solstices are phenomena that occur due to the movement of translation of the planet. This movement has direct consequences in our daily activities, such as the occurrence of solstices and equinoxes.
The solstice occurs at a time of year when one hemisphere receives more sunlight than the other, due to the angle of inclination that the Earth has in relation to its axis. With this difference in the incidence of sunlight, the day is longer than the night when the summer solstice occurs, or the night is longer when the winter solstice occurs.
Read too: Solstices and Equinoxes - Differences, Consequences, Dates
What is solstice?
THE Earth it has a tilt angle of 23º27’ on its axis. This tilt, combined with the translation, results in a difference in heat stroke (incidence of solar rays on the planet) in some days of the year when comparing the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
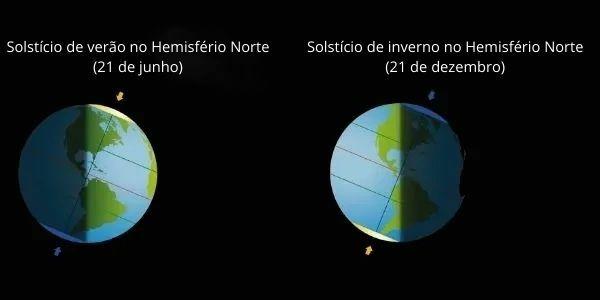
This difference equals the time when the sun moves away from equator line, generating longer days and shorter nights in the hemispheres. Approximately on the day December 21, it has the longest day in the Southern Hemisphere, besides the beginning of summer. The sun's rays fall on the Tropic of Capricorn, making the south more illuminated. In the Northern Hemisphere, the opposite occurs, with the beginning of Winter and the shortest day of the year.
The same fact reverses in both hemispheres in dayJune 21th, when the sun's rays fall on the Tropic of Cancer: it is the longest day in the north and the shortest day in the south.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
When we have Summer Solstice in the Southern Hemisphere, with the longest day of the year, in the Northern Hemisphere, there is the longest night of the year, as there is less incidence of sunlight in this area of the globe. This situation changes when there is the winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere, with the longest day in the north and the longest night in the south.
Read too: Summer time – a measure that seeks to make the most of sunlight
summer and winter solstice
With the movement around the Sun, the planet has four seasons, lasting approximately three months each one. Furthermore, as a consequence of this constant orbit, the Northern and Southern Hemispheres have opposite seasons. If in France (Northern Hemisphere) it is autumn, for example, here in Brazil (Southern Hemisphere) it will be spring, and vice versa.
See when the summer and winter solstice occur in the hemispheres:
→ June 21th:
Northern Hemisphere summer solstice (early summer);
Winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere (early winter);
→ December 21:
Summer Solstice in the Southern Hemisphere (early summer);
Winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere (early winter).
See too: Solar system - everything about the system that has the sun as its biggest component
What is Equinox?
Due to the angle of inclination of the Earth in relation to the Sun, solar lighting does not reach all regions equally. In this way, some areas receive more sunlight (areas close to the Equator) and others less (the poles of the planet).
US March 21st and September 23rd (beginning of spring or autumn in the hemispheres), the planet starts to receive solar rays perpendicular to the Equator Line. With that, days and nights are practically the same duration. Such phenomenon is called equinox of Prhyme orequinox of Oautumn, depending on the hemisphere and the period in which it happens.
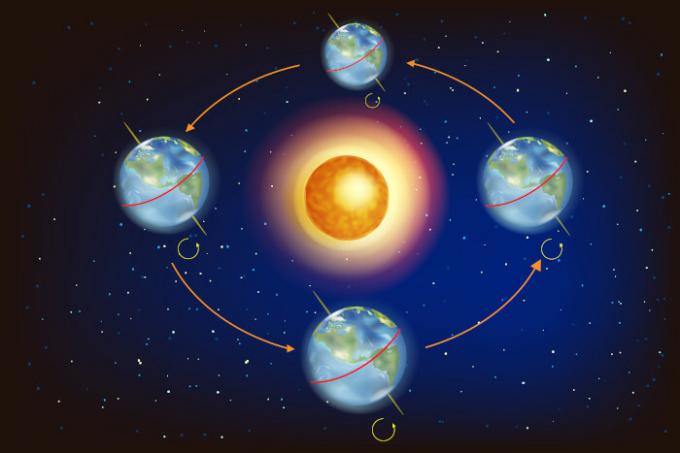
See when the spring and autumn equinox occurs in the hemispheres:
→ March 21st:
Spring Equinox in the Northern Hemisphere (Early Spring);
Autumn Equinox in the Southern Hemisphere (Early Autumn).
→ September 23th:
Spring Equinox in the Southern Hemisphere (Early Spring);
Autumn Equinox in the Northern Hemisphere (Early Autumn).
solved exercises
Question 1 - (UEG) During the Earth's trajectory around the Sun, there are only two occasions when the two hemispheres are equally lit by solar energy. This time of year is known as:
a) equinox.
b) solstice.
c) aphelion.
d) perihelion.
e) summer.
Resolution
Alternative “a”. The moment when the two hemispheres are equally illuminated is called the equinox.
Question 2 - Take a look at the tourist report below, which describes a music festival taking place in Iceland.
“And for those who like to travel beyond nature, Iceland's capital has an annual music festival during the summer, Secret Solstice. The festival takes place during the summer solstice, when the Midnight Sun phenomenon occurs, in which the Sun can be seen 24 hours a day. Secret Solstice lasts for three days in June and the sun never sets.”
This festival takes place at a time when the Earth is:
a) further away from the sun, generating insolation differences in the eastern and western hemispheres.
b) closer to the sun, which makes days and nights the same in the northern and southern hemispheres.
c) in the summer solstice, when, in the summer of the Northern Hemisphere, there is a greater incidence of sunlight in that hemisphere.
d) in the process known as the greenhouse effect, storing more solar light on the planet.
e) in the summer equinox, which results in days longer than nights.
Resolution
Alternative “c”. The Midnight Sun is a common event at the planet's poles during the summer. It happens due to the Earth's tilt, causing sunlight to fall almost perpendicular to the poles. Between October and March, the Midnight Sun can occur in the Southern Hemisphere. Between April and September, the same phenomenon can happen in the Northern Hemisphere. Solstices take place in June and December.
By Attila Matthias
Geography teacher