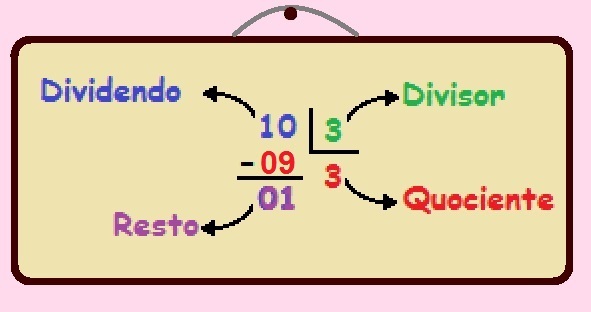
At length measurement units arise to meet the human need for measure various types of distances. There are several length measurement units, the one used in the international system of units is the meter, and its multiples (kilometer, hectometer and decameter) and submultiples (decimeter, centimeter millimeter).
In addition to the presented length measurement units, there are others such as those that use the body as a parameter: the span, the foot, the inch. Still, there are those that are not from the international system, but are used depending on the region, such as the league, the yard, the mile and the light-year.
Read too: Mass Measures - Units of Measure and Conversion
What are the length measurement units?
Measuring the distance between two reference points is a task performed by human beings since the earliest civilizations. Initially we used everyday objects as references, such as ropes or the human body itself. Adopted as a fundamental measure for distance in the international system of units, the scientific community uses the metro as a reference for measuring lengths.
To measure longer distances, there are what we call multiples of the subway, that are:
dekameter: 1 decameter corresponds to 10 meters,
hectometer: 1 hectometer corresponds to 100 meters,
kilometer: 1 kilometer corresponds to 1000 meters.
To measure the distance, for example, between two cities, it is more convenient to use kilometers instead of meters.
To measure shorter distances, there are metro submultiples, that are:
decimeter: 10 decimeters corresponds to 1 meter.
centimeter: 100 centimeters corresponds to 1 meter
millimeter: 1000 millimeters corresponds to 1 meter.
For smaller objects such as cutlery, it is more convenient to use the centimeter instead of the meter as the unit of measure.
The multiples and sub-multiples of the meter are represented by acronyms:
kilometer → km
hectometer → hm
dekameter → dam
subway → m
decimeter → dm
centimeter → cm
millimeter → mm
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Conversion of length measurements
To perform the conversion, we need to build the following table, respecting the order for the multiples and submultiples of the meter:

To convert a unit that is on the left to one that is on the right, we multiply by 10 each unit of measure.
Example:
Converting 1.2 m → cm
When analyzing the table, from meter to centimeter, there are two measurement units
m→ dm → cm. So we'll multiply by 10 each.
1.2 · 10 · 10 = 1.2 · 100 = 120 cm
To perform right-to-left conversions, we divide by 10 for each unit of measure.
Example 2:
Converting 7 500 mm → dam
When analyzing the table, from millimeter to decameter, there are four measurement units.
dam ← m ← dm ← cm ← mm
7500: 10: 10: 10: 10 = 7500: 10 000 = 0.75 dam
See too: Divisibility criteria - properties that facilitate the division operation
Other units of measurement of lengths
There are other very common length measurement units, namely:
• Inch: used to measure the screen of smartphones, notebooks and other electronic devices. It is usually denoted by the number followed by two quotation marks, for example 40” (read: 40 inches). One inch corresponds to 2.54 cm.
• Palm: used to measure objects a little larger than those we measure with inches, and is little used today. A span corresponds to 22.86 cm.
• Foot: used until today to situate itself in terms of the height of an airplane. To represent a distance measured in feet, we put the number followed by a quotation mark, for example 30’(read: 30 feet). One foot corresponds to 30.48 cm.
• Yard: used in the USA, being common in American football. One yard corresponds to 0.9144 m.
• League: Previously used to measure greater distances, the league was quite common in navigation. A league corresponds to 4,82803 kilometers.
• Mile: used to measure greater distances, having been quite common in ancient peoples. One mile corresponds to 1,60934 km.
• Light-year: used to measure the distance between stars, often confused with time measurement. One light-year corresponds to 9 460 730 472 580.8 km.

solved exercises
Question 1 - (Enem) A racing team mechanic needs the following measurements taken on a car to be taken in meters:
a) distance a between the front and rear axles;
b) height b between the ground and the pilot's backrest.
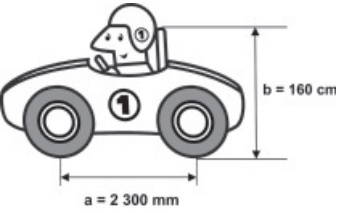
By choosing the measures a and b in meters, we obtain, respectively,
a) 0.23 and 0.16.
b) 2.3 and 1.6.
c) 23 and 16.
d) 230 and 160.
e) 2300 and 1600.
Resolution
Alternative B
Converting the measure of a = 2300 mm → m
m ← dm ← cm ← mm
For each unit of measure on the left, we divide by 10, so we'll divide the value of a by 1000.
2300: 1000 = 2.3 meters
Thus, the measure a = 2.3 meters
Converting the measure of b = 160 cm → m
m dm ← cm
Since we're going to walk two units of measurement to the left, we'll divide by 100.
160: 100 = 1,6
b = 1.6 m
During a football game, one player covered 22 consecutive yards. Knowing that 1 yard corresponds to 0.91 meters, this distance in yards is approximately equal to:
a) 25.09 meters
b) 30 meters
c) 20.02 meters
d) 23.12 meters
e) 24.18 meters
Resolution
Alternative C.
Knowing that he covered 22 yards, we just need to do the multiplication:
22 x 0.91 = 20.02
By Raul Rodrigues de Oliveira
Maths teacher