RNA (or RNA) is short for ribonucleic acid, a macromolecule essential for many biological functions.
As the name implies, RNA is a nucleic acid (just like DNA) and functions in the regulation, encoding, and decoding of genes. These acids, together with carbohydrates, lipids and proteins, make up the group of essential substances for all forms of life.
The main function of RNA is to produce proteins from information acquired from DNA. For this reason, one of the great premises of molecular biology is that “DNA makes RNA make proteins”.
RNA is synthesized from DNA through the process of transcription. This process is started with an enzyme called RNA polymerase, which promotes the opening of the DNA and guarantees the pairing of the nucleotides that will be transcribed.
RNA structure
RNA is made up of a chain of smaller substances called nucleotides. In RNA, nucleotides are composed of riboses, phosphates and nitrogenous bases which, in turn, are subdivided into:
- Purines: adenine (A) and guanine (G);
- Pyrimidines: cytosine (C) and uracil (U).
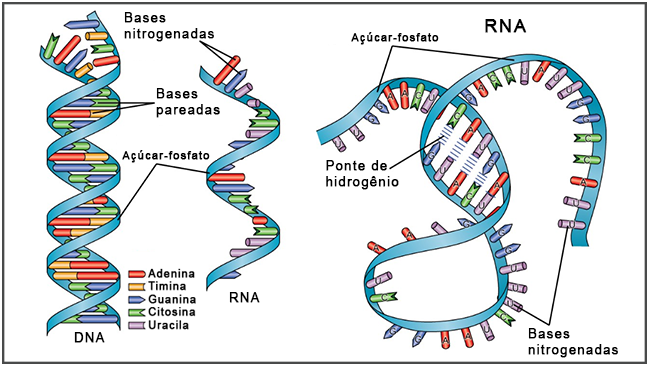
Unlike DNA, RNA is usually made up of a single strand (single strand). However, it is common for this single strand to fold around itself, bringing together complementary nitrogenous bases and creating pairings. In this way, it ends up forming a three-dimensional structure similar to DNA.
In structural terms, other differences between RNA and DNA are:
The pentose (sugar) present in RNA is ribose, while in DNA it is deoxyribose.
In RNA there is the nitrogenous base uracil, while in DNA there is thymine.
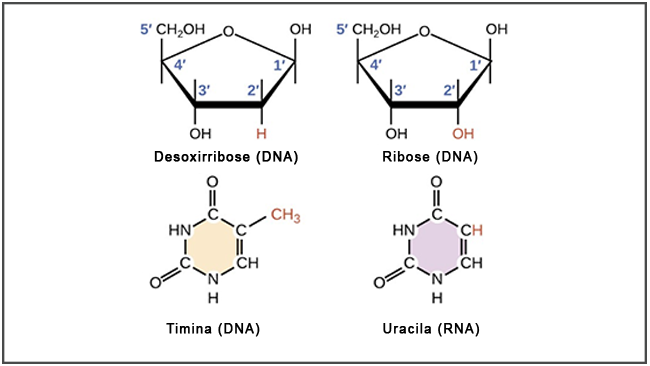
The subtle difference in pentose present in each acid gives DNA a higher level of stability, ideal for storing genetic information. On the other hand, the more unstable nature of RNA is sufficient for its shorter term functions.
RNA types and their functions
There are three types of RNA: messenger (mRNA), ribosomal (rRNA) and transporter (tRNA).
messenger RNA
Messenger RNA is the molecule responsible for carrying genetic information from DNA to the cytoplasm.
When a cell requires the production of a certain protein, the DNA starts the transcription process, through which the genetic code is copied, thus synthesizing an mRNA strip. This RNA works as a mobile copy of the DNA that carries the message to the cytoplasm and informs the type of protein that should be produced.
ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal (or ribosomal) RNA is the substance that makes up approximately 60% of the ribosome, the organelle in which protein synthesis occurs. Its function is to assist in translating the information carried by the messenger RNA.
Ribosomal RNA is synthesized in a dense region located in the cell nucleus called the nucleolus. As the main component of the ribosome, rRNA is essential for all organelle functions, especially for the correct pairing between messenger RNA and transporter RNA.
RNA transporter
The transporter (or transfer) RNA is the molecule responsible for taking amino acids to the ribosome in order to help in the synthesis of proteins.
When the messenger RNA informs the type of protein that must be produced, the ribosomal RNA helps to transfer the information to the transporter RNA. Based on the codons (a sequence of three nitrogenous bases), the genetic code is identified and the tRNA is in charge of transporting compatible amino acids for the production of the protein.
RNA characteristics
In summary, the main features of RNA are:
- it works in the regulation, encoding and decoding of genes;
- its main function is to produce proteins;
- are formed by riboses, phosphates and nitrogenous bases;
- it is formed by a simple chain (a single ribbon);
- can be classified into messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA and transporter RNA.
- messenger RNA is responsible for carrying DNA information to the cytoplasm;
- ribosomal RNA assists in translating information brought in from DNA;
- the transporter RNA delivers amino acids to the ribosome to aid in protein synthesis.
See too:
- DNA
- DNA: what is it, what is its function and structure
- DNA and RNA
- Proteins
- Biology
- Cell


