oil is a natural fuel, originated from thousands of years of decomposition processes. As it originates from a long process, it is also called fossil fuel.
It is found in deposits in the deepest layers of oceans, seas and lakes, and can also be found on land.
It is a non-renewable natural energy source, as the exploitation of this resource without control can eliminate existing reserves. It is mainly used as a raw material in the production of gasoline and diesel oil.
Origin and history of oil
Apparently, the use of oil is almost as old as human history. There are records that the product was used by very ancient peoples, such as the Egyptians and Persians. In regions such as Persia, Mesopotamia and Egypt, it was already used in the opening of roads and in other types of construction.
Modernly, the discovery of oil and the possibility of extraction and use only happened in the 19th century, when the first wells were found.
The record of the first discovery of an oil well took place in 1859 in the United States. It was its discoverer, Edwin Drake, who started oil exploration. In addition, Drake created the first used extraction system.
In Brazil, the first well was found 80 years later, in 1939, in Salvador. The person responsible was Manoel Ignácio de Bastos.
After the first discoveries, factors such as the creation of oil engines (widely used in industries) and the The emergence of cars with diesel and gasoline engines greatly influenced the growth of interest in the Petroleum.
Largest reserves and producers
The world's largest oil-producing regions are the Middle East and some European countries, which together account for half of the oil produced worldwide.
The largest reserves are in the Middle East, South and Central America and Europe. Together, these regions hold almost 85% of all the world's oil reserves.
The five countries that produce the most oil are: the United States, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Canada and Iraq. Brazil has almost 1% of world reserves and produces 3% of total oil.
Formation and composition of oil
Its origin is not yet definitively confirmed, but it is believed that the formation of oil is the result of a decomposition process of plankton, small organisms that live on the surface of waters of seas, lakes and rivers.
The formation of oil would happen by the accumulation of the remains of the decomposition of these organisms and the movement of terrestrial crusts are part of the process, transforming the waste into oil, which accumulates in the basins sedimentary The accumulation of debris and the formation of oil takes a few million years.
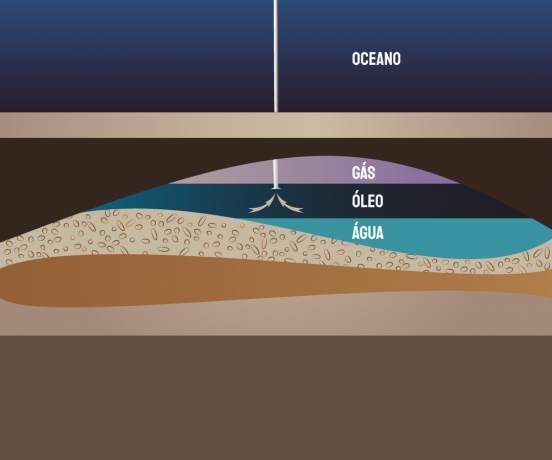 Oil is deposited in sedimentary basins.
Oil is deposited in sedimentary basins.
Chemical composition of petroleum
Oil is composed largely of molecules of carbon and hydrogen - hydrocarbons, such as butane (C4H10) and methane (CH4). These compounds are the bulk of petroleum, although other substances are part of its makeup.
In the chemical composition of petroleum, nitrogen, oxygen, salts and residues of some metals are also found in smaller amounts. The proportion of the elements that make it up is as follows:
- 82% carbon;
- 12% hydrogen;
- 4% nitrogen;
- 1% oxygen;
- 1% of salts and metal residues.
Oil characteristics
The main characteristics of oil are:
- dark coloration;
- oily composition;
- not soluble in water (do not mix);
- it is a flammable substance;
- it is less dense than water.
What is oil for?
Oil can be used in many ways, as a raw material for the formation of other substances and as an energy source.
It is widely used as source of energy, gas and fuel. Currently, about 40% of primary energy (originated from nature) comes from oil. Worldwide, approximately 8% of electricity still comes from oil exploration.
Petroleum-derived products arise from a process of refining, in which the elements that make up the oil are separated. This process is carried out at different temperatures, according to the desired by-product. For example: gasoline is obtained by refining up to 200 degrees, whereas diesel needs higher temperatures, up to 350 degrees.
