O polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic addition polymer, which is formed by the successive addition of monomers of the styrene, also called vinyl benzene, which is an oily liquid whose molecules are formed by benzene and ethylene:
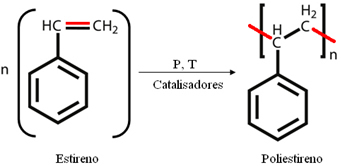
This polymer was discovered in 1839 and started to be commercially produced in 1930. It has many important properties such as the fact that it is low cost, has resistance to acids, alkalis (bases) and salts, in addition to being a great thermal, electrical and acoustic insulator.
It has a wide range of applications as it can be produced with different treatments and form three types of polystyrene. See each one:
Polystyrene: Since it has several benzene rings in its polymer chains, it has an appearance similar to glass, as these rings attract each other and make the plastic more hard. This packaging of the chains makes it transparent and with a high refractive index, that is, with a shine similar to that of glass.
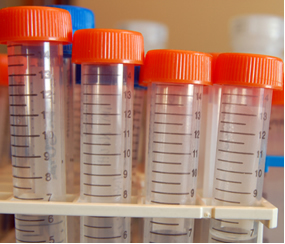
applications: disposable cups used to drink water, combs, brushes, compact powder packaging and eyeshadows, toys, CD cases and equipment such as disposable pipettes, plastic syringes, beakers and funnels, as well as centrifuge tubes such as those shown. bellow:
High impact polystyrene: It is produced by adding 10% polybutadiene or styrenebutadiene to polystyrene, making it very resistant.
Applications: Rigid household items such as combs, hangers, trays, plastic organizer boxes (shown below), toys, refrigerator door linings, margarine pots, circuit breakers and folders.

-
Expanded polystyrene (styrofoam): During the hot polymerization reaction, certain gases are added that lead to its expansion, forming the so-called styrofoam. Previously, the gases used in this process were CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), which are the main gases that destroy the ozone layer (read the text about this How is the ozone layer destroyed?).
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Fortunately, however, this problem has been resolved, as pentane is now used as a gas for the expansion of polystyrene, causing no damage to the ozone layer.
Applications: Since it is very light, expanded polystyrene is used in the form of slabs or blocks in the manufacture of slabs, reducing the effort on the structure and helping to save concrete. It is used inside packaging to protect household equipment well molded into the shape of such equipment, which reduces transportation costs. As it can be molded, it is used in helmets for protection. Other applications are: as an electrical or thermal insulator in homes and buildings, as a container for hot drinks and food, as a cooler, among others.

Styrofoam was also the target of criticism because it contributed to the increase in the amount of waste released into the environment. For example, the aforementioned packages that come in the shape of the object we buy cannot most of the time be reused later. However, this problem also has a solution: polystyrene can be recycled and its recycling symbol is shown below:

Its recycling produces pipes and garbage cans.
Another important point to be addressed about Styrofoam is the its microwave use. Some claim that it can release toxic and carcinogenic substances, but there is still no confirmation of this. So far it is known that it can be used without risks for a short time in the microwave, just to warm up. However, for longer periods, it is better to use another type of packaging, because Styrofoam can easily melt, ending up with drink or food, which can cause burns and damage the device.
In addition, Styrofoam burns very easily, melting and releasing a black smoke that releases carbon dioxide (CO2) for the environment. This is often controlled by adding fire-retardant additives to the Styrofoam.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry