
The amount of calories depends on the constitution of the food. Thus, to experimentally determine the amount of heat released by the food and that can be absorbed by the body, we use a device called calorimeter.
This device measures the heat released by the food when it is burned. There are several types of calorimeter; the first of them was created in 1780 by Lavoisier and Laplace and was a ice calorimeter.
Nowadays, the most used and that takes into account the calorie concept explained above is the water calorimeter. This device is covered with an insulating material to prevent heat loss from the medium; and the food to be analyzed is placed in the combustion chamber, which contains oxygen gas and electrodes. These electrodes undergo an electrical discharge and cause their ignition and combustion of food.
The known mass of water contained in the calorimeter absorbs the heat released by the burned food and a thermometer measures the increase in water temperature. In addition, the calorimeter contains a
agitator which allows the water temperature to remain uniform throughout its entirety.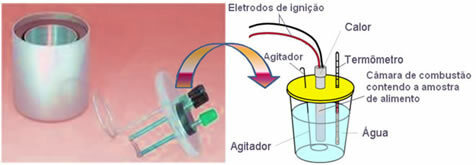
So, if we use, for example, a mass of 1 gram of sugar and the calorimeter has 1000 g of water, and we observe that in the end of the reaction, the water temperature went from 20°C to 24°C, that is, it increased by 4°C, we can then reach the energy value of the sugar. Like? Well, considering the initial calorie concept, we have:
| Raise from 1°C → 1 cal per gram of water |
| Raise from 4°C → 4 cal per gram of water |
So 1 g of water absorbs 4 lime. However, 1000 g of water were used and, considering that all the heat released in the combustion was absorbed by it, the total energy absorbed by the water was 4000 cal or 4 kcal. Therefore, we conclude that:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
| The energy value of sugar = 4000 cal/g or 4 kcal/g. |
Transforming to the SI:
1 kcal 4.18 kJ
4 kcal/g x
x = 16.72 kJ/g
In addition, we can use the following equation to calculate the amount of heat given up or absorbed by water:
| Q = m. ç. t |
Where:
Q = heat given up or absorbed by water;
m = mass of water;
c = specific heat of water, which equals 1.0 cal/g. °C or 4.18 J/g. °C;
Δt = variation of the temperature suffered by the water, which is given by the decrease in the final temperature by the initial one (tf – ti).
Using this formula we get the same result:
Q = m. ç. t
Q = 1000 g. 1.0 cal/g. °C. (24-20)°C
Q=4000 cal
Q = 4.0 kcal
or
Q = m. ç. t
Q = 1000 g. 4.18 kJ/g. °C. (24-20)°C
Q= 16.72 kJ
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Measuring Food Calories Using a Calorimeter"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/medindo-as-calorias-dos-alimentos-por-meio-um-calorimetro.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.


