Developed by the Greek mathematician Hipparchus in Ancient Greece, the astrolabe is an instrument used for calculate the position of the stars from geometric principles.
In addition to the position of the stars, the astrolabe was used to calculate the altitude of objects, the depth of wells and also to specify the hours and geographic locations.
From the 15th century onwards, the astrolabe became an important navigation tool. With it, it was possible to determine the latitude of the vessels and the directions in which they should sail.
The word astrolabe is derived from the Greek words “astro”, which means star and “lambanein”, which means to catch.
 11th century astrolabe.
11th century astrolabe.
The origin of the astrolabe
The first astrolabe was created by the Greek mathematician, astronomer and geographer Hipparchus of Nicea (180 - 120 yrs. C) during the Hellenistic period of Ancient Greece.
An important student of mathematics, Hipparchus was one of the creators of trigonometry and was the one who discovered the precession of the equinoxes and the possibility of dividing a circle in 360°.
Based on several mathematical theories, Hipparchus developed this complex instrument that could perform calculations similar to an analog computer.
The creation of the astrolabe was made possible by Hipparchus' description of the stereographic projection. This projection is a method that allows the transcription of 3 coordinates to a two-dimensional plane.
From the 8th century onwards, the astrolabe began to be used in the Islamic world and was discovered through the translation of materials written by the Greeks.
The Arabs used the astrolabe for navigation and also to determine the times of prayer and the location of Mecca, the direction in which they must turn when praying.
The Arabs took the astrolabe to Europe, where the instrument was simplified and improved in order to guide ships that set out in search of new lands.
This new astrolabe became known as nautical astrolabe and was developed by astronomer Abraão Zacuto in Portugal.
Unlike the ancient astrolabes, which performed various calculations, this new instrument had the sole purpose of determining geographic locations.
This instrument contributed to the discovery of the path of the Indian women and the arrival of the Portuguese in Brazil.
 Nautical astrolabe.
Nautical astrolabe.
What is the astrolabe for?
The astrolabe uses the positioning of the stars in the sky and principles of applied trigonometry to make several calculations. Among the functions of an astrolabe are:
- Precise the placement of planets and stars;
- Measure the height of mountains, buildings or the depth of wells;
- Determine the hours of the day and the seasons of the year;
- Determine the geographic positioning of vessels.
Importance of the astrolabe for the history of navigation
Maritime expansion began in the 15th century with the Iberians. At that time, the only reference points for navigators were the stars, which were used as guiding stars.
The Sun, the North Star and the Cruzeiro do Sul, for example, used to be important points for determining geographic locations in the high seas.
As navigation develops, mathematical and astronomical instruments and techniques are created for locating vessels, defining routes and discovering new lands.
The astrolabe, which was taken to Europe by the Arabs, became an important tool for boats, as it allowed the calculation of locations from the stars and planets.
In addition to astrolabes, navigators used compasses, crosshairs, compasses, tables of declination of the sun and studied mathematics and astronomy.
Understand the history of great navigations.
How does the astrolabe work?
The astrolabe is made on a circular metal plate on which several circular blades with different graduations are superimposed, such as hours of the day, degrees, months of the year and signs of the zodiac.
The nautical astrolabe is very similar to the first astrolabes, but its structure is simpler and usually has cutouts inside the metal plate.
In the middle of its structure is a pointer (medicina) linked to the circular plates and at the top a handle so that the astrolabe can be held suspended.
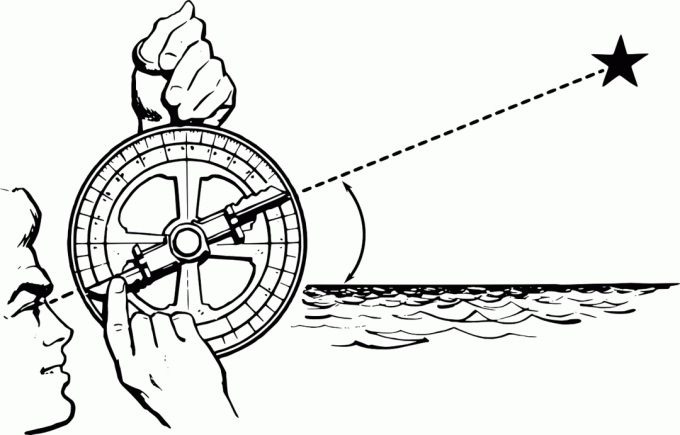
To use the astrolabe, the observer points the central ruler to the star used as a reference and then observes the instrument's graduations.
From this observation and based on knowledge of astronomy, navigators could determine their location at sea and calculate routes.
See also the meaning of geometry and astronomy.