THE Nuclear plant it is an industrial installation whose purpose is to produce electrical energy from nuclear reactions. Nuclear reactions of radioactive elements produce a large amount of thermal energy.
Generally, nuclear power plants are built by a containment shroud made of reinforced iron, concrete and steel, in order to protect the nuclear reactor from emitting radiation to the environment environment.
The most used element for the production of this energy is the uranium.
Phases of a Nuclear Plant
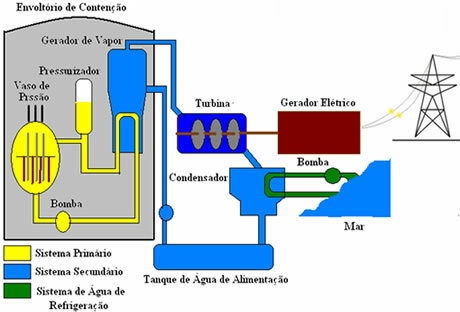
As shown in the figure below, a nuclear power plant is basically formed by three phases, the primary, the secondary and the refrigeration.
Initially, the uranium is placed in the pressure vessel. With fission, there is the production of thermal energy. In the primary system, water is used to cool the nuclear reactor core.
In the secondary system, the water heated by the primary system is transformed into water vapor in a system called a steam generator. The steam produced in the secondary system is used to move the turbine of an electric generator.
The water vapor produced in the secondary system is then transformed into water through a system of condensation, that is, through a condenser which, in turn, is cooled by a refrigeration system of water. This system pumps seawater, cold water, through cooling circuits that are inside the condenser.
Finally, the energy that is generated through the entire nuclear fission process reaches homes through electricity distribution networks.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Brazil School Team
Modern physics - Physics - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Domitiano Correa Marques da. "How does a nuclear plant work?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/como-funciona-uma-usina-nuclear.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.