mass number (represented by the capital letter A) is the denomination used to determine the quantity protons and neutrons present inside the nucleus of any atom (represented by the abbreviation X).
When we represent the mass number of any atom, the correct way to write it is on the upper right or left side of the atom's abbreviation, as we can see in the general pattern below:

Mass Number Representation Models
The number of protons in an atom is given by the atomic number (Z), which is always positioned to the left of the atom's abbreviation, at the bottom.
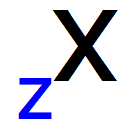
Representation of the atomic number in the initials of any atom
as the mass number always indicates the amount of protons (p) and neutrons (n) inside the nucleus, a formula was created based on this definition:
A = p + n
From this mathematical expression, we have the condition to determine:
Mass number: based on the number of protons and the number of neutrons;
number of protons: based on the mass number and the number of neutrons, rewriting the equation as follows:
p = A - n
-
Number of neutrons: based on the mass number and the number of protons, rewriting the equation as follows:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
n = A - p
1st Example: Determine the number of neutrons present in the nucleus of a chlorine atom, 17Cl35.
In the statement, we have two values in the acronym, one at the bottom left, which is the atomic number or the number of protons, and another one above, which is the mass number:
Z or p = 17
A = 35
To determine the number of neutrons, simply use the values provided in the expression used to calculate the atomic mass, rewritten as follows:
n = A - p
n = 35 - 17
n=18
2nd Example: What is the number of protons present inside the nucleus of a scandium atom, given that its mass number and neutron number are, respectively, 43 and 21?
The exercise provides two values, the mass number and neutron number. Soon:
A = 43
n = 21
To determine the number of protons, simply use the values provided in the expression used to calculate the atomic mass, rewritten as follows:
p = A - n
p = 43 - 21
p = 22
3rd Example: What is the mass number of an atom that has an atomic number equal to 60 and that has 88 neutrons inside its nucleus?
The exercise gives two values, the atomic number (or the number of protons) and the number of neutrons. Soon:
Z or p = 60
n = 88
To determine the number of neutrons, simply use the values provided in the expression used to calculate the mass number:
A = p + n
A = 60 + 88
A = 148
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is mass number?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-numero-massa.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.