Newton's third law, also called law of action and reaction, deals with the interaction of forces between two different bodies. According to this law, whenever a force is applied to a body, this body will exert another force of equal direction and intensity, but in the opposite direction.
This is the last of the laws of Isaac Newton, which explain the dynamics of the movement of bodies. These three laws were published in 1687, in his book entitled Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy.
See what the statement of this law says:
To every action there is always an opposite reaction of equal intensity: the mutual actions of two bodies on each other are always equal and directed in opposite directions.
This means that the forces act in pairs and that for every action there is a reaction. For example, if body A exerts a force FThe on body B, body B will exert a force FB of equal intensity over body A, ie FThe = FB, and of equal sense, since both are horizontal.
The direction of these forces, however, is opposite, as body A exerts the force from left to right and as a reaction, body B exerts force from right to left. Look at the image:
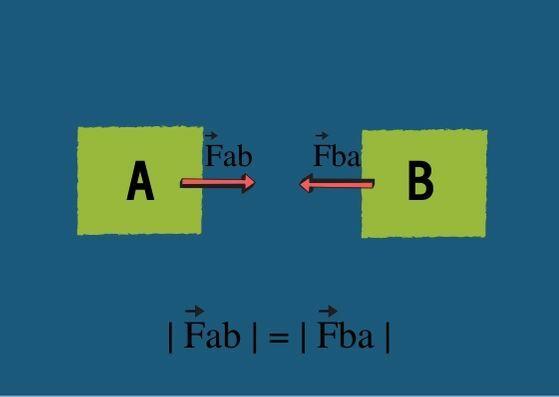
Unlike what happens in Newton's first and second laws, forces never cancel each other out in an action and reaction system, as they are applied to different bodies. Action and reaction will never be applied to the same body.
Learn more about Newton's first law and Newton's second law.
Action and Reaction Examples
- Rocket Launch: to be launched, rocket fuel is burned and the gases expand, applying a force to the ground. The surface applies a reaction force on the gases, which pushes the rocket upwards.
- Pool boost: to pick up momentum, a swimmer applies force to the pool wall. The wall will apply a force of the same intensity and direction, but opposite directions, causing the body to move.
- Firearm shooting: when a person shoots a weapon, the shooter is pushed back due to the reaction force in the opposite direction of the projectile's firing.
There are 5 criteria for Newton's third law to be applied, understand:
- The forces applied to the bodies have same intensity.
- The forces have the same direction (horizontal, vertical or diagonal).
- the forces have opposite senses (Right to left, top to bottom).
- Forces must be applied in different bodies.
- The action and reaction are simultaneous, that is, they start and end at the same moment.
See all Newton's laws.
The weight is normal
When we place an object on a surface, this object exerts the weight force vertically (from top to bottom), which is responded with a force from bottom to top, called Normal. This force acts in this direction in order to support the weight applied to the surface.
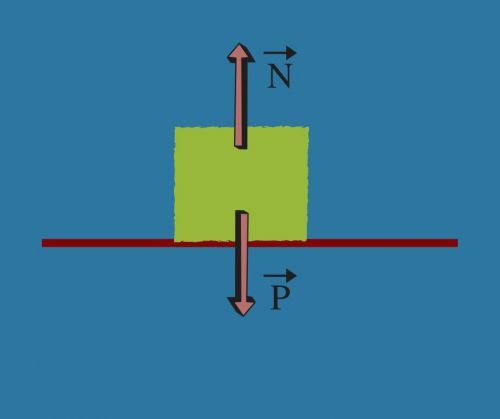
Normal force is not a reaction of weight force and therefore this is not a case where Newton's third lawcan be applied. The law of action and reaction, as already mentioned, always acts on different bodies and not on just one body.
See also the meaning of strength and gravity.