Despite being one of its main uses, oil is also used in the manufacture of many derivatives (by-products).
Petroleum products
There are many products that are derived from petroleum. Some of these by-products are: diesel oil, gasoline, household gas (LPG), kerosene, paraffin, asphalt and naphtha.
- Diesel oil and gasoline: used as fuel in transport;
- LPG: used in domestic and industrial kitchens;
- Kerosene: used in aircraft turbines and as a solvent;
- Paraffin: it is the basis of several products, such as waterproofing, waxes, rubber and chemical products;
- Asphalt: it is the raw material for the manufacture of asphalt cement;
- Naphtha: used for the production of chemical compounds such as benzene, propene and ethylene.
Petroleum can also be used in the formulation of other by-products for common and domestic use:
- plastic miscellaneous items;
- lubricant;
- make ups;
- medicines;
- synthetic fabrics;
- shoes and clothing;
- cleaning products;
- food coloring and preservatives;
- fertilizers.
oil exploration
Oil exploration is a complex process, comprising three main phases: survey or prospecting, drilling and extraction. Finally, there is also the refining of extracted oil.
1. Survey or prospecting
In this first stage, the oil deposits are located. To find the reserves, the responsible professionals use equipment capable of identifying the presence of the substance.
One of the most used instruments is the seismologist, a tool that, through the emission of shock waves, can confirm the presence of accumulated oil in a region.
2. Drilling
At this stage, after confirmation (or confirmation of high probability) of the location of an oil reserve, drilling is carried out to explore the deposits.
At first, the objective is to confirm the existence of oil and verify if extraction is viable. There are cases in which deposits are found, but conditions in the reserve itself or geographical difficulties can prevent oil extraction.
3. Extraction
The oil extraction process is not simple, as it is located in deep layers of sedimentary rocks.
For the extraction, powerful equipment is used, capable of drilling into the rocks and the extraction is done by installing platforms equipped with pumps that extract oil from the deposits. If the reserve is located on land, the equipment used pumps the oil until it reaches the surface.
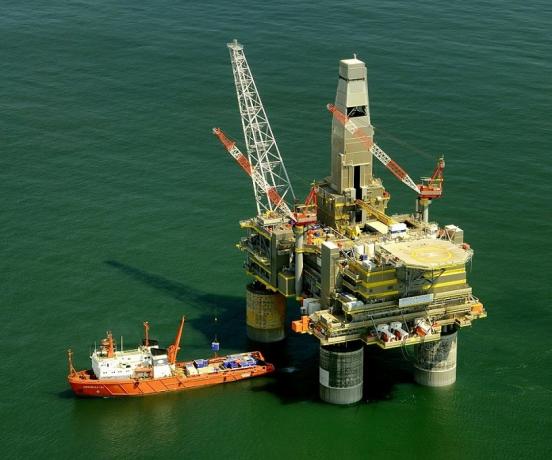 Offshore oil extraction platform.
Offshore oil extraction platform.
4. refining
After extraction, the oil undergoes a refining process that improves its quality and prepares it for exact use on demand. Depending on the fate that will be given to the oil, the refining process varies.
Oil in Brazil
Almost 15 years after the discovery of oil on Brazilian soil, Petrobras, a company that controls and explores oil in the country, was created. Petrobras was created in 1953, during the government of President Getúlio Vargas.
In 2006 the Pre-salt, an extensive area on the Brazilian coast where oil was found. The exploration of this reserve, which began in 2008, was responsible for 60% of Brazilian oil production.
Also read the meaning of Pre-salt.
Oil and environmental problems
The use of oil must be done properly to avoid damage to the environment and ecosystems.
One of the most serious environmental problems that can be caused by the careless use of oil is the water contamination, when the substance is dumped into seas, rivers, oceans or lakes. The presence of oil can be very harmful to aquatic ecosystems, contaminating the water and causing the death of animals.
 An oil spill in water can cause a lot of environmental damage.
An oil spill in water can cause a lot of environmental damage.
Another environmental problem is the pollution by the smoke that results from the use of oil in fuel-producing plants. Smoke contributes to the worsening of air quality and aggravates problems that already exist, such as the growth of the ozone hole and the greenhouse effect.
See also the meaning of fossil fuel know why oil is a non-renewable energy.

