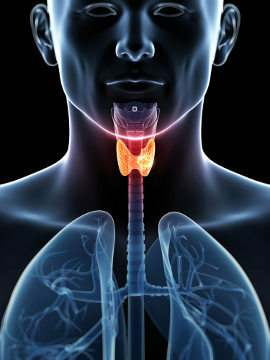
Goiter is the name given to the increase in the volume of gland thyroid. This condition has been known for a long time, being represented, for example, by the Egyptians in 2000 BC. Ç. Goiter has different causes, one of which is the low intake of iodine in food. It can also be related to thyroid disorders, such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
Read more: Endocrine system - complex and made up of the endocrine glands in our body
What is the thyroid?
The thyroid is a endocrine glandresponsible for the production of important hormones, highlighting the thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which act in the regulation of the metabolism. It is formed by two lobes, which are arranged on each side of the trachea and are connected in the midline by an isthmus. The thyroid is shaped like a butterfly and, in an adult, weighs from 20 g to 30 g. To learn more about this gland, read the text: Thyroid.
What is goiter?
The term goiter is used to refer to a large thyroid enlargement, regardless of its etiology or pathophysiology. According to physiological criteria, goiter is classified as simple or toxic. he is called
simple or non-toxic when thyroid hyperfunction is not observed. already the toxic goiter is the one in which the excessive production of hormone.According to epidemiological criteria, goiter can be classified as endemic or sporadic. When a person has a lack of iodine in their diet, it is called endemic. the denomination sporadic it is given when goiter is not related to iodine deficiency. It is important to point out that, since the mandatory supplementation of iodine in table salt was introduced in our country, endemic goiter has become a rare condition.

According to the shape of the goiter, it can be classified into diffuse or nodular, and the latter can be further classified into uninodular or multinodular. Diffuse goiter is one that does not have nodules, while in nodules, as the name suggests, nodules are observed.
Uninodular goiters have only one nodule, and multinodular goiters have more than one nodule. According to the Thyroid Department of the Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism (SBEM), nodular goiter is most often diagnosed after the age of 50 years.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
What are the symptoms of goiter?
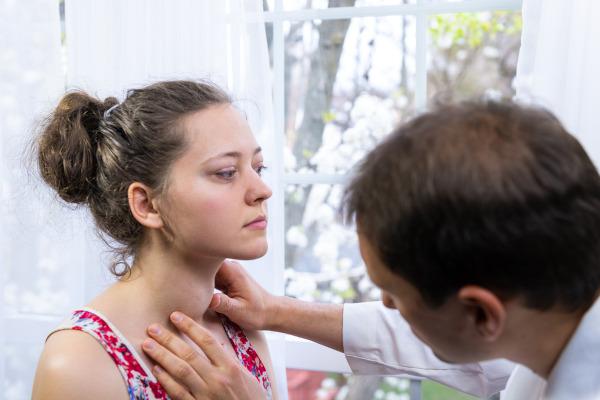
The goiter is characterized by the increased thyroid volume. It can be noticed by an increase in the neck region, and this increase is often seen by the patient or by friends and family. A person can notice the increase in the region when putting on a necklace, buttoning a shirt or shaving, for example.
Goiter can cause symptoms such as coughing, throat clearing and difficulty in swallowing and breathing, these difficulties being the result of compression caused by the increase in the thyroid in other organs, such as the trachea.
What causes goiter?
Goiter can have different causes, such as:
Iodine deficiency;
genetic failure of enzymes of hormonegenesis;
Use of drugs that inhibit the use of iodine;
Presence of goiter substances in the diet. They cause goiter by interfering with the production of thyroid hormones;
Hormonal changes during gestation or puberty.
Why can iodine deficiency cause goiter?
O iodine is a very important mineral salt for the body, as participates in the synthesis of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). These hormones are essential for our metabolism, acting, for example, in maintaining the normal flow of energy, neurological development and physical growth.
Iodine deficiency can trigger goiter as it affects the production of thyroid hormones. With the drop in hormone production, there is an excessive stimulation of the gland by the hormone-stimulating hormone. Thyroid (TSH), in an attempt to ensure a greater synthesis of hormones, and, with that, the thyroid increases in size.
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
O hypothyroidism it is a condition in which there is a reduction in the production of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) hormones. In most cases, this condition is caused by an autoimmune problem called Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Symptoms of hypothyroidism are excessive tiredness, drowsiness, hair loss, weight gain, constipated bowel, irregular menstruation, pain, decreased memory and decelerated beats cardiac.
O hyperthyroidism it is a condition in which an increase in the production of T3 and T4 hormones is observed. One of the causes of hyperthyroidism is called Graves' disease (an autoimmune disease that affects the functioning of the thyroid). The symptoms of hyperthyroidism are: tachycardia, irritation, anxiety, trembling hands, hair loss, loose bowels, changes in the menstrual cycle and considerable weight loss.
How can goiter be diagnosed?
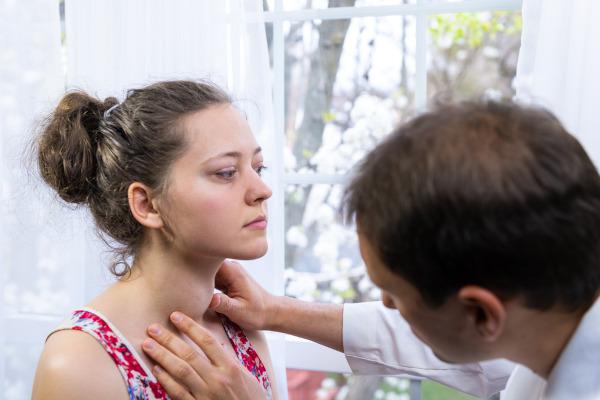

Goiter can be diagnosed through clinical examination palpation of the gland. In addition, additional exams should be recommended, such as ultrasound and blood tests, including the dosage of hormones such as TSH and free T4.
How is goiter treated?
The treatment of goiter varies from one person to another, being important analyze the type of goiter that if features, what are its symptoms and whether or not there are changes in thyroid function. Among the procedures that can be adopted for treatment, the use of certain drugs, surgeries and radioactive iodine therapy stand out. In case of iodine deficiency, treatment with iodine replacement in the diet is recommended.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher