Alkynes are unsaturated acyclic hydrocarbons with a triple bond. Only two of its carbons are joined by triple covalence, the rest being single bonds.
Acetylene (ethine) is an example of alkyne, it was first obtained by Berthelot, who established an arc between graphite electrodes in an atmosphere of hydrogen. Acetylene is a colorless, unstable, highly combustible gas and produces a high temperature flame (over 3000°C or 5400°F) in the presence of oxygen. This gas has a pleasant smell when pure, but its odor is commonly unpleasant due to the impurities that accompany it. Acetylene is the raw material in the manufacture of industrial solvents, synthetic rubber plastics, explosives, in the synthesis of organic compounds such as acetic acid and ethyl alcohol.
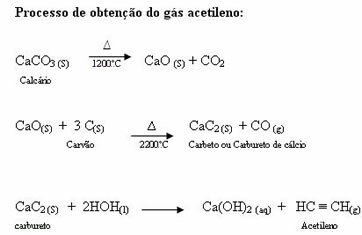
Acetylene being important in industry and not found in nature, it has to be manufactured from cheap natural products. The raw materials used in the manufacture of acetylene are limestone and stone coal (hard coal), which are abundant in nature. But what would be coal?
Coal: origin in material from plants deposited in swamps, this material is subjected to a process called degradative distillation, which occurs in the absence of oxygen, in which essences are obtained in the three states. physicists:
Gaseous: gas (fuel) lighting: CH4, H2, CO etc.
Liquid:
• ammonia waters: aqueous solutions containing nitrogen compounds (used by industries in the manufacture of fertilizers and fertilizers).
• coal tar: mixture of aromatic hydrocarbons (dark and viscous liquid, its main components being benzene, toluene, dimethylbenzenes, naphthalene and anthracene).
Solid: coking coal (used in steelmaking to obtain iron in blast furnaces).
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

Coke Coal
Physical properties of Acetylene:
Chemical formula: ...C2H2
Molecular weight: ...26.038 g/mol
Triple point: ...-80.75° C / 1.28 bar
Critical temperature:...36.3°C
Critical Pressure:...62.42 bar
Density (15°C /760 mmHg): ...1.11 Kg/m3
Oxygen ignition temperature...296°C
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUZA, Líria Alves de. "Acetylene"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/acetileno.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.