You lipids or fats are organic molecules insoluble in water and soluble in certain organic substances, such as alcohol, ether and acetone.
Also called lipids or lipids, these biomolecules are composed of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen.
They can be found in foods of plant and animal origin and their consumption must be done in a balanced way.
Lipid Functions
Lipids have important functions for the body, see below:
- Power reserve: used by the body in times of need, and is present in animals and plants;
- thermal insulation: in animals, fat cells form a layer that acts to maintain body temperature, which is essential for animals that live in cold climates;
- Fatty acids: are present in vegetable oils extracted from seeds, such as soy, sunflower, canola and corn, which are used in the synthesis of organic molecules and cell membranes.
- Vitamin absorption: help the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K which are fat soluble and dissolve in oils. As these molecules are not produced in the human body, it is important to consume these oils in food.
Also read about the Nutrients.
Lipid Structure
the lipids are esters, this means that they are composed of an acid (fatty acid) and an alcohol (glycerol or other) molecule.
They are insoluble in water because its molecules are non-polar, that is, they do not have an electrical charge and, for this reason, they do not have an affinity for the polar molecules of water.
Types of Lipids and Examples
Carotenoids
They are orange pigments present in the cells of all plants that participate in photosynthesis together with chlorophyll, but play an accessory role.
An example of a source of carotene is carrots, which when ingested, this substance becomes a precursor of vitamin A, essential for good vision.
Carotenoids also benefit the immune system and act as an anti-inflammatory.
waxes
They are present on the surfaces of plant leaves, on the body of some insects, on beeswax and even on the one inside the human ear.
This type of lipid is highly insoluble and prevents water loss through perspiration. They consist of an alcohol molecule (different from glycerol) and 1 or more fatty acids.
Phospholipids
These are the main components of the cell membranes, is a glyceride (a glycerol linked to fatty acids) combined with a phosphate.
Glycerides
They can have 1 to 3 fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule (an alcohol, with 3 carbons attached to hydroxyl-OH). The best known example is the triglyceride, which is composed of three fatty acid molecules.

steroids
They are composed of 4 interconnected carbon rings, linked to hydroxyls, oxygen and carbon chains.
As examples of steroids, we can mention the male sex hormones (testosterone), the female sex hormones (progesterone and estrogen), other hormones present in the body and the cholesterol.
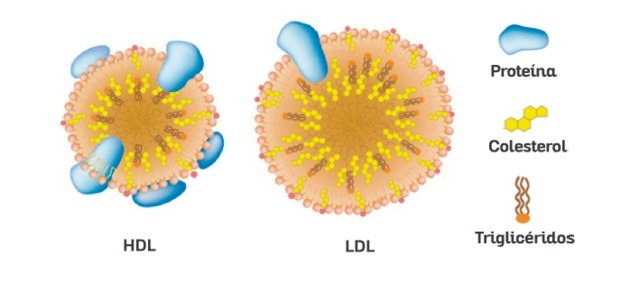
Cholesterol molecules associate with blood proteins (apoproteins), forming lipoproteins HDL or LDL, which are responsible for transporting steroids.
LDL lipoproteins carry cholesterol, which if consumed in excess builds up in the blood. HDL lipoproteins, on the other hand, remove excess cholesterol from the blood and take it to the liver, where it will be metabolized. For playing this "cleaning" role, HDLs are called good cholesterol.
Test your knowledge with lipid exercises.
Lipid-rich foods

The ingestion of lipids is essential, as it brings several health benefits, helping the body to function. You lipid rich foods they can be of animal and vegetable origin.
You animal foods lipid sources are:
- Red meat
- Fish
- Eggs
- Milk
- Butter
You plant foods lipid sources are:
- Coconut
- Avocado
- Oilseeds such as chestnuts, walnuts, almonds and sesame
- Olive oil
Read too:
- Carbohydrates or carbohydrates: what are they?
- Food pyramid
- Proteins
