Inside the skull we find the brain, a part of Nervous system Central (SNC) that receives, processes and generates responses to messages that reach it. O brain it is divided into several parts, the brain being one of them.
O brain, which is considered the core of our body's intelligence and learning, is the largest part of the brain, making up about 80% of the total mass of this part of the CNS. It can be divided into two parts, the left and right cerebral hemispheres, which are connected by corpus callosum, a structure formed by a thick bundle of nerve fibers.
According to some studies, the two cerebral hemispheres act in different functions. The left hemisphere, for example, is most often linked to language, performing calculations, some memories, problem solving and speaking. The right hemisphere is more related to image interpretation, non-verbal manual skills, intuitions, three-dimensional spaces, and music perception. In trained musicians, musical information is processed in both hemispheres of the brain.
It is also worth noting that, in most people, the hemispheres command opposite sides of the body. This means that the left side of the brain, for example, controls the movements and senses of the right side of the body.
Analyzing the cut of a brain, it is possible to see that the outermost region is darker (grey matter) when compared to the inner part (white substance). The outermost region, which has a thickness ranging from 1 to 4 mm, is called cerebral cortex and houses the cell bodies of the neurons. The inner part is rich in myelinated axon bundles, which ensures a lighter color.
The brain has a series of characteristic folds in the cortex region. These folds serve to increase the surface area of this structure, which has only the restricted space of the cranial cavity.
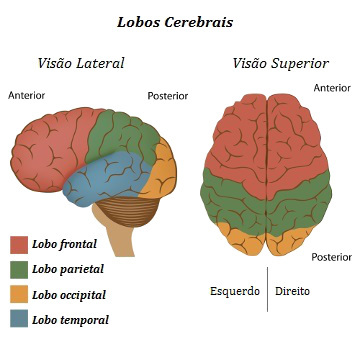
The brain has four lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital
We can divide the cerebral hemispheres into four lobes, named after the skull bone above it:
→ front lobe – Related to creative work, reasoning, personality, decision making, movement of skeletal muscles, among other functions;
→ temporal wolf – Acts mainly in communication, relating to speech, hearing and even writing;
→ parietal wolf – Related, among other functions, with the perception of pain, cold, heat and touch;
→ occipital lobe – It is related to the processing of visual information;
Interesting facts:
- Despite what many claim, humans do not use only 10% of their brain. A large portion of this part of our Nervous System works to ensure the proper functioning of the body, but it is impossible to assign a percentage to its functioning;
- the brain of Albert Einstein was withdrawn after his death for studies. The organ was photographed and several slides mounted in order to identify the reason for the scientist's great intelligence;
- Scientists claim that our reliance on saving information on cell phones, tablets and computers is affecting our memory capacity.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/cerebro-humano.htm

