Atmospheric pressure, also called barometric pressure, is the force that air in the atmosphere exerts on the Earth's surface and on all bodies.
This pressure is not the same anywhere on the planet, it varies according to weather and relief conditions and is related to air concentration:
- More concentrated air: higher pressure
- Less concentrated air: lower pressure
The main factors influencing air concentration and pressure are the altitude and the temperature.
Atmospheric pressure was first determined in 1643 by physicist and mathematician Evangelista Torricelli.
How to calculate atmospheric pressure?
Pressure is calculated by the ratio of force (F) to area (A).
In the case of atmospheric pressure, force refers to the weight that the column of air exerts on a certain surface area. Atmospheric pressure is measured in N/m2 (Newton per square meter) or pascal (Pa).
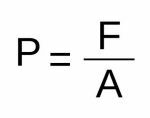
Where,
- F = force measured in N (Newton)
- THE = area measured in m2
- P = pressure measured in N/m2 or paschal (Pa)
Another way to calculate atmospheric pressure is using the following formula:
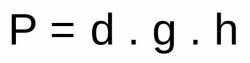
Where,
- d = density measured in kg/m³
- H = height measured in meters
- g = gravity measured in m/s²
- P = pressure measured in pa (Pa)
Atmospheric pressure at sea level
Applying the atmospheric pressure formula and using Torricelli's experiment as a reference for the values, we can calculate the atmospheric pressure at sea level. Under these conditions, the values are:
- Density of mercury: 13,6.103 km/m3
- Acceleration of gravity: 9.8 m/s2
- Height reached by mercury in the tube: 76 cm = 0.76 m
Applying the formula (P = d x g x h), we have:
P = 13.6.103 x 9.8 x 0.76
p = 1.013.105 Pan
The atmospheric pressure value at sea level can also be expressed by:
| 760 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) |
| 1 atm (atmosphere) |
| 100,000 N/m2 (Newton per square meter) |
| 1,013 bar (bars) |
| 14,696 psi (pound per square inch) |
Also understand what it is strength, density and gravity.
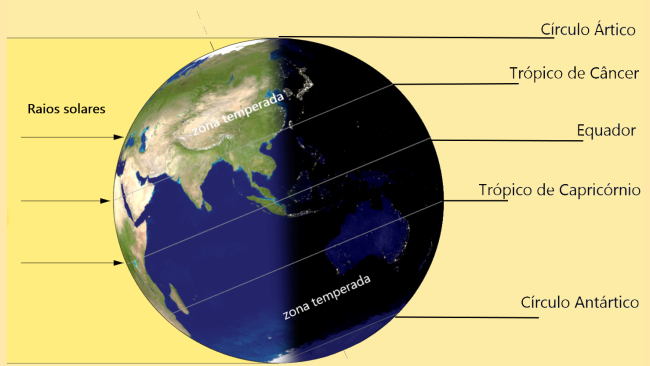
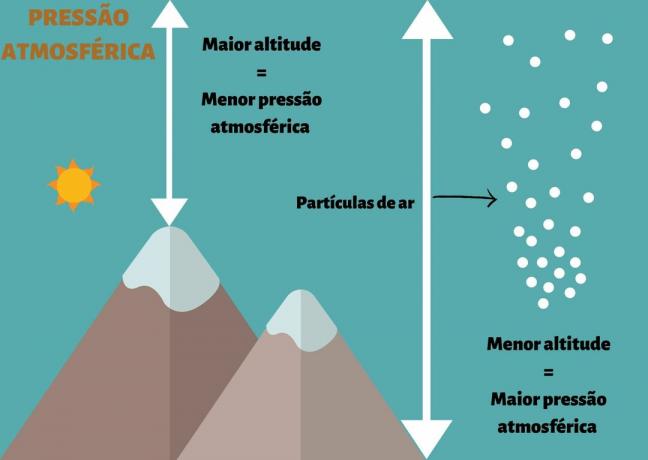
The higher the altitude, the lower the atmospheric pressure
Altitude is one of the main factors influencing atmospheric pressure. To understand how this relationship takes place, it is necessary to think about the structure of the atmosphere.
The atmosphere is an 800 km layer of air, composed of different gases, such as oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen. These gases have mass and weight and exert force on all bodies on the earth's surface.
If we consider that pressure is the force on the area, we must calculate the force that the column of air exerts on a given area.
The closer to sea level, the greater will be this column of atmospheric air and as we rise in relief, this column will decrease.
The greater the weight of the column, the more concentrated the air is, that is, the air molecules are closer together. On the other hand, as we go up in the relief, the molecules will be more spread out and the air will be less concentrated.
That's why climbers have difficulty breathing when climbing mountains. As the air concentration is lower, the particles are farther apart, making the air thin.
At sea level, on the other hand, the air is very concentrated, which makes breathing easier.
See also the meaning of altitude and meet the atmosphere layers.
The higher the temperature, the lower the atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is also influenced by temperature. Just remember that at high temperatures, the molecules of bodies move apart - so does air.
This means that at warmer temperatures, air molecules are more spread out and therefore atmospheric pressure tends to be lower.
In cold places, air molecules clump together, increasing the concentration of gases and consequently making the atmospheric pressure higher.
know more about temperature.
Practical examples of atmospheric pressure
Aircraft pressurization
Commercial planes usually fly about 11,000 meters above the Earth's surface. At this altitude the air is not very concentrated and the atmospheric pressure is too low, which makes human life impossible.
To allow breathing inside the cabin at this altitude, the aircraft are pressurized. This means that a large amount of air is injected into the cabin until a pressure suitable for humans is reached.
During the flight, the pressure inside the plane is much greater than the pressure in the atmosphere outside and for this pressure not to change, the cabin of the plane must be completely sealed.
As air flows from the higher density area to the lower density area, any leak in the cabin will cause the air to quickly escape out of the aircraft, causing depressurization.
know more about pressure.
Liquid in the straw
Drinking a liquid in a straw is only possible thanks to the action of atmospheric pressure. This is because atmospheric pressure is exerting a force on the liquid in the cup.
Inside the straw there is air and therefore pressure, but when we pull air from inside the straw, we reduce the pressure inside.
As there is an atmospheric pressure “pushing” the liquid down and as the liquid flows from the highest to the lowest pressure, the liquid will rise through the straw until reaching the mouth.
Barometer: an instrument to measure atmospheric pressure
The measurement of atmospheric pressure was first made in 1643 by Evangelista Torricelli, an Italian physicist and mathematician.
Torricelli created the mercury barometer, an instrument composed of a 1 meter long test tube and another lower container, similar to a bowl. Both containers were filled with mercury.
In his experiment, the test tube was placed in the bowl with the open end down so that no air could enter the tube.
The liquid began to flow from the tube into the bowl and the system came to equilibrium when the column of mercury reached 76 cm. At the top of the test tube, a vacuum formed.

System stabilization means that the atmospheric pressure that the column of mercury exerts on the liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure exerted by the atmosphere outside.
Thus, Torricelli determined that the atmospheric pressure at sea level would be equal to 76 cmHg or 760 mmHg.
See also the meaning of atmosphere.