrophs. They are part of the Kingdom Fungi.
Fungi have different types of habitat as they are found in soil, water, plants, animals, man and debris in general.
Given the large number of species, around 1.5 million, fungi are used for different purposes, such as in the production of medicines and even in the production of cheese.
The mushroom is a type of fungus that is very popular in cooking, as it is a source of protein.
Some fungi can be pathogenic. Among the diseases related to fungi are: mycoses, thrush, candidiasis and histoplasmosis.
Areas of study of microbiology
Microbiology covers a wide area of study and can be a source of different research.
The fields of action that microbiology can act on are:
- medical microbiology: focuses on the study of pathogenic microorganisms. Its performance is directly linked to disease control and prevention, thus being related to immunology.
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology: aims to study microorganisms that can contribute to the production of drugs, especially antibiotics.
- environmental microbiology: focuses on the study of bacteria and fungi that act in the decomposition of organic matter and chemical elements in nature. It is related to biogeochemical cycles.
- food microbiology: aims to study the microorganisms involved in the food industry, especially in the control of food production and industrialization.
- Microbiology Microbiology: focuses on processes that involve genetic and molecular manipulation of microorganisms.
know more about:
- Microorganisms
- Biotechnology
- Cytology