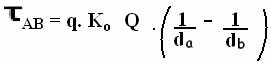You electrical receivers they are devices that transform electrical energy into another form of energy, be it mechanical, thermal, among others. An example of a receiver is O electric motor that transforms electricityin mechanical energy, being the basis for the operation of various devices, such as fans, mixers, blenders, etc.
On a electric circuit, the receivers cause a drop in the electromotive force supplied by the voltage source. This drop occurs because the energy supplied is used in the transformation intended by the device and its intensity depends on the value of the counter-electromotive force of the receiver and its resistance internal.
THE counter electromotive force (fcem) represents the useful potential difference between the two receiver terminals and is also called the output voltage. In the circuit, it is usually represented by E'. To calculate the potential drop (V) between the receiver terminals, we use the following equation:
V = E' + r'i
This relationship is known as receiver equation.
The value of "r'i" represents the amount of energy that was dissipated by the device in its internal resistance through the Joule Effect. Note in the diagram below how the receiver's operation is characterized:
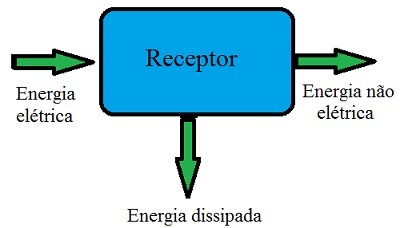
In the figure, we see that the receiver receives electrical energy, transforms a part into non-electrical energy and dissipates the rest
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
the prefix against of the term counter electromotive force is used because it is opposite to the electromotive force of the generator. Note in the following figure how the receiver is represented in an electrical circuit:
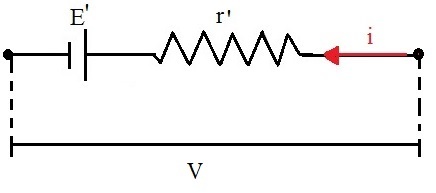
Representation of the electrical receiver in electrical circuits
This symbol is the same one used for generators, and the difference is in the sense of electric current. In a circuit with two components, we recognize the generator as having an electromotive force greater than the counterelectromotive force.
The generator equation can be graphed, and the value of E' and r' are constant. The graph obtained is a straight line, as shown in the following figure:
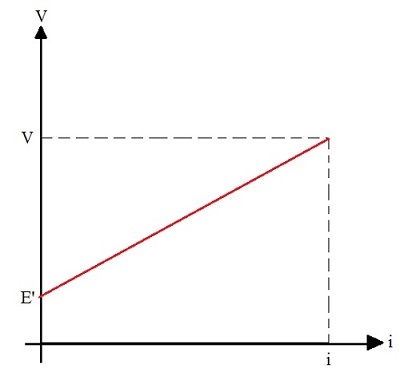
Diagram representing the operation of the electrical receiver
From the analysis of the graph, we can see that, when the electric current is equal to zero (i = 0), there is no dissipation of energy in the internal resistance, so that V = E'. Another conclusion that we can draw is that, when current i increases, the ddp between the receiver terminals also increases, since the value r'.i increases.
By Mariane Mendes
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
TEIXEIRA, Mariane Mendes. "Electrical Receivers"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/receptores-eletricos.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.