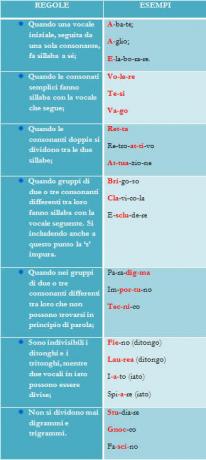
O stomach is one of the bodies that make up the digestive system. When we eat, all the food, after being chewed in the mouth, goes to the stomach, where digestion takes place. In the stomach, we find cells that produce enzymes and others that produce the hydrochloric acid. Lining the stomach, we have a mucosa that protects it from the action of this acid, and the gastritis is nothing more than inflammation of this lining mucosa.
There are two types of gastritis: a acute gastritis and the chronic gastritis.
THE acute gastritis it's a transient inflammation. When left untreated, it can progress to chronic gastritis. May cause bleeding from the mouth (haematemesis) or from the rectum (melena). The causes of acute gastritis are: use of medication (acetylsalicylic acid, corticoids, some anti-inflammatory drugs), physical and psychological stress; alcoholic beverage; accidental or suicidal ingestion of corrosive acidic substances.
Some cases of this disease can present severe bleeding as in people with head trauma, in patients with burns in different parts of the body, stress due to the long stay in ICUs or in patients with infection widespread.
At chronic gastritis, the bacteria Helicobacter pylori sometimes it is the cause of the infection. Because it lives very well in acidic environments, the Helicobacter pylori it can lead to the destruction of the mucosa that lines and protects the stomach wall, characterizing gastritis.
In the stomach mucosa there are several cells that are responsible for the production of enzymes and gastric acid. With the destruction of the mucosa by Helicobacter pylori, there is a decrease in these cells and, consequently, a decrease in the production of gastric acid and enzymes, making it difficult to sterilize the ingested food and its digestion.
Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
You gastritis symptoms are burning, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, feeling of fullness, digestive bleeding. Deficiency may occur in the absorption of some elements and vitamins, causing weakness and diarrhea.
When the type of gastritis is diagnosed, the doctor will start the treatment. If the diagnosis points to acute gastritis, the doctor may suspend the medication that is causing the pain, and add a medication that neutralizes, inhibits, or blocks the acidic secretions in the stomach.
When gastritis is chronic, the physician, based on endoscopy, can perform local treatments or even prescribe antibiotics to eradicate the bacteria Helicobacter pylori.
To avoid the onset of gastritis, it is good that the person avoid ingesting drugs that irritate the walls of the stomach, such as anti-inflammatories and aspirin, avoid the consumption of fruit salts and antacids that only serve for the indigestion. Alcoholic beverages and smoking can make gastritis worse.
We recommend that you do not self-medicate and that, in case of any feeling of stomach discomfort, seek a specialist.
Paula Louredo
Graduated in Biology