amphibians (Class Amphibia)they are animalsvertebrates that stand out for having representatives who spend part of their life cycle in the Water and another part in the terrestrial environment. The term amphibian is due to this characteristic, being derived from amphibious, which means “both types of life”. Despite this remarkable way of life, not all species of the group have it, being possible to find representatives strictly aquatic or strictly terrestrial.
Amphibians can be classified into three groups: Anura, Urodela and Apoda. Of these, the anuran group stands out as the most diversified, with many well-known representatives, such as toads and frogs. Currently, around 7000 different species of amphibians are recognized on the planet, 900 of which are found in our country. It is important to highlight that factors such as habitat loss and climate changes have caused the extinction of several species of these animals.
Read too: Toads, frogs and tree frogs - know the difference between these three groups of animals
General characteristics of amphibians
the amphibians are vertebrate animals ectotherms (they are not able to regulate body temperature by internal mechanisms, external sources being essential for this), and a of its most striking features is the presence of a life cycle with an aquatic larval stage and a terrestrial adult stage. Although it does not occur in all representatives, this characteristic makes these animals to be considered of "double life".

Amphibians are noteworthy for other important characteristics, such as the performance of gas exchange through the skin, thus presenting,skin breathing. In some species, cutaneous breathing complements the lung breathing, however, in some terrestrial species, the absence of a lung is observed, presenting exclusively cutaneous respiration. We must also not forget that amphibians that live in the aquatic environment present gill breathing.
Skin breathing makes these animals need to keep their skin moist in order to allow for gas exchange. Due to this, the most amphibians are found inhumid environments, such as forests. They can also be found in drier environments, but these species generally spend a great deal of time under leaves or in burrows that guarantee them greater humidity. In addition, amphibians have skin with glands that secrete substances that guarantee this moisture.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
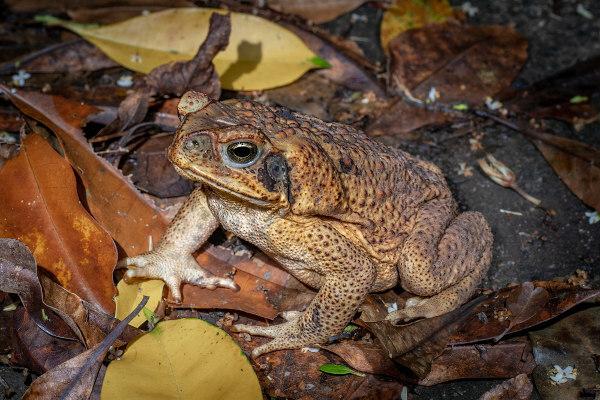
We cannot also forget the presence ofglands that secrete poison, which are responsible for the protection of these animals. They are found mainly in the dorsal region, however, the position of the glands as well as their quantity vary from one species to another. At the cururu frog, for example, in addition to observing the glands on the animal's back, there is the presence of large and developed glands, such as the paratoid, located in the region behind the eyes.
The cardiovascular system of amphibians is closed and the circulation is double, that is, the blood runs inside the blood vessels and, to complete a circuit, it passes through the heart twice. The amphibian heart is divided into three cavities. two atria and one ventricle. Due to the presence of only one ventricle, the oxygen-rich blood comes into contact with the carbon-rich blood, therefore, it is said that the circulation is incomplete.
With regard to the excretory system, it is worth highlighting the presence of kidneys. Many amphibians excrete ammonia when they are in their aquatic phase and completely change their excretion form when in the terrestrial environment, excreting urea.
An interesting feature about amphibians is the fact that these animals are the only vertebrates that have four digits in the hands (tails and anurans). In addition, anurans and caudates are vertebrates that use their eyes to ingest prey. That's because these animals are capable of lower and raise eyes within the orbit, a movement that helps to push the food.
Read more: Types of Animal Breathing
Amphibian reproduction
The way amphibians reproduce is extremely varied, showing marked differences from one species to another. Next, we'll talk a little about the reproduction of frogs, which include toads, tree frogs and frogs. In addition to reproduction, we will discuss the life cycle of these animals, which involves aquatic and terrestrial phases.
Anurans usually reproduce in the rainy season, and some species have very short reproductive periods. Males, in general, make sounds (croak) to attract the female, who chooses the male by evaluating the characteristics of his song. In some species, the female approaches the male and touches him, which leads to mating through the so-called embrace, which is the nuptial hug. This hug can be done in different ways, one of which is the male hug holding the female's pelvic girdle region.

Fertilization in most frogs is external, being the sperm are released onto the oocytes when the female deposits them. In frogs it is possible to observe different types of spawning, verifying, for example, species that lay their eggs in water, in foam nests and on rocks. It is noteworthy that, in some of them, the eggs are retained in the female's body.
From the eggs hatch the tadpoles, a larval stage of anurans. Tadpoles, for the most part, feed on plant debris found in water and slime. The larval stage has gills and a hydrodynamic shape. They have a tail that is reabsorbed as they develop and limbs appear.
Initially, the appearance of hind limbs is observed, then of forelimbs. During the metamorphosis, it also develops in the tadpole, lungs, eardrums, and the digestive system adapts to a carnivorous diet, observed in adults. The adult frog lives in the terrestrial environment and returns to the aquatic environment for its reproduction.
Read too: Anuran amphibians and their croaks
Amphibian classification
Amphibians are classified into three orders: Urodela,Anura and Apoda. See below the main characteristics of each of them:

-
Urodela or tail: as the name suggests, this order is made up of amphibians that have a tail, which is usually larger or the size of the animal's body. As representatives, we have the salamanders and newts.
The body of the representatives of this group is generally long and has similar sized fore and hind limbs. Some species live all their lives in water, others, however, live in this environment only during the larval stage. Also, there are terrestrial species. The retention of larval characteristics (pedomorphosis) is common in salamanders, this being the case in the axolotl.

Anura: stands out for being the most diversified and known order of amphibians. In this group are included toads, frogs and tree frogs, animals that, unlike the urodels, do not have a tail. The body of these animals is short and has four locomotor limbs in adults, the hind limbs being larger than the forequarters, which guarantees them the ability to jump. Many species are poisonous and have warning coloring that ward off predators. Most representatives of this group have the ability to vocalize.
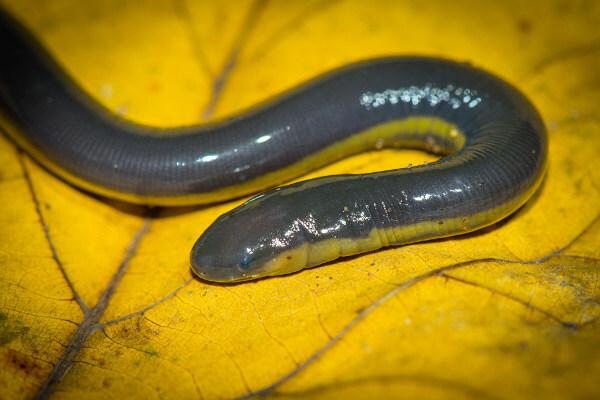

Apoda or gymnophiona: they do not have legs and live, with the exception of species that are predominantly aquatic, much of their life in galleries on the ground. The body is elongated and the eyes are small and not very functional. As representatives, we have the cecilias, also called blind snakes. To learn more about these very interesting animals, read: Amphibian classification.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher