light reflection it's the optical phenomenon and undulatory which consists of changing the direction of light propagation after its interaction with a surfacereflective. When light falls on such a surface, a portion of its energy can be transmitted, which is then refracted inside the material. Another portion of this energy can be absorbed, being converted into excitementthermal. It is also possible that part of the energy transmitted by the electromagnetic wave is reflected back to the original medium in which light propagated.
THE origin of the light reflection phenomenon é microscopic: the surface atoms of reflective materials are not able to absorb certain wavelengths and therefore reflect them back. It is also worth saying that reflection is a wave phenomenon, so any type of wave can suffer reflection: sounds, electromagnetic waves, mechanical waves, etc. During the reflection of a wave, it is possible that some other phenomena occur, such as phase inversion and polarization of transverse waves.
Types of reflection
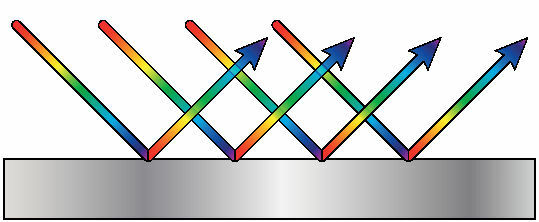
There are two types of reflection: regular and diffuse. THE regular reflection is the one in which it is possible to see a reflected image, while the diffuse one is the reflection that emanates of objects that do not have surfaces that are smooth enough to promote reflection regular.
At regular type reflection, the light rays are reflected at the same angle as the incident light rays, which angle is measured in relation to the perpendicular direction to the surface, known as normal. Also, according to the laws of reflection, these rays of light, incident and reflected, are contained in the same plane. Thus, in regular reflection, it is possible to clearly observe the formation of reflected images.
At reflectiondiffuse, the light rays incident on the surface are reflected in angles and plansseveral, so that it is possible to observe the reflected light, however no image is observed.
See too:ÇHow images are formed in concave and convex spherical mirrors
Laws of reflection
The laws of reflection serve to define the conditions under which there is regular reflection. The first law of reflection states that:
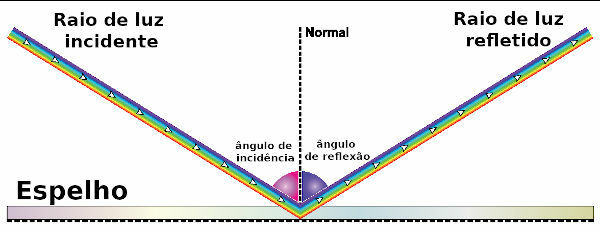
the normal direction and the incident and reflected light rays are contained in the same plane;
the angle of incidence of light rays, in relation to the normal line, is equal to the angle of reflection.
The following figure illustrates the principle of regular reflection described by the laws of reflection. Watch:
Examples of light reflection
Check out some examples of situations in which light reflection occurs.
When we look into a mirror and see our image being reflected, we are looking at a reflectionregular from light.
When we look at a pool of water or oil and see a reflected image, we observe a reflectionregular from light.
When we look at an illuminated painting – although we do not see a reflected image, we are seeing the painting, which is only seen because it reflects light – we are observing a diffuse reflection from light.
Reflection of light in plane mirrors
Flat mirrors are pretty surfaces smooth, reflective and polished, which causes the incident light to reflect on them in a coherent (regular) way. In this way, when we look at the reflecting surface of a flat mirror, we see clearly reflected images.
The image formed in the plane mirrors is virtual, produced by the crossing of the extensions of light rays that are reflected. In addition to being virtual, this image is straight and is rotated 180° in the horizontal direction. That's why the right hand becomes the left hand when reflected in the plane mirror. Want to know more about the subject? Then read our specific text: Differences between real and virtual images.
Reflection of light in spherical mirrors
THE light reflection on spherical surfaces follows the laws of reflection, as with the reflection of light on flat surfaces. However, the curvature of the surface causes the reflected light rays to intersect in different ways, giving rise to distorted images, which can be larger or smaller than your objects.
See too: After all, what is light?
Solved exercises on light reflection
Question 1 — Check the alternative that indicates a process in which does not occur the regular reflection of light.
a) When looking in the mirror
b) When looking at the car's rearview mirror
c) When observing the reflection of a window on a television
d) When reading a book with matte pages
Resolution:
The regular reflection of light is easily perceived by the formation of reflected images, so the only alternative that presents such images is the letter D.
Question 2 — In accordance with the laws of light reflection, mark the correct alternative.
a) The angles formed between the incident and refracted light rays with respect to the direction normal to the plane of reflection must be equal.
b) The incident and reflected light rays need to be contained in different planes.
c) The angle between the incident and reflected light rays must be equal to 90°.
d) The incident and reflected light rays must form the same angle with respect to the normal direction of the reflecting plane.
Resolution:
Let's look at the alternatives!
The) FALSE - The alternative talks about the refracted light ray and the question deals with the laws of reflection of light, and not of the laws of refraction of light.
B) FALSE – According to the laws of light reflection, the incident and reflected light rays must be contained in the same plane.
ç) FALSE – There is no restriction on the angle between the incident and reflected light rays according to the laws of reflection
d) TRUE.
Question 3 — On the reflection of light in flat mirrors, tick the correct alternative.
a) In flat mirrors, diffuse reflection of light occurs.
b) The image formed by the plane mirrors is obtained by crossing extensions of light rays.
c) In flat mirrors, light is diffusely reflected, so it is possible to see the formation of images on its surface
d) In flat mirrors, images are reflected in front of the mirror; for this reason, they are called virtual images.
Resolution:
Let's look at the alternatives!
The) FALSE - The reflection that takes place in flat mirrors is the regular reflection of light.
B) TRUE
ç) FALSE - In diffuse reflection, it is not possible to see reflected images.
d) FALSE – In flat mirrors, the formation of images takes place “behind” the reflecting surface of the mirror. In this case, we say that the images are virtual.
Based on the analysis of alternatives, the correct answer is letter B.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher