The animal cell is called eukaryotic cell, because it has a core attached to its membrane.
The animal cell differs from prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, because its DNA (genetic material) is found within the nucleus. Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, do not have a defined nucleus.
In addition to having a nucleus, animal cells also contain other membrane-bound organelles (structures) that carry out specific functions necessary for the proper functioning of the cell.
At animal cell organelles they are:
- Plasma membrane: selects what enters and leaves the cell;
- Cytoplasm: responsible for storing chemical substances;
- ribosome: produces protein for the cell;
- Lysosome: performs cell digestion;
- peroxisome: performs cell detoxification;
- mitochondria: is responsible for cellular respiration;
- Core: responsible for storing the genetic material (DNA);
- nucleolus: responsible for organizing and producing ribosomes;
- centriole: helps in cell division and production of cilia and flagella;
- Cytoskeleton: responsible for supporting the cell;
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum: synthesizes proteins that will be exported;
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: responsible for producing lipids, which make up the plasma membrane;
- Golgi Complex: responsible for receiving, modifying and sending protein to other parts of the cell.
The animal cell is present in beings that are multicellular, that is, that have more than two cells. They act in an integrated way (together) for the functioning of the animal body.
A human being, for example, has about 10 trillion cells that together perform various functions in the body, such as:
- production of energy for the body;
- reproduction;
- nutrition;
- Muscular contraction;
- transport of gases.
The structure of the animal cell
A cell is basically formed by organelles, that is, structures, which have specific functions for the general functioning of the cell.
Organelles are the parts of each cell, as shown in the image below, protected and separated by a membrane, a type of thin structure that protects the inner and outer sides of the cell.
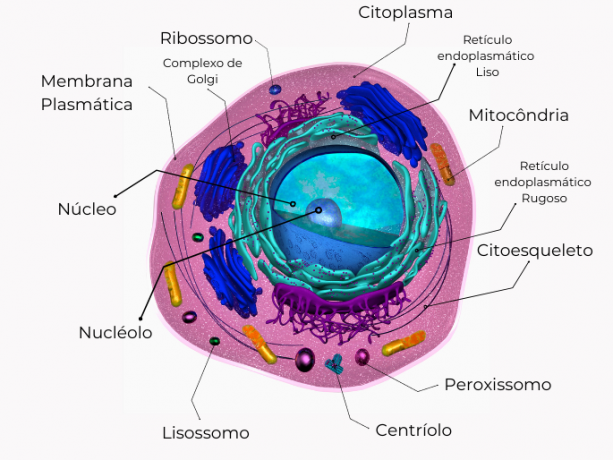
Animal cell organelles.
The functions of animal cell organelles
Plasma membrane
Occupation: has the function of selective permeability, that is, it selects the molecules that enter and leave the animal cell.
What is: it is a thin structure, with a bilayer, that surrounds and protects each cell from the external environment. This bilayer is made up of lipids and proteins.
Cytoplasm
Occupation: stores chemical substances that are important for the proper functioning of the cell. Furthermore, within the cytoplasm there is the cytoskeleton, a kind of protein chain that supports the cell.
What is: it is an organelle formed by water and nutrients, which is found between the plasma membrane and the cell nucleus.
ribosome
Occupation: synthesize proteins, meaning they function as a protein factory for the cell.
What is: is an organelle that can be found in both animal and plant cells.
There are two types of ribosomes, those found freely in the cytoplasm, or those that are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Lysosome
Occupation: digests substances that will later be used by the cell. It works as a recycling of substances, which can be reused by the cell.
What is: it is the organelle that has several digestive enzymes that digest some substances. Among the enzymes present in the lysosome, we can highlight protease, lipase and nuclease.
peroxisome
Occupation: is responsible for cell detoxification, through oxidative reactions. While the lysosome does the digestion, the peroxisome does the detox.
What is: the prefix peroxy comes from the term hydrogen peroxide, which is hydrogen peroxide. Peroxisome contains an enzyme called catalase, which is responsible for breaking down hydrogen peroxide, a type of toxic substance.
Mitochondria
Occupation: is responsible for cellular respiration. It uses oxygen from the respiratory system and glucose from the digestive system to generate energy for the entire cell
What is: it is one of the main organelles, as it produces energy for the cell to stay alive. One of the main features is that the mitochondria has two types of membranes, an internal and an external one, different from other organelles.
Core
Occupation: is responsible for storing and protecting genetic material, DNA, an organic compound that transmits hereditary information.
What is: is considered the largest organelle in the cell. The nucleus is covered by the nuclear envelope and communicates with the cytoplasm through the nuclear pores.
nucleolus
Occupation: its function is to guarantee the necessary production of ribosomes for the cell.
What is: is a structure found inside the core. It is made of ribosomal RNA and proteins, which are synthesized from DNA commands that are in the nucleus.
centriole
Roles: aid in cell division and generate the cilia and flagella that move the cell. When there is cell division, centrioles have a great capacity to double and move towards the cell poles.
What is: is an organelle that is in the cytoplasm and has a cylindrical shape.
Cytoskeleton
Occupation: is responsible for supporting the cell.
What is: The cytoskeleton is the skeleton of the cell, that is, its structure. It is formed by networks of protein fibers. Its 3 formation proteins are: microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules.
Rough (or granular) Endoplasmic Reticulum
Occupation: is responsible for synthesizing proteins for export.
What is: is an organelle formed by labyrinth-shaped membranous structures, and is linked to the ribosome. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is also known as granular because it has a rough appearance due to the presence of ribosomes.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Occupation: is responsible for the production of molecules, lipids that make up the plasma membrane, in addition to asteroids, such as sex hormones, testosterone, progesterone and estrogen. Furthermore, they may be responsible for cell detoxification.
What is: it is an organelle with a large labyrinth-shaped membranous structure and which, unlike the rough endoplasmic reticulum, does not have the presence of ribosomes, so it has a smooth appearance.
Golgiense Complex or Golgi Complex
Occupation: The function of the golgi complex is to receive, modify and send these ribosomal proteins to other regions of the cell or beyond.
When the rough endoplasmic reticulum produces the protein, it sends it to the golgiense complex to release them.
What is: is an organelle made up of a type of fold membrane and vesicles. These vesicles are responsible for exporting proteins out of the cell.
Differences between animal and plant cell
Even being eukaryotes like the animal cell, the plant cell has 3 aspects that differentiate it from the animal cell. Are they:
- cell wall: an outer shell of the cell, formed by cellulose, is a rigid membrane, different from the plasma membrane contained in the animal cell;
- Plasts: It is responsible for photosynthesis and storage of substances. A great example is the chloroplast, which has chlorophyll in its interior.
Chlorophyll is a pigment responsible for photosynthesis and the green color of the plant. The animal cell has no plastids.
- large vacuoles: they occupy a large part of the plant cell and have the function of intracellular digestion and storage of substances.

See also the meaning of:
- eukaryote;
- Recombinant DNA;
- Zygote;
- heterotrophs;
- Cell;
- genome.


