it's a climate humid mesothermal, that is, it has seasons with well-defined climates and is located in the temperate zone of the Earth Globe.
The great feature of the temperate zone is that the hot and cold seasons of the seasons are well defined.
It is within this zone that, among other climates, the subtropical climate.
It is located between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle and between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle, as shown in the image below.
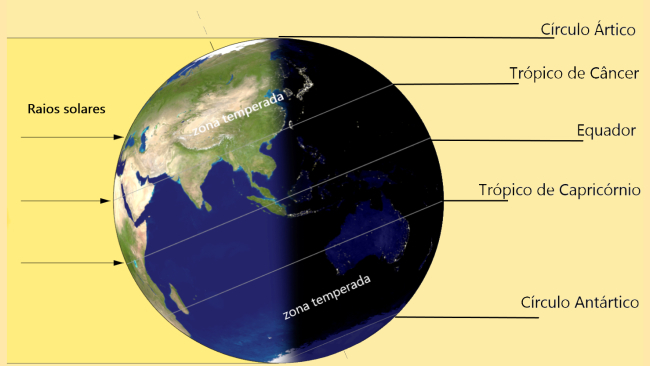 Indication of the temperate zone on the globe.
Indication of the temperate zone on the globe.
Subtropical climate characteristics
Among the relevant features of the climate, we have:
- In the subtropical climate, there is a drop in temperature during the winter, but it is not usually as rigorous a season as in climates in European areas, for example. Temperatures can be between 0° and -10°, as occurs in southern Brazil;
- There is considerable rainfall throughout the year. The rains are well distributed over the months and occur with a certain frequency;
- It is a climate that is influenced by some air masses, such as the Atlantic polar mass;
- Typically, the subtropical climate zone has a long, dry, hot summer, a short, mild, wet winter, and very short transition seasons (spring and autumn);
- During the summer months, the subtropical climate is influenced by tropical air masses. In the winter months it is absolutely possible to form a snow cove.
 Snow in São Joaquim, interior of Santa Catarina - southern state of Brazil.
Snow in São Joaquim, interior of Santa Catarina - southern state of Brazil.
Subtropical climate zones
An interesting fact of the subtropical climate is that, despite its limited territorial distribution, this climatic zone houses a large part of the human population.
This mood can be found at:
- part of northern Mexico;
- southern US;
- parts of southern Brazil and Uruguay;
- central parts of Chile and Argentina;
- the south of most of Africa;
- Australia's south coast;
- the North Island of New Zealand;
- part of southern Japan;
- parts of Southeast Asia;
- Mediterranean basins.
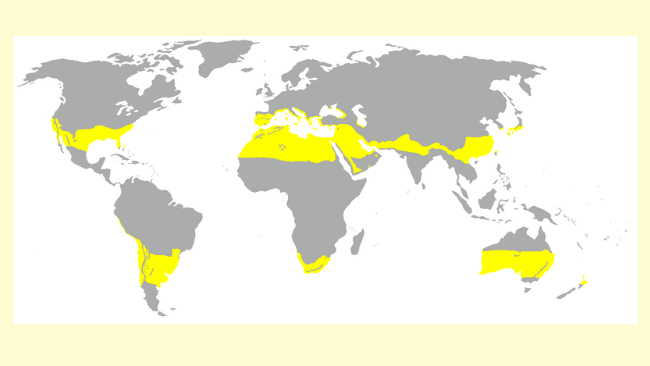 On the map, the yellow colored zones are those with a subtropical climate.
On the map, the yellow colored zones are those with a subtropical climate.
The subtropical climate can be very different in each zone, depending on the geographic conditions of the place. The Mediterranean, for example, has a milder climate than subtropical climate zones elsewhere in the world.
One reason is the high mountain ranges that separate colder northern Europe from the southern parts of the continent.
Tropical and subtropical forests
The main difference between a tropical rainforest and a subtropical rainforest is location.
Tropical forests are located near the equator, between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. Temperate forests are located north of the Tropic of Cancer and south of the Tropic of Capricorn.
When comparing tropical and subtropical forests it is important to consider the amount of rain they receive. Although the rainfall received by the subtropical forest is high, the tropical forest can reach 4 times more during the year.
 Amazon forest: example of a tropical forest.
Amazon forest: example of a tropical forest.
This is because the climate of the rainforest is warmer than that of the subtropical rainforest. Moisture levels in the rainforest biome range from 70% to 90%.
This hot climate causes dead organic matter to decompose extremely quickly, so the soil layer in the rainforest is very thin and devoid of nutrients.
The rainforest climate experiences temperatures that rarely fall below freezing and normally do not reach more than 27°C in summer.
The subtropical forest's consistently cooler temperatures slow down decomposition, creating a very large layer of soil full of nutrients and dead organic matter.
Countries that experience this temperate subtropical forest climate include parts of Canada and the United States, as well as Chile, New Zealand and Norway.
See too:
- what is weather?
- what is tropical climate?
- what is polar climate?
- what is equatorial climate?
- Types of weather

