THE urban macrocephaly is an urban phenomenon characterized by concentration of services, economic activities and population in a particular city or urban area. It occurs mainly in underdeveloped countries like Brazil.
Its causes are linked to a rapid process of urbanization and intensification of population movements from the countryside to the city and the formation of large urban centers. Among the consequences of the swelling of cities are the slums and the deepening of socio-spatial segregation.
Read too: World urban hierarchy — form of organization and classification of cities
What is urban macrocephaly?
Urban macrocephaly is a phenomenon that occurs in large cities, especially in underdeveloped countries or regions of the world, and which can be described as the unequal spatial concentration of people and services of the most varied types in a particular city or urban agglomeration. It is directly associated with the process of formation of metropolises, but its occurrence is not restricted to metropolitan regions|1|.
The non-homogeneous distribution of infrastructure, technologies, economic and productive activities, services and, therefore, the population has consequences for the individuals who live there and who build daily the urban space, for the environment and, in general, for the urban fabric. These consequences are linked to the lack of structure in cities to receive new population groups.
In short, urban macrocephaly is characterized by intense and disorderly urban growth and by the lack of physical and economic structure to support these transformations.

What causes urban macrocephaly?
Urban macrocephaly dates back to the way the process of urbanization in underdeveloped countries and absence or inefficiency of urban planning and management by the government.
The growth of urban areas in countries like Brazil started from the industrialization, which occurred late compared to developed nations. This process accelerated from the second half of the 20th century, driven by the modernization of the countryside and the intensification of the migratory flow from rural to urban areas (rural exodus). Furthermore, conditioned by historical and economic factors, productive activities, services and infrastructure are unevenly distributed in space, focusing on certain urban centers.
The events described above led to a fast and disorderly growth of big cities, which do not have the structure to adequately handle and serve the entire population. Therefore, a macrocephalic picture is installed.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
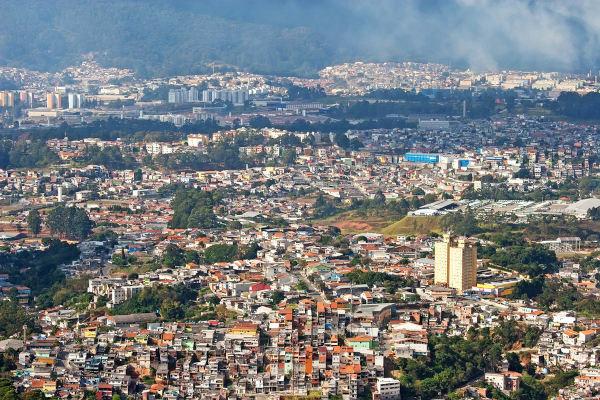
Consequences of urban macrocephaly
The urban swelling observed mainly in large cities and metropolises results in social, economic and environmental consequences. One of the most obvious is the marginalization of a portion of the urban population, which is due to several factors, such as the lack of opportunities in the labor market or low qualification, increasing the number of informal workers and also from unemployed. With this, there is an increase in precarious housing, sometimes in irregular areas, generating the process of slums andthe intensification ofurban segregation.
Given this picture, other infrastructure problems of big cities, such as access to basic services such as sanitation, whose networks do not serve the entire population, the precariousness of public transport and the lack of a more comprehensive transport network that promotes greater integration between the different parts of the city and other issues related to urban mobility.
Many environmental imbalances they are also caused by the lack of urban planning and poor infrastructure, such as the different types of pollution, especially from rivers and soil.

Milton Santos and urban macrocephaly
Milton Santos is one of the main names in Brazilian geography and one of the greatest thinkers in the country. In his vast bibliography, the geographer talked about the theme of territorial organization of underdeveloped countries, discussing the urbanization process guided by the unequal spatial distribution that happened in the countries underdeveloped.
In his writings, Milton Santos makes clear the notion that the concentration of production, consequently of capital and technology in some cities, as well as population concentration are at the heart of the macrocephaly phenomenon. urban. In works like Space Economy and For A New Geography, the author describes the urban macrocephaly as a result of technical modernization and spatial concentration that they cause in some selected cities|1| — or that have locational advantages.
In The Divided Space, Santos presents a definition for urban macrocephaly widely used in academic texts that focus on the study of urban phenomena. The technical and productive concentration that occurs in certain cities becomes, in addition to an attraction for greater diversity of economic and productive agents, a population attraction, thus redirecting the flow of people to these centers. From this movement, a series of problems that are characteristic of areas with urban swelling are unleashed, ranging from unemployment to precarious occupations and issues related to public safety|2|.
See too: What is the role of cities?
solved exercises
Question 1 - Urban macrocephaly is a characteristic phenomenon in underdeveloped countries. Examples of cities that can be considered macrocephalic are São Paulo, Mexico City and Lima. Some factors are listed as responsible for urban swelling, except:
A) the lack of infrastructure in urban centers to support the new population flow.
B) the process of slums and deepening of spatial segregation.
C) the intensification of the rural exodus.
D) the unequal distribution of productive activities in space.
E) accelerated urbanization driven by industrialization.
Resolution
Alternative B. The deepening of spatial segregation is pointed out as one of the consequences related to the rapid and disorderly growth of large urban centers.
Question 2 - (Unifal) Read the following statements.
I - The rural exodus is one of the causes of the accelerated urbanization that causes, among other problems, the increase in unemployment and the growth of the informal sector of cities in industrializing countries late.
II – The growth in the urbanization rate implies a marked improvement in the living conditions of the population of underdeveloped countries.
III – The increase in slums, clandestine subdivisions and the homeless population can be seen as a consequence of the rural exodus and growing urbanization.
Based on these statements about urbanization, mark the correct alternative.
A) Only I and II are correct.
B) Only I and III are correct.
C) All alternatives are correct.
D) Only III is correct.
Resolution
Alternative B. The only incorrect statement is the second. The rapid growth of the urbanization rate in underdeveloped countries led to the deepening of socioeconomic problems in cities and the process of exclusion of a part of the population.
Grades
|1| SAINTS, Milton. For a New Geography: From the Critique of Geography to a Critical Geography. São Paulo: University of São Paulo Publisher, 2004. (Milton Santos Collection; 2)
|2| SAINTS, Milton. the EDivided space: The Two Circuits of the Urban Economy of Underdeveloped Countries. São Paulo: University of São Paulo Publisher, 2004, 2nd edition.
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher