You regimestotalitarian were political regimes that existed in the first half of the 20th century and were based on totalitarianism, a political system based on controlabsolute of a party or a leader over every nation. Within the totalitarian system, the leader or political party has broad powers over public and private life and thus represents the state.
Totalitarian regimes were based on a strong militarism, that served a lot to intimidate and silence dissenting voices. Along with the power of intimidation, totalitarianism rested on an intense advertisingideological with the objective of indoctrinating the population and highlighting the supposed improvements carried out by the regime. Another important brand, very much in association with militarism, was the horror. Within totalitarian regimes, terror was used to persecute opponents.
Also access: Neo-Nazis: A New Threat Affecting Today's Democracy
How did totalitarianism come about?
The height of totalitarianism happened in the 1920s and 1930s, in Europe, and the emergence of this political system is directly related to the
post-war consequences. THE First World War was a landmark event in world history and, at the end of this conflict, the balance left was destruction, death and a lot of crisis – both political and economic.After World War I, material destruction and the death toll had reached unprecedented levels. In addition, the outcome of the conflict had left a series of resentments, the growth of communism frightened the middle and upper classes of Western Europe, and the criseseconomical it affected everyone and bankrupted countries.
All these elements have led many to question the qualities of liberal democracy and, with that, the authoritarianism came to be seen as the solution to all the problems that beset the world. This defense of authoritarianism caused countless democracies to collapse in Europe, and very few countries managed to sustain their democratic political institutions in that period.
The term "totalitarianism” appeared in the 1920s and was created, at first, to refer to Italian fascism, the first totalitarian regime that was implemented. It was from the success of Italian fascism that fascism gained the strength to spread as alternativepolitics across Europe.
The height of totalitarianism in Europe came when the Nazis came to power in Germany in 1933. From there, movements in support of totalitarian ideals of far right spread around the world and even arrived in Brazil - the integralism. On the political spectrum of left, totalitarianism was manifested through the political regime of Joseph Stalin.
Characteristics of totalitarianism
The three great totalitarian regimes in history were the fascism, O Nazism and O Stalinism. These were the great totalitarian regimes of the 20th century, although there are scholars who point to the existence of other totalitarian governments throughout history, such as the Khmer Rouge, who ruled the Cambodia from 1975 to 1979, and the current regime of North Korea.
Despite the ideological differences, there are some characteristics in common between the three totalitarian regimes mentioned, but it is It is important to emphasize that each of the totalitarian regimes focused on in this text had characteristics that were peculiar to itself. exclusively. The common features were:
Cultto theleader: The leader was revered in all three regimes, and images of them were spread across the country.
Censorship: the media could not issue opinions that were not approved by the government. The existence of opponents was also prohibited and they were forcibly silenced.
SuppressionFrompartiespoliticians: in the three regimes, only the government party existed. All others were prohibited.
Creation of internal and/or external enemies: the totalitarian rhetoric created internal/external enemies, and the fight against these groups justified the taking of extremely authoritarian measures.
The totalitarian regimes, moreover, promoted the centralization of power in the leader or in the party, indoctrinated ideologically its population, promoted terror to intimidate opponents, etc.
Also access: Crisis of 1929: one of the most tense moments in the period between the world wars
totalitarian regimes in Europe
As already mentioned, Europe had three great totalitarians: the fascism (1922-1945), the Nazism (1933-1945) and the Stalinism (1924-1953). The first two were aligned with the far right and the third was aligned with the far left. In this excerpt of the text, we will highlight some information about each of these three regimes.
Fascism
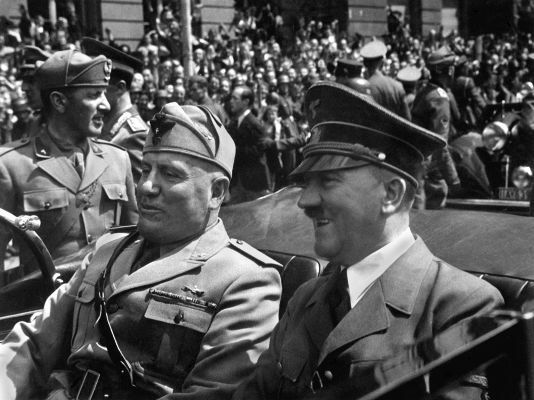

Benito Mussolini (left) was the great leader of Italian fascism.¹
Fascism was the firstmovementtotalitarian to be deployed in Europe. They occupied power in Italy in 1922, when BenitoMussolini was appointed prime minister after the completion of the March on Rome. Fascism, in turn, emerged in 1919 when the Italian Combat Groups were founded. (Fasci Italiani di Combattimento).
Mussolini's rise to power took place in a context of political and economic crisis in Italy and the growth of communism in the country. Thus, in the early 1920s, fascist forces began to act violently against groups such as the communists and garnered the support of the liberals. Through pressure from the fascists, the Italian king ended up appointing Benito Mussolini as prime minister in 1922. In 1925, Benito Mussolini proclaimed himself dictator of Italy and consolidated the totalitarian system in Italy.
Fascism is understood as the regime precursor of conservative movements in Europe and within fascism, the exaltation of conservative and traditional values, romanticization and construction of a heroic past, contempt for socialism, anti-liberalism, etc., can be highlighted.
Fascism was the great ally of Nazism in Europe and during the Second World War, was part of the Axis together with Germans and Japanese. The fascist regime ruled Italy between 1922 and 1945 and was overthrown from power as a result of the defeat of the Axis in World War II.
Nazism

Nazi salute given during the 1936 Olympic Games. The salute was a part of the cult of the leader imposed by the Nazis.¹
Nazism emerged in Germany, in 1919, under the name of National Socialist Party of German Workers. adolf hitler he was one of the first members of the party and over time became leader of the party. Hitler's growth in Nazi cadres is attributed as a result of his ability to mobilize crowds based on his capacityrhetoric.
Nazism gained strength in Germany throughout the 1920s, and the strengthening of that party is related to the country's defeat in the First World War. The defeat spread a sense that the country had been the victim of a plot that forced German surrender. Furthermore, the view in German society was that the country had been humiliated under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles.
The postwar situation in Germany, associated with Nazi rhetoric, pushed many people in German society towards the defense of authoritarian measures. With the growth of Nazism, the assault troops (SA) Nazis gained strength and began to persecute the Communists and Social Democrats.
The Nazi ideology was summarized by Adolf Hitler in his book written during the period he was imprisoned – the Mein Kampf. One of the pillars of the Nazi ideology was the anti-Semitism, name by which we know the hatred against the Jews. O anti-Semitism it was an ideology already widespread in German society since the 19th century and was exploited by the Nazis.
The growth of anti-Semitism within German society ended up resulting in the Holocaust during World War II. O Holocaust caused the death of 6 million people, of which the majority were Jews. Those killed during the Holocaust were killed in a variety of ways, most notably shootings and death in the gas chambers.
Nazism included, in its ideology, anti-Marxism, anti-liberalism, exaltation of war, state control, nationalism extreme, the cult of the leader and defended the idea of the superiority of the German race (they called the Germans Aryans). Another important point of the Nazi ideology was the defense of an “innate space”, a territory supposedly of right where the Aryans/Germans would form their Third Reich.
As a result, the Nazis began to impose a expansionismterritorial, so they invaded and annexed Austria and Czechoslovakia. When they invaded Poland in 1939, the French and the British declared war on the Germans. start of WWII.
Read too: Night of Crystals: the episode that started the mass imprisonment of the Jews
Stalinism

Josef Stalin ruled the Soviet Union between 1924 and 1953.²
Stalinism was the totalitarian regime imposed during the period when the Unitysoviet was ruled by Joseph Stalin. There is a debate among historians about the totalitarian character of Stalinism, since there are historians who question this classification, although most historians agree that Stalinism was totalitarian.
Josef Stalin was one of the members of the highstepofgovernmentsoviet, but ended up taking power in the country after Lenin died in 1924. In 1929 he became the leadersupreme of the Soviet Union and ruled the country in a totalitarian manner until 1953, the year of his death.
One of the hallmarks of Stalinism was the leader's image worship so much so that when Stalin died in 1953, the reaction of many was one of astonishment. This is because part of Soviet society could not imagine the country without the leader in power. It can be seen that the figure of the leader and the state got mixed up during the years of Stalinism.
In Stalinism, another very evident mark was the persecution of all opponents and all those who were perceived as a threat to the state. Many of those being persecuted were tortured or summarily executed or sent to forced labor camps known as gulag. Even civil servants fell victim to Stalin during the purges of the 1930s.
One of the best known moments of Stalinism was the collectivization of farms, that happened in the 1930s. During this time, the peasants of the Soviet Union were forced to surrender their land and possessions to the state (private property was prohibited in the country). Peasants also worked on these lands and what was produced was handed over to the state at low prices.
The purpose of collectivization was to finance the industrialization of the Soviet Union and resulted in the death of millions of people due to insufficient food. This event was known in history as Holodomor. In addition to those who died of hunger, there are also thousands of peasants who were executed for resisting the collectivization of land.
Also access: Discover the history of one of the most used weapons in all of humanity
totalitarian regimes in Brazil
Brazil has never lived under a totalitarian regime, despite the fact that, throughout our history, we have been governed by dictatorial regimes, such as the new state, between 1937 and 1945, and the Military dictatorship who ruled the country between 1964 and 1985. Despite this, political groups emerged in our country that were inspired by the ideals of totalitarian regimes, such as the aforementioned integralism.
¹Image credits: Everett Historical and Shutterstock
²Image credits: chrisdorney and Shutterstock
By Daniel Neves
Graduated in History
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiag/regime-totalitario.htm