A nuclear reactor is a device used in power plants to control the nuclear fission reaction. This reaction occurs in an uncontrolled way, for example, in the explosion of atomic bombs; but reactors have mechanisms that prevent this, causing the reaction to be controlled and reused to generate electrical energy.
This is achieved because the reactor is assembled in a way that interleaves bars offissile fuel – which is usually enriched uranium (uranium with a large amount of uranium 235) or plutonium 239 –; with neutron moderator bars. These moderators can be carbon bars in the form of graphite, cadmium, or heavy water (D2O), which is used in most modern reactors. Heavy water or deuterated water is different from normal water because, in its constitution, instead of ordinary hydrogen atoms, it has atoms of deuterium, which is an isotope heavier than the hydrogen.
Parts of the neutrons released in nuclear fission collide with the nuclei of the moderators, which absorb the neutrons without undergoing fission. The result is that the fission chain reaction is controlled, as only one of the neutrons released in each fission can react again.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The energy generated in the form of heat causes the temperature of the water to rise inside the reactor, to the point where it is transformed into steam. This steam drives a turbine, which generates electrical energy.
After leaving the turbine, the steam passes through a heat exchanger, which works as a condenser, where the steam is cooled by a natural external source. located close to the plant (usually it is water from a river, lake or sea) and returns in liquid form to the main circuit, starting again the whole process. That's why nuclear power plants are usually found in regions close to the sea.
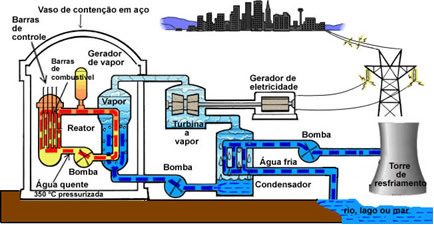
Brazil has three nuclear reactors at the Angra dos Reis Plant, located on the coast of the state of Rio de Janeiro. There are currently 438 nuclear reactors in operation worldwide, which correspond to 14% of the world's electric energy production. The United States has 104 reactors, France 59 and Japan 55.

By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Nuclear reactor"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/reator-nuclear.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry

Get to know some clean energy sources, such as: wind, solar, tidal, geothermal, hydraulic, nuclear and biofuels.



